Proteolysis-Targeting Chimeras as Therapeutics and Tools for Biological Discovery
- PMID: 31955850
- PMCID: PMC7319047
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.11.031
Proteolysis-Targeting Chimeras as Therapeutics and Tools for Biological Discovery
Abstract
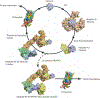
New biological tools provide new techniques to probe fundamental biological processes. Here we describe the burgeoning field of proteolysis-targeting chimeras (PROTACs), which are capable of modulating protein concentrations at a post-translational level by co-opting the ubiquitin-proteasome system. We describe the PROTAC technology and its application to drug discovery and provide examples where PROTACs have enabled novel biological insights. Furthermore, we provide a workflow for PROTAC development and use and discuss the benefits and issues associated with PROTACs. Finally, we compare PROTAC-mediated protein-level modulation with other technologies, such as RNAi and genome editing.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests C.M.C. is a founder, consultant, and shareholder in Arvinas, which supports research in his lab. C.M.C. is an inventor of the following patents: 9500653 (Small-Molecule Hydrophobic Tagging of Fusion Proteins and Induced Degradation of Same), 9632089 (Small-Molecule Hydrophobic Tagging of Fusion Proteins and Induced Degradation of Same), 10145848 (Small-Molecule Hydrophobic Tagging of Fusion Proteins and Induced Degradation of Same), 9938264 (Proteolysis-Targeting Chimera Compounds and Methods of Preparing and Using Same), 7041298 (Proteolysis-Targeting Chimeric Pharmaceutical), 7208157 (Proteolysis-Targeting Chimeric Pharmaceutical), and 10071164 (Estrogen-Related Receptor Alpha-Based PROTAC Compounds and Associated Methods of Use).
Figures
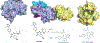
Similar articles
-
Proteolysis-targeting chimeras (PROTACs) in cancer therapy.Mol Cancer. 2022 Apr 11;21(1):99. doi: 10.1186/s12943-021-01434-3. Mol Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35410300 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PROteolysis TArgeting Chimeras (PROTACs) - Past, present and future.Drug Discov Today Technol. 2019 Apr;31:15-27. doi: 10.1016/j.ddtec.2019.01.002. Epub 2019 Feb 13. Drug Discov Today Technol. 2019. PMID: 31200855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vivo synthetic chemistry of proteolysis targeting chimeras (PROTACs).Bioorg Med Chem. 2021 Jul 1;41:116221. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2021.116221. Epub 2021 May 19. Bioorg Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34034148 Review.
-
Developing PROteolysis TArgeting Chimeras (PROTACs) for hematologic malignancies.Cancer Lett. 2022 Sep 28;544:215808. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2022.215808. Epub 2022 Jun 25. Cancer Lett. 2022. PMID: 35764266
-
PROteolysis TArgeting Chimeras (PROTACs) as emerging anticancer therapeutics.Oncogene. 2020 Jun;39(26):4909-4924. doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-1336-y. Epub 2020 May 31. Oncogene. 2020. PMID: 32475992 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Developing HDAC4-Selective Protein Degraders To Investigate the Role of HDAC4 in Huntington's Disease Pathology.J Med Chem. 2022 Sep 22;65(18):12445-12459. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c01149. Epub 2022 Sep 13. J Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 36098485 Free PMC article.
-
Tackling Drug Resistance in EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutant Lung Cancer.Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2021 Mar 9;14:301-317. doi: 10.2147/PGPM.S242045. eCollection 2021. Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2021. PMID: 33727854 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ligand Design for Cereblon Based Immunomodulatory Therapy.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2020 May 8;11(6):1088-1089. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.0c00214. eCollection 2020 Jun 11. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2020. PMID: 32550984 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Discovery of PRMT3 Degrader for the Treatment of Acute Leukemia.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Oct;11(38):e2405963. doi: 10.1002/advs.202405963. Epub 2024 Aug 9. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 39120042 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of Apoptosis in Cancer Cells by Glutathione Transferase Inhibitor Mediated Hydrophobic Tagging Molecules.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2021 May 3;12(5):720-725. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.0c00627. eCollection 2021 May 13. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2021. PMID: 34055217 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altmann K-H, Johannes B, Kessler H, Diederich F, Krautler B, Lippard S, Liskamp R, Muller K, Nolan EM, Samori B, et al. (2009). The State of the Art of Chemical Biology. ChemBioChem 10, 16–29. - PubMed
-
- Amm I, Sommer T, and Wolf DH (2014). Protein quality control and elimination of protein waste: The role of the ubiquitin–proteasome system. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research 1843, 182–196. - PubMed
-
- Ardley HC, and Robinson PA (2005). E3 ubiquitin ligases. Essays In Biochemistry 41, 15–30. - PubMed
-
- Argiropoulos B, Yung E, and Humphries RK (2007). Unraveling the crucial roles of Meis1 in leukemogenesis and normal hematopoiesis. Genes & Development 21, 2845–2849. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

