Prognostic utility of heart-type fatty acid-binding protein in patients with stable coronary artery disease and impaired glucose metabolism: a cohort study
- PMID: 32041617
- PMCID: PMC7011523
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-020-0992-0
Prognostic utility of heart-type fatty acid-binding protein in patients with stable coronary artery disease and impaired glucose metabolism: a cohort study
Abstract
Background: Heart-type fatty acid-binding protein (H-FABP) is a novel marker of myocardial injury and has been reported to be associated with cardiovascular diseases (CVD) including patients with diabetes mellitus (DM). Unfortunately, its prognostic value in patients with CVD and impaired glucose metabolism (IGM) is unclear. The objective of this study was to investigate the prognostic value of H-FABP in CVD patients with IGM.
Methods: A total of 4594 patients with angiography-proven coronary artery disease (CAD) were enrolled and divided into subgroup according to glucose metabolism status (normal glucose regulation [NGR], pre-DM, and DM). Baseline levels of H-FABP were measured using latex immunoturbidimetric method. The cardiovascular events (CVE) were defined as cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, stroke and coronary revascularization. Cox regression and Kaplan-Meier analysis were used to evaluate the relations of H-FABP and glucose metabolism status to CVEs.
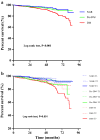
Results: During the follow-up period with up to 7.1 years, 380 CVEs occurred. Patients with CVE had higher levels of H-FABP compared to those without CVE (p < 0.001). Interestingly, H-FABP levels were also elevated in DM and pre-DM groups compared with NGR group (p < 0.001), when combined glucose metabolism status with H-FABP stratification, patients in the highest tertile of H-FABP appeared to have higher risk of CVEs with pre-DM (adjusted hazard ratio [HR]: 1.855, 95% confidential intervals [CIs] 1.076-3.214; p = 0.033) and DM (adjusted HR: 2.560, 95% CIs 1.409-4.650; p = 0.002). The Kaplan-Meier curve indicated that DM patients with the highest H-FABP levels were associated with the greatest risk of CVEs (p < 0.05).
Conclusions: Our data firstly showed that elevated H-FABP levels were associated with worse outcomes in CAD patients with pre-DM and DM, which provided the novel information that H-FABP might be a prognostic marker for clinical outcomes among patients with CAD and IGM.
Keywords: Coronary artery disease; Heart-type fatty acid-binding protein; Impaired glucose metabolism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Heart-type fatty acid binding protein predicts cardiovascular events in patients with stable coronary artery disease: a prospective cohort study.Ann Transl Med. 2020 Nov;8(21):1349. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-2493. Ann Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 33313094 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoprotein(a) and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients With Coronary Artery Disease and Prediabetes or Diabetes.Diabetes Care. 2019 Jul;42(7):1312-1318. doi: 10.2337/dc19-0274. Epub 2019 May 10. Diabetes Care. 2019. PMID: 31076417
-
Association of small dense low-density lipoprotein with cardiovascular outcome in patients with coronary artery disease and diabetes: a prospective, observational cohort study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020 Apr 3;19(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s12933-020-01015-6. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020. PMID: 32245386 Free PMC article.
-
Risk stratification in acute pulmonary embolism with heart-type fatty acid-binding protein: A meta-analysis.J Crit Care. 2015 Oct;30(5):1151.e1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2015.05.026. Epub 2015 Jun 3. J Crit Care. 2015. PMID: 26111917 Review.
-
Heart-type fatty acid-binding protein in cardiovascular disease: A systemic review.Clin Chim Acta. 2017 Nov;474:44-53. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2017.09.007. Epub 2017 Sep 11. Clin Chim Acta. 2017. PMID: 28911997 Review.
Cited by
-
H-FABP: A beacon of hope for prediabetic heart disease.J Family Med Prim Care. 2020 Jul 30;9(7):3421-3428. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_296_20. eCollection 2020 Jul. J Family Med Prim Care. 2020. PMID: 33102307 Free PMC article.
-
Association between adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein with left ventricular remodelling and diastolic function in type 2 diabetes: a prospective echocardiography study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020 Nov 24;19(1):197. doi: 10.1186/s12933-020-01167-5. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020. PMID: 33234149 Free PMC article.
-
Fatty Acid Binding Proteins 3 and 4 Predict Both All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality in Subjects with Chronic Heart Failure and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Mar 4;12(3):645. doi: 10.3390/antiox12030645. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36978893 Free PMC article.
-
An update of new/potential cardiovascular markers: a narrative review.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Jan 22;51(1):179. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08978-1. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38252393 Review.
-
Circulating Biomarkers for Cardiovascular Disease Risk Prediction in Patients With Cardiovascular Disease.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Oct 1;8:713191. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.713191. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34660715 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

