Viral MicroRNAs: Interfering the Interferon Signaling
- PMID: 31924149
- PMCID: PMC7476571
- DOI: 10.2174/1381612826666200109181238
Viral MicroRNAs: Interfering the Interferon Signaling
Abstract
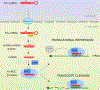
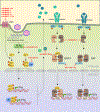
Interferons are secreted cytokines with potent antiviral, antitumor and immunomodulatory functions. As the first line of defense against viruses, this pathway restricts virus infection and spread. On the contrary, viruses have evolved ingenious strategies to evade host immune responses including the interferon pathway. Multiple families of viruses, in particular, DNA viruses, encode microRNA (miR) that are small, non-protein coding, regulatory RNAs. Virus-derived miRNAs (v-miR) function by targeting host and virus-encoded transcripts and are critical in shaping host-pathogen interaction. The role of v-miRs in viral pathogenesis is emerging as demonstrated by their function in subverting host defense mechanisms and regulating fundamental biological processes such as cell survival, proliferation, modulation of viral life-cycle phase. In this review, we will discuss the role of v-miRs in the suppression of host genes involved in the viral nucleic acid detection, JAK-STAT pathway, and cytokine-mediated antiviral gene activation to favor viral replication and persistence. This information has yielded new insights into our understanding of how v-miRs promote viral evasion of host immunity and likely provide novel antiviral therapeutic targets.
Keywords: JAK-STAT; Viruses; immune response; interferons; post-transcriptional silencing; viral microRNA..
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.net.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors have stated explicitly that there are no conflicts of interest in connection with this article.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A MicroRNA Screen Identifies the Wnt Signaling Pathway as a Regulator of the Interferon Response during Flavivirus Infection.J Virol. 2017 Mar 29;91(8):e02388-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02388-16. Print 2017 Apr 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28148804 Free PMC article.
-
Inducible MicroRNA-3570 Feedback Inhibits the RIG-I-Dependent Innate Immune Response to Rhabdovirus in Teleost Fish by Targeting MAVS/IPS-1.J Virol. 2018 Jan 2;92(2):e01594-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01594-17. Print 2018 Jan 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29093090 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA hsa-miR-324-5p Suppresses H5N1 Virus Replication by Targeting the Viral PB1 and Host CUEDC2.J Virol. 2018 Sep 12;92(19):e01057-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01057-18. Print 2018 Oct 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 30045983 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory roles of human herpesvirus-encoded microRNA in host-virus interaction.Rev Med Virol. 2020 Jan;30(1):e2081. doi: 10.1002/rmv.2081. Epub 2019 Aug 20. Rev Med Virol. 2020. PMID: 31432608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs in virus-induced tumorigenesis and IFN system.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015 Apr;26(2):183-94. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2014.11.002. Epub 2014 Nov 13. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015. PMID: 25466647 Review.
Cited by
-
The emerging role of miRNAs in the pathogenesis of COVID-19: Protective effects of nutraceutical polyphenolic compounds against SARS-CoV-2 infection.Int J Med Sci. 2022 Jul 18;19(8):1340-1356. doi: 10.7150/ijms.76168. eCollection 2022. Int J Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 35928726 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of microRNAs in solving COVID-19 puzzle from infection to therapeutics: A mini-review.Virus Res. 2022 Jan 15;308:198631. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2021.198631. Epub 2021 Nov 14. Virus Res. 2022. PMID: 34788642 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human and herpesvirus microRNAs in periodontal disease.Periodontol 2000. 2021 Oct;87(1):325-339. doi: 10.1111/prd.12404. Periodontol 2000. 2021. PMID: 34463985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computational analysis of microRNA-mediated interactions in SARS-CoV-2 infection.PeerJ. 2020 Jun 5;8:e9369. doi: 10.7717/peerj.9369. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 32547891 Free PMC article.
-
Covid-19 and oral diseases: Crosstalk, synergy or association?Rev Med Virol. 2021 Nov;31(6):e2226. doi: 10.1002/rmv.2226. Epub 2021 Mar 1. Rev Med Virol. 2021. PMID: 33646645 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

