Group II p21-activated kinase, PAK4, is needed for activation of focal adhesion kinases, MAPK, GSK3, and β-catenin in rat pancreatic acinar cells
- PMID: 31984786
- PMCID: PMC7099487
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00229.2019
Group II p21-activated kinase, PAK4, is needed for activation of focal adhesion kinases, MAPK, GSK3, and β-catenin in rat pancreatic acinar cells
Abstract
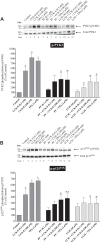
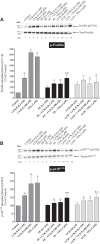
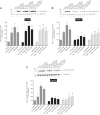
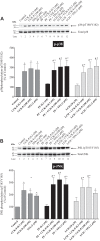
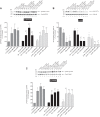
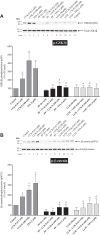
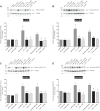
PAK4 is the only member of the Group II p21-activated kinases (PAKs) present in rat pancreatic acinar cells and is activated by gastrointestinal hormones/neurotransmitters stimulating PLC/cAMP and by various pancreatic growth factors. However, little is known of the role of PAK4 activation in cellular signaling cascades in pancreatic acinar cells. In the present study, we examined the role of PAK4's participation in five different cholecystokinin-8 (CCK-8)-stimulated signaling pathways (PI3K/Akt, MAPK, focal adhesion kinase, GSK3, and β-catenin), which mediate many of its physiological acinar-cell effects, as well as effects in pathophysiological conditions. To define PAK4's role, the effect of two different PAK4 inhibitors, PF-3758309 and LCH-7749944, was examined under experimental conditions that only inhibited PAK4 activation and not activation of the other pancreatic PAK, Group I PAK2. The inhibitors' effects on activation of these five signaling cascades by both physiological and pathophysiological concentrations of CCK, as well as by 12-O-tetradecanoylphobol-13-acetate (TPA), a PKC-activator, were examined. CCK/TPA activation of focal adhesion kinases(PYK2/p125FAK) and the accompanying adapter proteins (paxillin/p130CAS), Mek1/2, and p44/42, but not c-Raf or other MAPKs (JNK/p38), were mediated by PAK4. Activation of PI3K/Akt/p70s6K was independent of PAK4, whereas GSK3 and β-catenin stimulation was PAK4-dependent. These results, coupled with recent studies showing PAK4 is important in pancreatic fluid/electrolyte/enzyme secretion and acinar cell growth, show that PAK4 plays an important role in different cellular signaling cascades, which have been shown to mediate numerous physiological and pathophysiological processes in pancreatic acinar cells.NEW & NOTEWORTHY In pancreatic acinar cells, cholecystokinin (CCK) or 12-O-tetradecanoylphobol-13-acetate (TPA) activation of focal adhesion kinases (p125FAK,PYK2) and its accompanying adapter proteins, p130CAS/paxillin; Mek1/2, p44/42, GSK3, and β-catenin are mediated by PAK4. PI3K/Akt/p70s6K, c-Raf, JNK, or p38 pathways are independent of PAK4 activation.
Keywords: CCK; MAPK; PAK4; cell signaling; focal adhesion kinase; pancreatic acini.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
P21-activated kinase 4 in pancreatic acinar cells is activated by numerous gastrointestinal hormones/neurotransmitters and growth factors by novel signaling, and its activation stimulates secretory/growth cascades.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2018 Aug 1;315(2):G302-G317. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00005.2018. Epub 2018 Apr 19. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29672153 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase A and EPAC mediate VIP and secretin stimulation of PAK4 and activation of Na+,K+-ATPase in pancreatic acinar cells.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2019 Feb 1;316(2):G263-G277. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00275.2018. Epub 2018 Dec 6. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30520694 Free PMC article.
-
Gastrointestinal hormones/neurotransmitters and growth factors can activate P21 activated kinase 2 in pancreatic acinar cells by novel mechanisms.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Oct;1853(10 Pt A):2371-82. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2015.05.011. Epub 2015 May 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25979836 Free PMC article.
-
Cholecystokinin activates a variety of intracellular signal transduction mechanisms in rodent pancreatic acinar cells.Pharmacol Toxicol. 2002 Dec;91(6):297-303. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0773.2002.910606.x. Pharmacol Toxicol. 2002. PMID: 12688372 Review.
-
Cholecystokinin (CCK) Regulation of Pancreatic Acinar Cells: Physiological Actions and Signal Transduction Mechanisms.Compr Physiol. 2019 Mar 14;9(2):535-564. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c180014. Compr Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30873601 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of p21-Activated Kinases in Cancer and Beyond: Where Are We Heading?Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Mar 16;9:641381. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.641381. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33796531 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cofilin activation in pancreatic acinar cells plays a pivotal convergent role for mediating CCK-stimulated enzyme secretion and growth.Front Physiol. 2023 Apr 17;14:1147572. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1147572. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37138671 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

