WormQTL2: an interactive platform for systems genetics in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 31960906
- PMCID: PMC6971878
- DOI: 10.1093/database/baz149
WormQTL2: an interactive platform for systems genetics in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
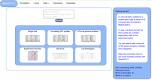
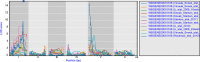
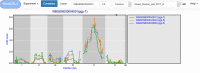
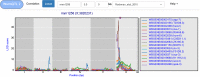
Quantitative genetics provides the tools for linking polymorphic loci to trait variation. Linkage analysis of gene expression is an established and widely applied method, leading to the identification of expression quantitative trait loci (eQTLs). (e)QTL detection facilitates the identification and understanding of the underlying molecular components and pathways, yet (e)QTL data access and mining often is a bottleneck. Here, we present WormQTL2, a database and platform for comparative investigations and meta-analyses of published (e)QTL data sets in the model nematode worm C. elegans. WormQTL2 integrates six eQTL studies spanning 11 conditions as well as over 1000 traits from 32 studies and allows experimental results to be compared, reused and extended upon to guide further experiments and conduct systems-genetic analyses. For example, one can easily screen a locus for specific cis-eQTLs that could be linked to variation in other traits, detect gene-by-environment interactions by comparing eQTLs under different conditions, or find correlations between QTL profiles of classical traits and gene expression. WormQTL2 makes data on natural variation in C. elegans and the identified QTLs interactively accessible, allowing studies beyond the original publications. Database URL: www.bioinformatics.nl/WormQTL2/.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
From QTL to gene: C. elegans facilitates discoveries of the genetic mechanisms underlying natural variation.Trends Genet. 2021 Oct;37(10):933-947. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2021.06.005. Epub 2021 Jul 3. Trends Genet. 2021. PMID: 34229867 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The genetics of gene expression in a Caenorhabditis elegans multiparental recombinant inbred line population.G3 (Bethesda). 2021 Sep 27;11(10):jkab258. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkab258. G3 (Bethesda). 2021. PMID: 34568931 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-organism eQTL mapping at cellular resolution with single-cell sequencing.Elife. 2021 Mar 18;10:e65857. doi: 10.7554/eLife.65857. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33734084 Free PMC article.
-
A multi-parent recombinant inbred line population of C. elegans allows identification of novel QTLs for complex life history traits.BMC Biol. 2019 Mar 12;17(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s12915-019-0642-8. BMC Biol. 2019. PMID: 30866929 Free PMC article.
-
Caenorhabditis elegans as a platform for molecular quantitative genetics and the systems biology of natural variation.Genet Res (Camb). 2010 Dec;92(5-6):331-48. doi: 10.1017/S0016672310000601. Genet Res (Camb). 2010. PMID: 21429266 Review.
Cited by
-
The genetic architecture underlying body-size traits plasticity over different temperatures and developmental stages in Caenorhabditis elegans.Heredity (Edinb). 2022 May;128(5):313-324. doi: 10.1038/s41437-022-00528-y. Epub 2022 Apr 5. Heredity (Edinb). 2022. PMID: 35383317 Free PMC article.
-
Punctuated Loci on Chromosome IV Determine Natural Variation in Orsay Virus Susceptibility of Caenorhabditis elegans Strains Bristol N2 and Hawaiian CB4856.J Virol. 2021 May 24;95(12):e02430-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02430-20. Print 2021 May 24. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33827942 Free PMC article.
-
Natural variation in C. elegans short tandem repeats.Genome Res. 2022 Oct;32(10):1852-1861. doi: 10.1101/gr.277067.122. Epub 2022 Oct 4. Genome Res. 2022. PMID: 36195344 Free PMC article.
-
From QTL to gene: C. elegans facilitates discoveries of the genetic mechanisms underlying natural variation.Trends Genet. 2021 Oct;37(10):933-947. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2021.06.005. Epub 2021 Jul 3. Trends Genet. 2021. PMID: 34229867 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasticity of maternal environment-dependent expression-QTLs of tomato seeds.Theor Appl Genet. 2023 Feb 22;136(2):28. doi: 10.1007/s00122-023-04322-0. Theor Appl Genet. 2023. PMID: 36810666 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

