Polygenic risk score for Alzheimer's disease and trajectories of cardiometabolic risk factors in children
- PMID: 31984241
- PMCID: PMC6971849
- DOI: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.15359.1
Polygenic risk score for Alzheimer's disease and trajectories of cardiometabolic risk factors in children
Abstract
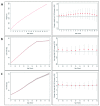
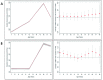
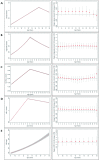
Introduction: Cardiometabolic factors are implicated in the aetiology of Alzheimer's disease and may lie on the pathways linking genetic variants to Alzheimer's disease across the life course. We examined whether polygenic risk scores (PRS) were associated with cardiometabolic health indicators through childhood and adolescence. Methods: In 7,977 participants from the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children, we tested whether a PRS for Alzheimer's disease was associated with trajectories of cardiometabolic risk factors. We examined trajectories for height at 1-18 years; lean and fat mass at 9-18 years; systolic and diastolic blood pressure at 7-18 years; glucose and C-reactive protein at 9-18 years; insulin at 10-18 years; and high and low-density lipoproteins and triglycerides birth at 18 years. We also examined birthweight and interleukin-6 (IL-6) at age 9 years and physical activity at ages 11, 12, and 15 years. Results: No consistent associations were observed between the PRS excluding genetic variants in the apolipoprotein E gene region and cardiometabolic factors trajectories across childhood and adolescence. Conclusions: We did not detect evidence to suggest that the PRS for Alzheimer's disease acts through childhood and adolescent cardiometabolic risk factors. Further studies should examine whether these associations emerge later in adulthood when variation in cardiometabolic risk factors is likely to be greater.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; cardiometabolic; polygenic risk scores; trajectories.
Copyright: © 2019 Korologou-Linden R et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Maternal prenatal anxiety and depression and trajectories of cardiometabolic risk factors across childhood and adolescence: a prospective cohort study.BMJ Open. 2021 Dec 15;11(12):e051681. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-051681. BMJ Open. 2021. PMID: 34911713 Free PMC article.
-
Polygenic risk for depression, anxiety and neuroticism are associated with the severity and rate of change in depressive symptoms across adolescence.J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2021 Dec;62(12):1462-1474. doi: 10.1111/jcpp.13422. Epub 2021 Mar 28. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 33778956
-
Polygenic risk scores for Alzheimer's disease, and academic achievement, cognitive and behavioural measures in children from the general population.Int J Epidemiol. 2019 Dec 1;48(6):1972-1980. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyz080. Int J Epidemiol. 2019. PMID: 31056667 Free PMC article.
-
Sedentary time in late childhood and cardiometabolic risk in adolescence.Pediatrics. 2015 Jun;135(6):e1432-41. doi: 10.1542/peds.2014-3750. Epub 2015 May 18. Pediatrics. 2015. PMID: 25986017 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Genetic Risk Variants With Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Trajectories in the General Population.JAMA Psychiatry. 2016 Dec 1;73(12):1285-1292. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2016.2817. JAMA Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 27806167 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Neuroticism polygenic risk predicts conversion from mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer's disease by impairing inferior parietal surface area.Hum Brain Mapp. 2024 May;45(7):e26709. doi: 10.1002/hbm.26709. Hum Brain Mapp. 2024. PMID: 38746977 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of DNA Base Excision Repair and Antioxidant Enzyme Genetic Risk Scores with Biomarker of Systemic Inflammation.Front Aging. 2022 May 4;3:897907. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2022.897907. eCollection 2022. Front Aging. 2022. PMID: 36338835 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant enzyme and DNA base repair genetic risk scores' associations with systemic oxidative stress biomarker in pooled cross-sectional studies.Front Aging. 2023 Apr 21;4:1000166. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2023.1000166. eCollection 2023. Front Aging. 2023. PMID: 37152862 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of genetic predisposition to late-onset neurodegenerative diseases on early life outcomes and brain structure.Transl Psychiatry. 2024 Apr 11;14(1):185. doi: 10.1038/s41398-024-02898-9. Transl Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38605018 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polygenic Score Models for Alzheimer's Disease: From Research to Clinical Applications.Front Neurosci. 2021 Mar 29;15:650220. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.650220. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33854414 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
- R01 DK077659/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG032984/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG016976/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG033193/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MR/P014437/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G9815508/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 HL071248/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG021886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_19009/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_15018/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

