Localized Inhibition of Protein Phosphatase 1 by NUAK1 Promotes Spliceosome Activity and Reveals a MYC-Sensitive Feedback Control of Transcription
- PMID: 32006464
- PMCID: PMC7086158
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.01.008
Localized Inhibition of Protein Phosphatase 1 by NUAK1 Promotes Spliceosome Activity and Reveals a MYC-Sensitive Feedback Control of Transcription
Erratum in
-
Localized inhibition of protein phosphatase 1 by NUAK1 promotes spliceosome activity and reveals a MYC-sensitive feedback control of transcription.Mol Cell. 2021 Jun 3;81(11):2495. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.05.013. Mol Cell. 2021. PMID: 34087181 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
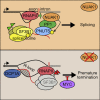
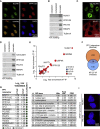
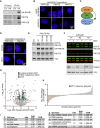
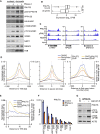
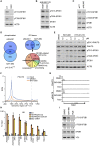
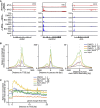
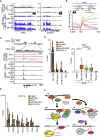
Deregulated expression of MYC induces a dependence on the NUAK1 kinase, but the molecular mechanisms underlying this dependence have not been fully clarified. Here, we show that NUAK1 is a predominantly nuclear protein that associates with a network of nuclear protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) interactors and that PNUTS, a nuclear regulatory subunit of PP1, is phosphorylated by NUAK1. Both NUAK1 and PNUTS associate with the splicing machinery. Inhibition of NUAK1 abolishes chromatin association of PNUTS, reduces spliceosome activity, and suppresses nascent RNA synthesis. Activation of MYC does not bypass the requirement for NUAK1 for spliceosome activity but significantly attenuates transcription inhibition. Consequently, NUAK1 inhibition in MYC-transformed cells induces global accumulation of RNAPII both at the pause site and at the first exon-intron boundary but does not increase mRNA synthesis. We suggest that NUAK1 inhibition in the presence of deregulated MYC traps non-productive RNAPII because of the absence of correctly assembled spliceosomes.
Keywords: ARK5; MYC; NUAK1; PNUTS; PP1; Protein Phosphatase 1; Spliceosome.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests L.W., F.P., and D.M. are employees and shareholders of Bayer AG. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Comment in
-
High-MYC Cells Depend on NUAK1 to Prevent Stalled Transcription.Cancer Discov. 2020 Apr;10(4):485. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-RW2020-022. Epub 2020 Feb 14. Cancer Discov. 2020. PMID: 32060055
-
Splice or Die: When MYC Is Driving, Transcription Needs NUAK1 to Avoid Fatal Pileups.Mol Cell. 2020 Mar 19;77(6):1157-1158. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.02.025. Mol Cell. 2020. PMID: 32200795 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
MYC dephosphorylation by the PP1/PNUTS phosphatase complex regulates chromatin binding and protein stability.Nat Commun. 2018 Aug 29;9(1):3502. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05660-0. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30158517 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium signalling links MYC to NUAK1.Oncogene. 2018 Feb 22;37(8):982-992. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.394. Epub 2017 Nov 6. Oncogene. 2018. PMID: 29106388 Free PMC article.
-
Splice or Die: When MYC Is Driving, Transcription Needs NUAK1 to Avoid Fatal Pileups.Mol Cell. 2020 Mar 19;77(6):1157-1158. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.02.025. Mol Cell. 2020. PMID: 32200795 Free PMC article.
-
Reciprocal regulatory links between cotranscriptional splicing and chromatin.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2014 Aug;32:2-10. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.03.010. Epub 2014 Mar 19. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 24657193 Review.
-
Co-transcriptional splicing and the CTD code.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2016 Sep;51(5):395-411. doi: 10.1080/10409238.2016.1230086. Epub 2016 Sep 13. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27622638 Review.
Cited by
-
Cytoplasmic forces functionally reorganize nuclear condensates in oocytes.Nat Commun. 2022 Aug 29;13(1):5070. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32675-5. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36038550 Free PMC article.
-
MYC protein interactors in gene transcription and cancer.Nat Rev Cancer. 2021 Sep;21(9):579-591. doi: 10.1038/s41568-021-00367-9. Epub 2021 Jun 29. Nat Rev Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34188192 Review.
-
Tox4 regulates transcriptional elongation and reinitiation during murine T cell development.Commun Biol. 2023 Jun 7;6(1):613. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-04992-y. Commun Biol. 2023. PMID: 37286708 Free PMC article.
-
Protein phosphatases in the RNAPII transcription cycle: erasers, sculptors, gatekeepers, and potential drug targets.Genes Dev. 2021 May 1;35(9-10):658-676. doi: 10.1101/gad.348315.121. Epub 2021 Apr 22. Genes Dev. 2021. PMID: 33888562 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TOX4 facilitates promoter-proximal pausing and C-terminal domain dephosphorylation of RNA polymerase II in human cells.Commun Biol. 2022 Apr 1;5(1):300. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03214-1. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 35365735 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Austenaa L.M., Barozzi I., Simonatto M., Masella S., Della Chiara G., Ghisletti S., Curina A., de Wit E., Bouwman B.A., de Pretis S. Transcription of mammalian cis-regulatory elements is restrained by actively enforced early termination. Mol. Cell. 2015;60:460–474. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

