The Promises and Challenges of Toxico-Epigenomics: Environmental Chemicals and Their Impacts on the Epigenome
- PMID: 31950866
- PMCID: PMC7015548
- DOI: 10.1289/EHP6104
The Promises and Challenges of Toxico-Epigenomics: Environmental Chemicals and Their Impacts on the Epigenome
Abstract
Background: It has been estimated that a substantial portion of chronic and noncommunicable diseases can be caused or exacerbated by exposure to environmental chemicals. Multiple lines of evidence indicate that early life exposure to environmental chemicals at relatively low concentrations could have lasting effects on individual and population health. Although the potential adverse effects of environmental chemicals are known to the scientific community, regulatory agencies, and the public, little is known about the mechanistic basis by which these chemicals can induce long-term or transgenerational effects. To address this question, epigenetic mechanisms have emerged as the potential link between genetic and environmental factors of health and disease.
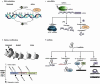
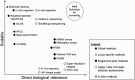
Objectives: We present an overview of epigenetic regulation and a summary of reported evidence of environmental toxicants as epigenetic disruptors. We also discuss the advantages and challenges of using epigenetic biomarkers as an indicator of toxicant exposure, using measures that can be taken to improve risk assessment, and our perspectives on the future role of epigenetics in toxicology.
Discussion: Until recently, efforts to apply epigenomic data in toxicology and risk assessment were restricted by an incomplete understanding of epigenomic variability across tissue types and populations. This is poised to change with the development of new tools and concerted efforts by researchers across disciplines that have led to a better understanding of epigenetic mechanisms and comprehensive maps of epigenomic variation. With the foundations now in place, we foresee that unprecedented advancements will take place in the field in the coming years. https://doi.org/10.1289/EHP6104.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Epigenomics in stress tolerance of plants under the climate change.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Jul;50(7):6201-6216. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08539-6. Epub 2023 Jun 9. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37294468 Review.
-
Toxicoepigenetics and Environmental Health: Challenges and Opportunities.Chem Res Toxicol. 2022 Aug 15;35(8):1293-1311. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.1c00445. Epub 2022 Jul 25. Chem Res Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35876266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Applications in Adverse Outcome Pathways and Environmental Risk Evaluation.Environ Health Perspect. 2018 Apr 12;126(4):045001. doi: 10.1289/EHP2322. Environ Health Perspect. 2018. PMID: 29669403 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic memory of environmental organisms: a reflection of lifetime stressor exposures.Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2014 Apr;764-765:10-7. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2013.10.003. Epub 2013 Oct 17. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2014. PMID: 24141178 Review.
-
Environmental chemical exposures and human epigenetics.Int J Epidemiol. 2012 Feb;41(1):79-105. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyr154. Epub 2011 Dec 13. Int J Epidemiol. 2012. PMID: 22253299 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Molecular and cell phenotype programs in oral epithelial cells directed by co-exposure to arsenic and smokeless tobacco.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 15:2024.10.14.618077. doi: 10.1101/2024.10.14.618077. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39463997 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Phytocompounds targeting epigenetic modulations: an assessment in cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Mar 26;14:1273993. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1273993. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38596245 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thyroid hormone links environmental signals to DNA methylation.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2024 Mar 25;379(1898):20220506. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2022.0506. Epub 2024 Feb 5. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38310936 Review.
-
Gene-environment interactions in Alzheimer disease: the emerging role of epigenetics.Nat Rev Neurol. 2022 Nov;18(11):643-660. doi: 10.1038/s41582-022-00714-w. Epub 2022 Sep 30. Nat Rev Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36180553 Review.
-
Epigenome-wide association studies of occupational exposure to benzene and formaldehyde.Epigenetics. 2022 Dec;17(13):2259-2277. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2022.2115604. Epub 2022 Aug 25. Epigenetics. 2022. PMID: 36017556 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alofe O, Kisanga E, Inayat-Hussain SH, Fukumura M, Garcia-Milian R, Perera L, et al. . 2019. Determining the endocrine disruption potential of industrial chemicals using an integrative approach: public databases, in vitro exposure, and modeling receptor interactions. Environ Int 131:104969, PMID: 31310931, 10.1016/j.envint.2019.104969. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

