Incubation period of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) infections among travellers from Wuhan, China, 20-28 January 2020
- PMID: 32046819
- PMCID: PMC7014672
- DOI: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.5.2000062
Incubation period of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) infections among travellers from Wuhan, China, 20-28 January 2020
Abstract
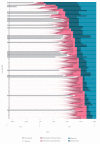
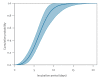
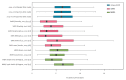
A novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) is causing an outbreak of viral pneumonia that started in Wuhan, China. Using the travel history and symptom onset of 88 confirmed cases that were detected outside Wuhan in the early outbreak phase, we estimate the mean incubation period to be 6.4 days (95% credible interval: 5.6-7.7), ranging from 2.1 to 11.1 days (2.5th to 97.5th percentile). These values should help inform 2019-nCoV case definitions and appropriate quarantine durations.
Keywords: 2019-nCoV; Wuhan; exposure; incubation period; novel coronavirus; symptom onset.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pattern of early human-to-human transmission of Wuhan 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV), December 2019 to January 2020.Euro Surveill. 2020 Jan;25(4):2000058. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.4.2000058. Euro Surveill. 2020. PMID: 32019669 Free PMC article.
-
Passengers' destinations from China: low risk of Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) transmission into Africa and South America.Epidemiol Infect. 2020 Feb 26;148:e41. doi: 10.1017/S0950268820000424. Epidemiol Infect. 2020. PMID: 32100667 Free PMC article.
-
The Incubation Period of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) From Publicly Reported Confirmed Cases: Estimation and Application.Ann Intern Med. 2020 May 5;172(9):577-582. doi: 10.7326/M20-0504. Epub 2020 Mar 10. Ann Intern Med. 2020. PMID: 32150748 Free PMC article.
-
The reproductive number of COVID-19 is higher compared to SARS coronavirus.J Travel Med. 2020 Mar 13;27(2):taaa021. doi: 10.1093/jtm/taaa021. J Travel Med. 2020. PMID: 32052846 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2): a review.Mol Cancer. 2020 Jun 2;19(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01218-1. Mol Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32487159 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
30-Day postoperative COVID-19 outcomes in 398 patients from regional hospitals utilising a designated COVID-19 minimal surgical site pathway.Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2021 Jun;103(6):395-403. doi: 10.1308/rcsann.2020.7072. Epub 2021 May 6. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2021. PMID: 33956529 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge and perceptions about COVID-19 among the medical and allied health science students in India: An online cross-sectional survey.Clin Epidemiol Glob Health. 2021 Jan-Mar;9:104-109. doi: 10.1016/j.cegh.2020.07.008. Epub 2020 Aug 12. Clin Epidemiol Glob Health. 2021. PMID: 32838066 Free PMC article.
-
Spread and Impact of COVID-19 in China: A Systematic Review and Synthesis of Predictions From Transmission-Dynamic Models.Front Med (Lausanne). 2020 Jun 18;7:321. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.00321. eCollection 2020. Front Med (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 32626719 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 pandemic: An overview.Adv Biol Regul. 2020 Aug;77:100736. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2020.100736. Epub 2020 Jun 17. Adv Biol Regul. 2020. PMID: 32773099 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nonlinear control of infection spread based on a deterministic SEIR model.Chaos Solitons Fractals. 2021 Aug;149:111051. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2021.111051. Epub 2021 Jun 5. Chaos Solitons Fractals. 2021. PMID: 34108820 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). WHO Statement Regarding Cluster of Pneumonia Cases in Wuhan, China. Beijing: WHO; 9 Jan 2020. [Accessed 26 Jan 2020]. https://www.who.int/china/news/detail/09-01-2020-who-statement-regarding...
-
- Imai N, Dorigatti I, Cori A, Donnelly C, Riley S, Ferguson NM. Report 2: Estimating the potential total number of novel Coronavirus cases in Wuhan City, China. London; 2020. Available from: https://www.imperial.ac.uk/media/imperial-college/medicine/sph/ide/gida-...
-
- Leung K, Wu JT, Leung GM. Nowcasting and forecasting the potential domestic and international spread of the 2019-nCoV outbreak originating in Wuhan, China: a modelling study. Lancet. 31 Jan 2020. Available from: https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(20)30260... - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

