Vindoline Inhibits RANKL-Induced Osteoclastogenesis and Prevents Ovariectomy-Induced Bone Loss in Mice
- PMID: 32038256
- PMCID: PMC6987431
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01587
Vindoline Inhibits RANKL-Induced Osteoclastogenesis and Prevents Ovariectomy-Induced Bone Loss in Mice
Abstract
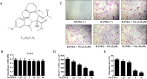
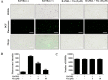
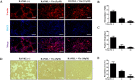
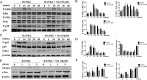
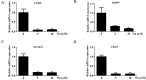
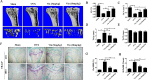
Osteolytic bone diseases, for example postmenopausal osteoporosis, arise from the imbalances between osteoclasts and osteoblasts in the bone remodeling process, whereby osteoclastic bone resorption greatly exceeds osteoblastic bone formation resulting in severe bone loss and deterioration in bone structure and microarchitecture. Therefore, the identification of agents that can inhibit osteoclast formation and/or function for the treatment of osteolytic bone disease has been the focus of bone and orthopedic research. Vindoline (Vin), an indole alkaloid extracted from the medicinal plant Catharanthus roseus, has been shown to possess extensive biological and pharmacological benefits, but its effects on bone metabolism remains to be documented. Our study demonstrated for the first time, that Vin could inhibit osteoclast differentiation from bone marrow macrophages (BMMs) precursor cells as well as mature osteoclastic bone resorption. We further determined that the underlying molecular mechanism of action of Vin is in part due to its inhibitory effect against the activation of MAPK including p38, JNK, and ERK and intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. This effect ultimately suppressed the induction of c-Fos and NFATc1, which consequently downregulated the expression of the genes required for osteoclast formation and bone resorption. Consistent with our in vitro findings, in vivo administration of Vin protected mice against ovariectomy (OVX)-induced bone loss and trabecular bone deterioration. These results provided promising evidence for the potential therapeutic application of Vin as a novel treatment option against osteolytic diseases.
Keywords: MAPK; NFATc1; osteoclast; osteoporosis; vindoline.
Copyright © 2020 Zhan, Liang, Tian, Che, Wang, Yang, Su, Lin, Song, Zhao, Xu, Liu and Zhou.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hederagenin protects mice against ovariectomy-induced bone loss by inhibiting RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption.Life Sci. 2020 Mar 1;244:117336. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117336. Epub 2020 Jan 20. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 31972206
-
Xanthotoxin prevents bone loss in ovariectomized mice through the inhibition of RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis.Osteoporos Int. 2016 Jul;27(7):2335-2344. doi: 10.1007/s00198-016-3496-8. Epub 2016 Jan 25. Osteoporos Int. 2016. PMID: 26809192
-
Pharmacological inhibition of protein S-palmitoylation suppresses osteoclastogenesis and ameliorates ovariectomy-induced bone loss.J Orthop Translat. 2023 Jul 17;42:1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2023.06.002. eCollection 2023 Sep. J Orthop Translat. 2023. PMID: 37521493 Free PMC article.
-
Pseurotin A Inhibits Osteoclastogenesis and Prevents Ovariectomized-Induced Bone Loss by Suppressing Reactive Oxygen Species.Theranostics. 2019 Feb 28;9(6):1634-1650. doi: 10.7150/thno.30206. eCollection 2019. Theranostics. 2019. PMID: 31037128 Free PMC article.
-
Pregnenolone Inhibits Osteoclast Differentiation and Protects Against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Bone Destruction and Ovariectomy-Induced Bone Loss.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Mar 27;11:360. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00360. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32292342 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
GSK 650394 Inhibits Osteoclasts Differentiation and Prevents Bone Loss via Promoting the Activities of Antioxidant Enzymes In Vitro and In Vivo.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Sep 17;2022:3458560. doi: 10.1155/2022/3458560. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 36164394 Free PMC article.
-
Allicin Alleviates Lead-Induced Bone Loss by Preventing Oxidative Stress and Osteoclastogenesis Via SIRT1/FOXO1 Pathway in Mice.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2021 Jan;199(1):237-243. doi: 10.1007/s12011-020-02136-5. Epub 2020 Apr 21. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2021. PMID: 32314144
-
Phosphatidyl Inositol 3-Kinase (PI3K)-Inhibitor CDZ173 protects against LPS-induced osteolysis.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jan 6;13:1021714. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1021714. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36686650 Free PMC article.
-
miR-452-3p inhibited osteoblast differentiation by targeting Smad4.PeerJ. 2021 Sep 28;9:e12228. doi: 10.7717/peerj.12228. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 34692253 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of action and synergetic formulas of plant-based natural compounds from traditional Chinese medicine for managing osteoporosis: a literature review.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Aug 28;10:1235081. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1235081. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37700771 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bardwell A. J., Abdollahi M., Bardwell L. (2003). Docking sites on mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) kinases, MAPK phosphatases and the Elk-1 transcription factor compete for MAPK binding and are crucial for enzymic activity. Biochem. J. 370 (Pt 3), 1077–1085. 10.1042/bj20021806 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

