Kinesin-13 and Kinesin-8 Function during Cell Growth and Division in the Moss Physcomitrella patens
- PMID: 31919299
- PMCID: PMC7054034
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.19.00521
Kinesin-13 and Kinesin-8 Function during Cell Growth and Division in the Moss Physcomitrella patens
Abstract
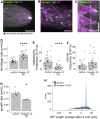
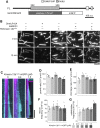
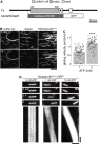
Kinesin-13 and Kinesin-8 are well-known microtubule (MT) depolymerases that regulate MT length and chromosome movement in animal mitosis. While much is unknown about plant Kinesin-8, Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) and rice (Oryza sativa) Kinesin-13 have been shown to depolymerize MTs in vitro. However, the mitotic function of both kinesins has yet to be determined in plants. Here, we generated complete null mutants of Kinesin-13 and Kinesin-8 in moss (Physcomitrella patens). Both kinesins were found to be nonessential for viability, but the Kinesin-13 knockout (KO) line had increased mitotic duration and reduced spindle length, whereas the Kinesin-8 KO line did not display obvious mitotic defects. Surprisingly, spindle MT poleward flux, which is mediated by Kinesin-13 in animals, was retained in the absence of Kinesin-13. MT depolymerase activity was not detectable for either kinesin in vitro, while MT catastrophe-inducing activity (Kinesin-13) or MT gliding activity (Kinesin-8) was observed. Interestingly, both KO lines showed waviness in their protonema filaments, which correlated with positional instability of the MT foci in their tip cells. Taken together, the results suggest that plant Kinesin-13 and Kinesin-8 have diverged in both mitotic function and molecular activity, acquiring roles in regulating MT foci positioning for directed tip growth.
© 2020 American Society of Plant Biologists. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
NACK kinesin is required for metaphase chromosome alignment and cytokinesis in the moss Physcomitrella patens.Cell Struct Funct. 2015;40(1):31-41. doi: 10.1247/csf.14016. Cell Struct Funct. 2015. PMID: 25748359
-
RNAi screening identifies the armadillo repeat-containing kinesins responsible for microtubule-dependent nuclear positioning in Physcomitrella patens.Plant Cell Physiol. 2015 Apr;56(4):737-49. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcv002. Epub 2015 Jan 13. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25588389
-
Microtubule poleward flux in human cells is driven by the coordinated action of four kinesins.EMBO J. 2020 Dec 1;39(23):e105432. doi: 10.15252/embj.2020105432. Epub 2020 Oct 19. EMBO J. 2020. PMID: 33073400 Free PMC article.
-
A model of microtubule depolymerization by kinesin-8 motor proteins.Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2024;141:87-122. doi: 10.1016/bs.apcsb.2023.12.002. Epub 2023 Dec 28. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2024. PMID: 38960488 Review.
-
Non-canonical functions of the mitotic kinesin Eg5.Thorac Cancer. 2018 Aug;9(8):904-910. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.12792. Epub 2018 Jun 21. Thorac Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29927078 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Kinesin-4 optimizes microtubule orientations for responsive tip growth guidance in moss.J Cell Biol. 2023 Sep 4;222(9):e202202018. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202202018. Epub 2023 Jun 30. J Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 37389658 Free PMC article.
-
Two Is Company, but Four Is a Party-Challenges of Tetraploidization for Cell Wall Dynamics and Efficient Tip-Growth in Pollen.Plants (Basel). 2021 Nov 5;10(11):2382. doi: 10.3390/plants10112382. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34834745 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Armadillo repeat-containing kinesin represents the versatile plus-end-directed transporter in Physcomitrella.Nat Plants. 2023 May;9(5):733-748. doi: 10.1038/s41477-023-01397-x. Epub 2023 May 4. Nat Plants. 2023. PMID: 37142749
-
SABRE populates ER domains essential for cell plate maturation and cell expansion influencing cell and tissue patterning.Elife. 2021 Mar 9;10:e65166. doi: 10.7554/eLife.65166. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33687329 Free PMC article.
-
Microtubule-associated phase separation of MIDD1 tunes cell wall spacing in xylem vessels in Arabidopsis thaliana.Nat Plants. 2024 Jan;10(1):100-117. doi: 10.1038/s41477-023-01593-9. Epub 2024 Jan 3. Nat Plants. 2024. PMID: 38172572
References
-
- Collonnier C., Epert A., Mara K., Maclot F., Guyon-Debast A., Charlot F., White C., Schaefer D.G., Nogué F. (2017). CRISPR-Cas9-mediated efficient directed mutagenesis and RAD51-dependent and RAD51-independent gene targeting in the moss Physcomitrella patens. Plant Biotechnol. J. 15: 122–131. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cove D. (2005). The moss Physcomitrella patens. Annu. Rev. Genet. 39: 339–358. - PubMed
-
- Desai A., Verma S., Mitchison T.J., Walczak C.E. (1999). Kin I kinesins are microtubule-destabilizing enzymes. Cell 96: 69–78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

