The association of telomere length and telomerase activity with adverse outcomes in older patients with non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome
- PMID: 31923255
- PMCID: PMC6953865
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227616
The association of telomere length and telomerase activity with adverse outcomes in older patients with non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome
Abstract
Background: Non-ST elevation acute coronary syndrome (NSTEACS) occurs more frequently in older patients with an increased occurrence of recurrent cardiac events following the index presentation. Telomeres are structures consisting of repeated DNA sequences as associated shelterin proteins at the ends of chromosomes. We aim to determine whether telomere length (TL) and telomerase activity (TA) predicted poor outcomes in older patients presenting with NSTEACS undergoing invasive care.
Method: Older patients undergoing invasive management for NSTEACS were recruited to the ICON-1 biomarker study (NCT01933581). Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) were recovered on 153 patients. DNA was isolated and mean TL was measured by quantitative PCR expressed as relative T (telomere repeat copy number) to S (single copy gene number) ratio (T/S ratio), and a telomere repeat amplification assay was used to assess TA during index presentation with NSTEACS. Primary clinical outcomes consisted of death, myocardial infarction (MI), unplanned revascularisation, stroke and significant bleeding recorded at 1 year. TL and TA were divided into tertile groups for analysis. Cox proportional hazards regression was performed. Ordinal regression was performed to evaluate the relationship between TL and TA and traditional cardiovascular risk factors at baseline.
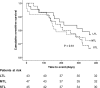
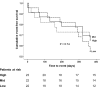
Results: 298 patients were recruited in the ICON-1 study of which 153 had PBMC recovered. The mean age was 81.0 ± 4.0 years (64% male). Mean telomere length T/S ratio was 0.47 ± 0.25 and mean TA was 1.52 ± 0.61 units. The primary composite outcome occurred in 44 (28.8%) patients. There was no association between short TL or low TA and incidence of the primary composite outcome (Hazard Ratio [HR] 1.50, 95% Confidence Interval [CI] 0.68-3.34, p = 0.32 and HR 1.33, 95% CI 0.52-3.36, p = 0.51 respectively).
Conclusion: TL and TA are not found to be associated with the incidence of adverse outcomes in older patients presenting with NSTEACS undergoing invasive care.
Clinical trial registration: URL: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov Unique identifier: NCT01933581.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist. VK has received research funding from NIHR BRC Newcastle, AstraZeneca, and British Heart Foundation. WQ is salaried by Sanofi Genzyme. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of Telomere Length With Myocardial Infarction: A Prospective Cohort From the Population Based HUNT 2 Study.Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2017 May-Jun;59(6):649-655. doi: 10.1016/j.pcad.2017.04.001. Epub 2017 Apr 23. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2017. PMID: 28442329 Review.
-
Telomerase activity and telomere length as prognostic factors of adult T-cell leukemia.Leuk Lymphoma. 2005 Mar;46(3):393-9. doi: 10.1080/10428190400018349. Leuk Lymphoma. 2005. PMID: 15621829
-
The association between vitamin D status and clinical events in high-risk older patients with non-ST elevation acute coronary syndrome undergoing invasive management.PLoS One. 2019 Jun 12;14(6):e0217476. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0217476. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31188902 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
One-year clinical outcomes in older patients with non-ST elevation acute coronary syndrome undergoing coronary angiography: An analysis of the ICON1 study.Int J Cardiol. 2019 Jan 1;274:45-51. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2018.09.086. Epub 2018 Sep 28. Int J Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 30287058
-
The telomere world and aging: Analytical challenges and future perspectives.Ageing Res Rev. 2019 Mar;50:27-42. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2019.01.004. Epub 2019 Jan 4. Ageing Res Rev. 2019. PMID: 30615937 Review.
Cited by
-
The effects of aspirin and N-3 fatty acids on telomerase activity in adults with diabetes mellitus.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2020 Sep 24;30(10):1795-1799. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2020.06.014. Epub 2020 Jun 25. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2020. PMID: 32723580 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Telomere Length: A Cardiovascular Biomarker and a Novel Therapeutic Target.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 16;23(24):16010. doi: 10.3390/ijms232416010. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555658 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Leukocyte Telomere Length as a Molecular Biomarker of Coronary Heart Disease.Genes (Basel). 2022 Jul 12;13(7):1234. doi: 10.3390/genes13071234. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35886017 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disease-modifying effects of sodium selenate in a model of drug-resistant, temporal lobe epilepsy.Elife. 2023 Mar 9;12:e78877. doi: 10.7554/eLife.78877. Elife. 2023. PMID: 36892461 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tunstall-Pedoe H, Kuulasmaa K, Amouyel P, Arveiler D, Rajakangas AM, Pajak A. Myocardial infarction and coronary deaths in the World Health Organization MONICA Project. Registration procedures, event rates, and case-fatality rates in 38 populations from 21 countries in four continents. Circulation. 1994;90(1):583–612. Epub 1994/07/01. 10.1161/01.cir.90.1.583 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zaman MJ, Stirling S, Shepstone L, Ryding A, Flather M, Bachmann M, et al. The association between older age and receipt of care and outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndromes: a cohort study of the Myocardial Ischaemia National Audit Project (MINAP). Eur Heart J. 2014;35(23):1551–8. Epub 2014/03/20. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehu039 . - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

