Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells contribute to the uptake and degradation of entero bacterial viruses
- PMID: 31965000
- PMCID: PMC6972739
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-57652-0
Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells contribute to the uptake and degradation of entero bacterial viruses
Abstract
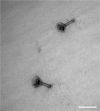
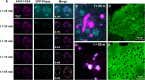
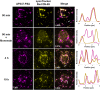
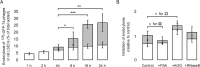
The liver is constantly exposed to dietary antigens, viruses, and bacterial products with inflammatory potential. For decades cellular uptake of virus has been studied in connection with infection, while the few studies designed to look into clearance mechanisms focused mainly on the role of macrophages. In recent years, attention has been directed towards the liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSECs), which play a central role in liver innate immunity by their ability to scavenge pathogen- and damage-associated molecular patterns. Every day our bodies are exposed to billions of gut-derived pathogens which must be efficiently removed from the circulation to prevent inflammatory and/or immune reactions in other vascular beds. Here, we have used GFP-labelled Enterobacteria phage T4 (GFP-T4-phage) as a model virus to study the viral scavenging function and metabolism in LSECs. The uptake of GFP-T4-phages was followed in real-time using deconvolution microscopy, and LSEC identity confirmed by visualization of fenestrae using structured illumination microscopy. By combining these imaging modalities with quantitative uptake and inhibition studies of radiolabelled GFP-T4-phages, we demonstrate that the bacteriophages are effectively degraded in the lysosomal compartment. Due to their high ability to take up and degrade circulating bacteriophages the LSECs may act as a primary anti-viral defence mechanism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Liver sinusoidal cells eliminate blood-borne phage K1F.mSphere. 2024 Mar 26;9(3):e0070223. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00702-23. Epub 2024 Feb 28. mSphere. 2024. PMID: 38415633 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse Hepatitis Virus Infection Induces a Toll-Like Receptor 2-Dependent Activation of Inflammatory Functions in Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells during Acute Hepatitis.J Virol. 2016 Sep 29;90(20):9096-113. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01069-16. Print 2016 Oct 15. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27489277 Free PMC article.
-
Rat liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSECs) express functional low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1 (LRP-1).J Hepatol. 2011 Dec;55(6):1346-52. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2011.03.013. Epub 2011 Apr 13. J Hepatol. 2011. PMID: 21703209
-
Cooperation of liver cells in health and disease.Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2001;161:III-XIII, 1-151. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-56553-3. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11729749 Review.
-
Role of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.J Hepatol. 2019 Jun;70(6):1278-1291. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.02.012. Epub 2019 Feb 21. J Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 30797053 Review.
Cited by
-
The Hepatic Sinusoid in Chronic Liver Disease: The Optimal Milieu for Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Nov 15;13(22):5719. doi: 10.3390/cancers13225719. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34830874 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacteriophage Interactions With Epithelial Cells: Therapeutic Implications.Front Microbiol. 2021 Jan 18;11:631161. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.631161. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33537024 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The Role of Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells in the Axis of Inflammation and Cancer Within the Liver.Front Physiol. 2020 Aug 28;11:990. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00990. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32982772 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in cancer liver metastasis.Am J Cancer Res. 2021 May 15;11(5):1845-1860. eCollection 2021. Am J Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34094657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Scavenger Function of Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells in Health and Disease.Front Physiol. 2021 Oct 11;12:757469. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.757469. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34707514 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Slopek S, Weber-Dabrowska B, Dabrowski M, Kucharewicz-Krukowska A. Results of bacteriophage treatment of suppurative bacterial infections in the years 1981–1986. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. (Warsz). 1987;35:569–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

