Antitumor activity of celastrol by inhibition of proliferation, invasion, and migration in cholangiocarcinoma via PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway
- PMID: 31957323
- PMCID: PMC6970044
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.2719
Antitumor activity of celastrol by inhibition of proliferation, invasion, and migration in cholangiocarcinoma via PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway
Abstract
Aim: Cholangiocarcinoma is a malignant tumor originating from bile duct epithelium. Currently, the treatment strategy is very limited and the prognosis is poor. Recent studies reported celastrol exhibits antigrowth and antimetastasis properties in many tumors. Our study aimed to assess the anti-CCA effects of cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) and the mechanisms involved in it.
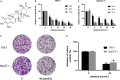
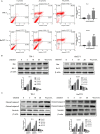
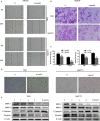
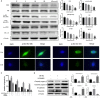
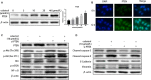
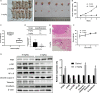
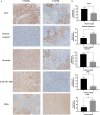
Methods: In this study, the long-term and short-term antiproliferation effects was determined using colony formation and Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assays, respectively. Flow cytometry was performed to quantify apoptosis. Furthermore, wound healing and transwell assays were performed to determine the cell migration and invasion capabilities, respectively. To further find the mechanism involved in the celastrol-induced biological functions, LY204002, a PI3K/Akt signaling inhibitor, and an Akt-1 overexpression plasmid were employed to find whether PI3K/Akt pathway was involved in the celastrol-induced CCA cell inhibition. Additionally, short interfering RNA (siRNA) was also used to investigate the mechanism involved in the celastrol-induced PI3K/Akt signaling inhibition. Western blotting and immunofluorescence assays were also performed to detect the degree of relative proteins. Moreover, we validated the antiproliferation and antimetastasis effects of celastrol in vivo by constructing subcutaneous and lung metastasis nude mice models.
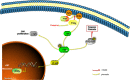
Results: We discovered that celastrol effectively induced apoptotic cell death and inhibited the capacity of migration and invasion in CCA cells. Further mechanistic study identified that celastrol regulated the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway, and the antitumor efficacy was likely due to the upregulation of PTEN, a negative regulator of PI3K/Akt. Blockage of PTEN abolished the celastrol-induced PI3K/Akt signaling inhibition. Additionally, in vivo experiments conformed celastrol inhibited the tumor growth and lung metastasis with no serious side effects.
Conclusions: Overall, our study elucidated a mechanistic framework for the anti-CCA effects of celastrol via PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway.
Keywords: Akt; apoptosis; celastrol; epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition; phosphatase and tensin homolog.
© 2019 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A PLCB1-PI3K-AKT Signaling Axis Activates EMT to Promote Cholangiocarcinoma Progression.Cancer Res. 2021 Dec 1;81(23):5889-5903. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-21-1538. Epub 2021 Sep 27. Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34580062 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway offer a promising therapeutic strategy for cholangiocarcinoma patients with high doublecortin-like kinase 1 expression.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024 Jul 9;150(7):342. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05875-3. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38980538 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-92a promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition through activation of PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer metastasis.Int J Oncol. 2017 Jul;51(1):235-244. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2017.3999. Epub 2017 May 16. Int J Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28534966
-
Research Progress of PI3K/PTEN/AKT Signaling Pathway Associated with Renal Cell Carcinoma.Dis Markers. 2022 Aug 21;2022:1195875. doi: 10.1155/2022/1195875. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. Retraction in: Dis Markers. 2023 Jul 19;2023:9756735. doi: 10.1155/2023/9756735. PMID: 36046376 Free PMC article. Retracted. Review.
-
Cholangiocarcinoma: molecular pathways and therapeutic opportunities.Semin Liver Dis. 2014 Nov;34(4):456-64. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1394144. Epub 2014 Nov 4. Semin Liver Dis. 2014. PMID: 25369307 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
miR‑224‑5p regulates the proliferation, migration and invasion of pancreatic mucinous cystadenocarcinoma by targeting PTEN.Mol Med Rep. 2021 May;23(5):346. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.11985. Epub 2021 Mar 24. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 33760113 Free PMC article.
-
Terpenoids, Cannabimimetic Ligands, beyond the Cannabis Plant.Molecules. 2020 Mar 29;25(7):1567. doi: 10.3390/molecules25071567. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32235333 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rintatolimod: a potential treatment in patients with pancreatic cancer expressing Toll-like receptor 3.Am J Cancer Res. 2023 Jun 15;13(6):2657-2669. eCollection 2023. Am J Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37424830 Free PMC article.
-
BCL2L1 is identified as a target of naringenin in regulating ovarian cancer progression.Mol Cell Biochem. 2022 May;477(5):1541-1553. doi: 10.1007/s11010-022-04389-1. Epub 2022 Feb 19. Mol Cell Biochem. 2022. PMID: 35184257
-
Adaptor protein XB130 regulates the aggressiveness of cholangiocarcinoma.PLoS One. 2021 Nov 15;16(11):e0259075. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0259075. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34780466 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carpino G, Cardinale V, Renzi A, et al. Activation of biliary tree stem cells within peribiliary glands in primary sclerosing cholangitis. J Hepatol. 2015;63:1220‐1228. - PubMed
-
- Udali S, Guarini P, Moruzzi S, et al. Global DNA methylation and hydroxymethylation differ in hepatocellular carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma and relate to survival rate. Hepatology. 2015;62:496‐504. - PubMed
-
- Loosen SH, Roderburg C, Kauertz KL, et al. Elevated levels of circulating osteopontin are associated with a poor survival after resection of cholangiocarcinoma. J Hepatol. 2017;67:749‐757. - PubMed
-
- Baron TH. Chemotherapy impregnated plastic biliary endoprostheses: one small step for man(agement) of cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology. 2000;32:1170‐1171. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

