Targeting GPCR Signaling for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Therapies
- PMID: 32008852
- PMCID: PMC7856568
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tips.2019.12.008
Targeting GPCR Signaling for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Therapies
Abstract
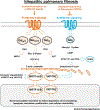
A variety of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) have been implicated in the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis, largely through their promotion of profibrotic fibroblast activation. By contrast, recent work has highlighted the beneficial effects of Gαs-coupled GPCRs on reducing fibroblast activation and fibrosis. This review highlights how fibrosis-promoting and -inhibiting GPCR signaling converges on downstream signaling and transcriptional effectors, and how the diversity and dynamics of GPCR expression challenge efforts to identify effective therapies for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). Next-generation strategies to overcome these challenges, focusing on target selection, polypharmacology, and personalized medicine approaches, are discussed as a path towards more effective GPCR-targeted therapies for pulmonary fibrosis.
Keywords: G protein-coupled receptor; MRTF; ROCK; TAZ; YAP; fibrosis.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
GPCRs and fibroblast heterogeneity in fibroblast-associated diseases.FASEB J. 2023 Aug;37(8):e23101. doi: 10.1096/fj.202301091. FASEB J. 2023. PMID: 37486603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Antifibrotic Activity of Prostacyclin Receptor Agonism Is Mediated through Inhibition of YAP/TAZ.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2019 May;60(5):578-591. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2018-0142OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30537446
-
TBK1 regulates YAP/TAZ and fibrogenic fibroblast activation.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2020 May 1;318(5):L852-L863. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00324.2019. Epub 2020 Mar 11. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32159970 Free PMC article.
-
GPCR-induced YAP activation sensitizes fibroblasts to profibrotic activity of TGFβ1.PLoS One. 2020 Feb 13;15(2):e0228195. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228195. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32053631 Free PMC article.
-
The Rho kinases: critical mediators of multiple profibrotic processes and rational targets for new therapies for pulmonary fibrosis.Pharmacol Rev. 2015;67(1):103-17. doi: 10.1124/pr.114.009381. Pharmacol Rev. 2015. PMID: 25395505 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Negative Feedback of the cAMP/PKA Pathway Regulates the Effects of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Induced NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation on Type II Alveolar Epithelial Cell Pyroptosis as a Novel Mechanism of BLM-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis.J Immunol Res. 2022 Aug 18;2022:2291877. doi: 10.1155/2022/2291877. eCollection 2022. J Immunol Res. 2022. PMID: 36033388 Free PMC article.
-
Study on Potential Differentially Expressed Genes in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis by Bioinformatics and Next-Generation Sequencing Data Analysis.Biomedicines. 2023 Nov 21;11(12):3109. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11123109. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 38137330 Free PMC article.
-
Gα12 and Gα13: Versatility in Physiology and Pathology.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Feb 14;10:809425. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.809425. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35237598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Implant Fibrosis and the Underappreciated Role of Myofibroblasts in the Foreign Body Reaction.Cells. 2021 Jul 15;10(7):1794. doi: 10.3390/cells10071794. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34359963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
lncRNA-mRNA Co-Expression and Regulation Analysis in Lung Fibroblasts from Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.Noncoding RNA. 2024 Apr 17;10(2):26. doi: 10.3390/ncrna10020026. Noncoding RNA. 2024. PMID: 38668384 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

