Barrel cortex VIP/ChAT interneurons suppress sensory responses in vivo
- PMID: 32027647
- PMCID: PMC7029879
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000613
Barrel cortex VIP/ChAT interneurons suppress sensory responses in vivo
Abstract
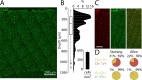
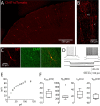
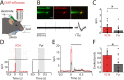
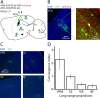
Cortical interneurons expressing vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) and choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) are sparsely distributed throughout the neocortex, constituting only 0.5% of its neuronal population. The co-expression of VIP and ChAT suggests that these VIP/ChAT interneurons (VChIs) can release both γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and acetylcholine (ACh). In vitro physiological studies quantified the response properties and local connectivity patterns of the VChIs; however, the function of VChIs has not been explored in vivo. To study the role of VChIs in cortical network dynamics and their long-range connectivity pattern, we used in vivo electrophysiology and rabies virus tracing in the barrel cortex of mice. We found that VChIs have a low spontaneous spiking rate (approximately 1 spike/s) in the barrel cortex of anesthetized mice; nevertheless, they responded with higher fidelity to whisker stimulation than the neighboring layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons (Pyrs). Analysis of long-range inputs to VChIs with monosynaptic rabies virus tracing revealed that direct thalamic projections are a significant input source to these cells. Optogenetic activation of VChIs in the barrel cortex of awake mice suppresses the sensory responses of excitatory neurons in intermediate amplitudes of whisker deflections while increasing the evoked spike latency. The effect of VChI activation on the response was similar for both high-whisking (HW) and low-whisking (LW) conditions. Our findings demonstrate that, despite their sparsity, VChIs can effectively modulate sensory processing in the cortical microcircuit.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Recruitment of GABAergic Interneurons in the Barrel Cortex during Active Tactile Behavior.Neuron. 2019 Oct 23;104(2):412-427.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2019.07.027. Epub 2019 Aug 26. Neuron. 2019. PMID: 31466734 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing VIP Neurons in the Barrel Cortex of VIPcre/tdTomato Mice Reveals Layer-Specific Differences.Cereb Cortex. 2015 Dec;25(12):4854-68. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhv202. Epub 2015 Sep 24. Cereb Cortex. 2015. PMID: 26420784 Free PMC article.
-
Prefrontal cortical ChAT-VIP interneurons provide local excitation by cholinergic synaptic transmission and control attention.Nat Commun. 2019 Nov 21;10(1):5280. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13244-9. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31754098 Free PMC article.
-
Cortical VIP+ /ChAT+ interneurons: From genetics to function.J Neurochem. 2021 Sep;158(6):1320-1333. doi: 10.1111/jnc.15263. Epub 2021 Jan 20. J Neurochem. 2021. PMID: 33301603 Review.
-
Spike timing and synaptic dynamics at the awake thalamocortical synapse.Prog Brain Res. 2005;149:91-105. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(05)49008-1. Prog Brain Res. 2005. PMID: 16226579 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting prefrontal cortex GABAergic microcircuits for the treatment of alcohol use disorder.Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2022 Aug 29;14:936911. doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2022.936911. eCollection 2022. Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36105666 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-throughput morphometric and transcriptomic profiling uncovers composition of naïve and sensory-deprived cortical cholinergic VIP/CHAT neurons.EMBO J. 2023 Jan 4;42(1):e110565. doi: 10.15252/embj.2021110565. Epub 2022 Nov 15. EMBO J. 2023. PMID: 36377476 Free PMC article.
-
VIP-Expressing GABAergic Neurons: Disinhibitory vs. Inhibitory Motif and Its Role in Communication Across Neocortical Areas.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Feb 10;16:811484. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.811484. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35221922 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dense functional and molecular readout of a circuit hub in sensory cortex.Science. 2022 Jan 7;375(6576):eabl5981. doi: 10.1126/science.abl5981. Epub 2022 Jan 7. Science. 2022. PMID: 34990233 Free PMC article.
-
Cholinergic blockade of neuroinflammation: from tissue to RNA regulators.Neuronal Signal. 2022 Feb 11;6(1):NS20210035. doi: 10.1042/NS20210035. eCollection 2022 Apr. Neuronal Signal. 2022. PMID: 35211331 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

