PPM1A Controls Diabetic Gene Programming through Directly Dephosphorylating PPARγ at Ser273
- PMID: 32024237
- PMCID: PMC7072254
- DOI: 10.3390/cells9020343
PPM1A Controls Diabetic Gene Programming through Directly Dephosphorylating PPARγ at Ser273
Abstract
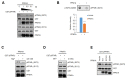
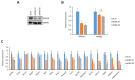
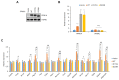
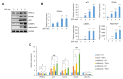
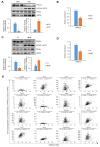
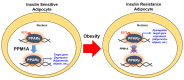
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) is a master regulator of adipose tissue biology. In obesity, phosphorylation of PPARγ at Ser273 (pSer273) by cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (CDK5)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) orchestrates diabetic gene reprogramming via dysregulation of specific gene expression. Although many recent studies have focused on the development of non-classical agonist drugs that inhibit the phosphorylation of PPARγ at Ser273, the molecular mechanism of PPARγ dephosphorylation at Ser273 is not well characterized. Here, we report that protein phosphatase Mg2+/Mn2+-dependent 1A (PPM1A) is a novel PPARγ phosphatase that directly dephosphorylates Ser273 and restores diabetic gene expression which is dysregulated by pSer273. The expression of PPM1A significantly decreases in two models of insulin resistance: diet-induced obese (DIO) mice and db/db mice, in which it negatively correlates with pSer273. Transcriptomic analysis using microarray and genotype-tissue expression (GTEx) data in humans shows positive correlations between PPM1A and most of the genes that are dysregulated by pSer273. These findings suggest that PPM1A dephosphorylates PPARγ at Ser273 and represents a potential target for the treatment of obesity-linked metabolic disorders.
Keywords: PPARγ S273 phosphorylation; PPM1A; diabetic gene reprogramming; insulin sensitivity; obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Thrap3 docks on phosphoserine 273 of PPARγ and controls diabetic gene programming.Genes Dev. 2014 Nov 1;28(21):2361-9. doi: 10.1101/gad.249367.114. Epub 2014 Oct 14. Genes Dev. 2014. PMID: 25316675 Free PMC article.
-
An ERK/Cdk5 axis controls the diabetogenic actions of PPARγ.Nature. 2015 Jan 15;517(7534):391-5. doi: 10.1038/nature13887. Epub 2014 Nov 17. Nature. 2015. PMID: 25409143 Free PMC article.
-
PPARγ S273 Phosphorylation Modifies the Dynamics of Coregulator Proteins Recruitment.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020 Nov 27;11:561256. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.561256. eCollection 2020. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 33329381 Free PMC article.
-
The therapeutic potential of inhibiting PPARγ phosphorylation to treat type 2 diabetes.J Biol Chem. 2021 Sep;297(3):101030. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101030. Epub 2021 Jul 31. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 34339734 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A comprehensive overview of PPM1A: From structure to disease.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2022 Mar;247(6):453-461. doi: 10.1177/15353702211061883. Epub 2021 Dec 3. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2022. PMID: 34861123 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Circulating triglycerides are associated with human adipose tissue DNA methylation of genes linked to metabolic disease.Hum Mol Genet. 2023 May 18;32(11):1875-1887. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddad024. Hum Mol Genet. 2023. PMID: 36752523 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of a Novel CLK1-THRAP3-PPARγ Axis Improves Insulin Sensitivity.Front Physiol. 2021 Aug 30;12:699578. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.699578. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34526909 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic deletion of MMP12 ameliorates cardiometabolic disease by improving insulin sensitivity, systemic inflammation, and atherosclerotic features in mice.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023 Nov 28;22(1):327. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-02064-3. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023. PMID: 38017481 Free PMC article.
-
AM-879, a PPARy non-agonist and Ser273 phosphorylation blocker, promotes insulin sensitivity without adverse effects in mice.Metabol Open. 2022 Dec 21;17:100221. doi: 10.1016/j.metop.2022.100221. eCollection 2023 Mar. Metabol Open. 2022. PMID: 36588655 Free PMC article.
-
Positive Reinforcing Mechanisms between GPR120 and PPARγ Modulate Insulin Sensitivity.Cell Metab. 2020 Jun 2;31(6):1173-1188.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.04.020. Epub 2020 May 14. Cell Metab. 2020. PMID: 32413335 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Clinical Guidelines on the Identification, Evaluation, and Treatment of Overweight and Obesity in Adults--The Evidence Report. National Institutes of Health. Obes. Res. 1998;6 Suppl 2:51S–209S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

