Ping-Pong-Tumor and Host in Pancreatic Cancer Progression
- PMID: 31921628
- PMCID: PMC6927459
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01359
Ping-Pong-Tumor and Host in Pancreatic Cancer Progression
Abstract
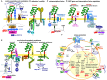
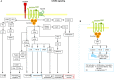
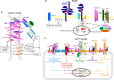
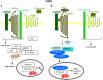
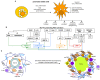
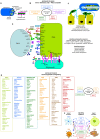
Metastasis is the main cause of high pancreatic cancer (PaCa) mortality and trials dampening PaCa mortality rates are not satisfying. Tumor progression is driven by the crosstalk between tumor cells, predominantly cancer-initiating cells (CIC), and surrounding cells and tissues as well as distant organs, where tumor-derived extracellular vesicles (TEX) are of major importance. A strong stroma reaction, recruitment of immunosuppressive leukocytes, perineural invasion, and early spread toward the peritoneal cavity, liver, and lung are shared with several epithelial cell-derived cancer, but are most prominent in PaCa. Here, we report on the state of knowledge on the PaCIC markers Tspan8, alpha6beta4, CD44v6, CXCR4, LRP5/6, LRG5, claudin7, EpCAM, and CD133, which all, but at different steps, are engaged in the metastatic cascade, frequently via PaCIC-TEX. This includes the contribution of PaCIC markers to TEX biogenesis, targeting, and uptake. We then discuss PaCa-selective features, where feedback loops between stromal elements and tumor cells, including distorted transcription, signal transduction, and metabolic shifts, establish vicious circles. For the latter particularly pancreatic stellate cells (PSC) are responsible, furnishing PaCa to cope with poor angiogenesis-promoted hypoxia by metabolic shifts and direct nutrient transfer via vesicles. Furthermore, nerves including Schwann cells deliver a large range of tumor cell attracting factors and Schwann cells additionally support PaCa cell survival by signaling receptor binding. PSC, tumor-associated macrophages, and components of the dysplastic stroma contribute to perineural invasion with signaling pathway activation including the cholinergic system. Last, PaCa aggressiveness is strongly assisted by the immune system. Although rich in immune cells, only immunosuppressive cells and factors are recovered in proximity to tumor cells and hamper effector immune cells entering the tumor stroma. Besides a paucity of immunostimulatory factors and receptors, immunosuppressive cytokines, myeloid-derived suppressor cells, regulatory T-cells, and M2 macrophages as well as PSC actively inhibit effector cell activation. This accounts for NK cells of the non-adaptive and cytotoxic T-cells of the adaptive immune system. We anticipate further deciphering the molecular background of these recently unraveled intermingled phenomena may turn most lethal PaCa into a curatively treatable disease.
Keywords: cancer-initiating cell markers; exosomes; immunosuppression; metabolism; metastasis; pancreatic cancer; perineural invasion; stellate cells.
Copyright © 2019 Mu, Wang and Zöller.
Figures

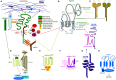

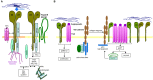


Similar articles
-
Tspan8, CD44v6 and alpha6beta4 are biomarkers of migrating pancreatic cancer-initiating cells.Int J Cancer. 2013 Jul 15;133(2):416-26. doi: 10.1002/ijc.28044. Epub 2013 Feb 15. Int J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23338841
-
CD44v6-competent tumor exosomes promote motility, invasion and cancer-initiating cell marker expression in pancreatic and colorectal cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2016 Aug 23;7(34):55409-55436. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10580. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27419629 Free PMC article.
-
The Pancreatic Cancer-Initiating Cell Marker CD44v6 Affects Transcription, Translation, and Signaling: Consequences for Exosome Composition and Delivery.J Oncol. 2019 Aug 7;2019:3516973. doi: 10.1155/2019/3516973. eCollection 2019. J Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31485223 Free PMC article.
-
Pancreatic cancer stem cell markers and exosomes - the incentive push.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Jul 14;22(26):5971-6007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i26.5971. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27468191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes, metastases, and the miracle of cancer stem cell markers.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2019 Jun;38(1-2):259-295. doi: 10.1007/s10555-019-09793-6. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2019. PMID: 31030373 Review.
Cited by
-
Neural Component of the Tumor Microenvironment in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Oct 26;14(21):5246. doi: 10.3390/cancers14215246. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36358664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The key roles of cancer stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Mar 8;6(1):109. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00499-2. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021. PMID: 33678805 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer: a mirrored room between tumor bulk and tumor microenvironment.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Jun 28;40(1):217. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-02022-5. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34183054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Purinergic Signaling in Pancreas-From Physiology to Therapeutic Strategies in Pancreatic Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 20;21(22):8781. doi: 10.3390/ijms21228781. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33233631 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Schwann Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment: Need More Attention.J Oncol. 2022 Feb 10;2022:1058667. doi: 10.1155/2022/1058667. eCollection 2022. J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35186076 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

