Human Cytomegalovirus Decreases Major Histocompatibility Complex Class II by Regulating Class II Transactivator Transcript Levels in a Myeloid Cell Line
- PMID: 31915281
- PMCID: PMC7081919
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01901-19
Human Cytomegalovirus Decreases Major Histocompatibility Complex Class II by Regulating Class II Transactivator Transcript Levels in a Myeloid Cell Line
Abstract
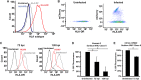
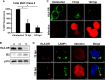
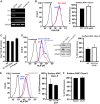
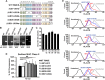
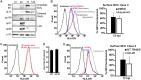
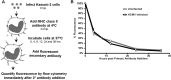
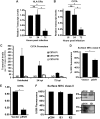
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) is a ubiquitous pathogen that encodes many proteins to modulate the host immune response. Extensive efforts have led to the elucidation of multiple strategies employed by HCMV to effectively block NK cell targeting of virus-infected cells and the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I-primed CD8+ T cell response. However, viral regulation of the MHC class II-mediated CD4+ T cell response is understudied in endogenous MHC class II-expressing cells, largely because the popular cell culture systems utilized for studying HCMV do not endogenously express MHC class II. Of the many cell types infected by HCMV in the host, myeloid cells, such as monocytes, are of particular importance due to their role in latency and subsequent dissemination throughout the host. We investigated the impact of HCMV infection on MHC class II in Kasumi-3 cells, a myeloid-progenitor cell line that endogenously expresses the MHC class II gene, HLA-DR. We observed a significant reduction in the expression of surface and total HLA-DR at 72 h postinfection (hpi) and 120 hpi in infected cells. The decrease in HLA-DR expression was independent of the expression of previously described viral genes that regulate the MHC class II complex or the unique short (US) region of HCMV, a region expressing many immunomodulatory genes. The altered surface level of HLA-DR was not a result of increased endocytosis and degradation but was a result of a reduction in HLA-DR transcripts due to a decrease in the expression of the class II transactivator (CIITA).IMPORTANCE Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) is an opportunistic herpesvirus that is asymptomatic for healthy individuals but that can lead to severe pathology in patients with congenital infections and immunosuppressed patients. Thus, it is important to understand the modulation of the immune response by HCMV, which is understudied in the context of endogenous MHC class II regulation. Using Kasumi-3 cells as a myeloid progenitor cell model endogenously expressing MHC class II (HLA-DR), this study shows that HCMV decreases the expression of HLA-DR in infected cells by reducing the transcription of HLA-DR transcripts early during infection independently of the expression of previously implicated genes. This is an important finding, as it highlights a mechanism of immune evasion utilized by HCMV to decrease the expression of MHC class II in a relevant cell system that endogenously expresses the MHC class II complex.
Keywords: Kasumi-3; MHC class II; cytomegalovirus; myeloid.
Copyright © 2020 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Human cytomegalovirus decreases constitutive transcription of MHC class II genes in mature Langerhans cells by reducing CIITA transcript levels.Mol Immunol. 2011 May;48(9-10):1160-7. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2011.02.010. Epub 2011 Mar 31. Mol Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21458073 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of the MHC class II antigen presentation pathway by human cytomegalovirus.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2002;269:101-15. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-59421-2_7. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12224504 Review.
-
Escape of human cytomegalovirus from HLA-DR-restricted CD4(+) T-cell response is mediated by repression of gamma interferon-induced class II transactivator expression.J Virol. 1999 Aug;73(8):6582-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.8.6582-6589.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 10400755 Free PMC article.
-
Human Cytomegalovirus Antigen Presentation by HLA-DR+ NKG2C+ Adaptive NK Cells Specifically Activates Polyfunctional Effector Memory CD4+ T Lymphocytes.Front Immunol. 2019 Apr 3;10:687. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00687. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31001281 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Modulation of HLA expression in human cytomegalovirus immune evasion.Cell Mol Immunol. 2007 Apr;4(2):91-8. Cell Mol Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17484802 Review.
Cited by
-
Correspondence on editorial regarding "Novel role of MHC class II transactivator in hepatitis B virus replication and viral counteraction".Clin Mol Hepatol. 2024 Oct;30(4):1028-1030. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2024.0515. Epub 2024 Jul 9. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 38978449 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The Dual Role of the Innate Immune System in the Effectiveness of mRNA Therapeutics.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 1;24(19):14820. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914820. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834268 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhanced Immunomodulatory Effects of Thymosin-Alpha-1 in Combination with Polyanionic Carbosilane Dendrimers against HCMV Infection.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 6;25(4):1952. doi: 10.3390/ijms25041952. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38396631 Free PMC article.
-
The MHC Class II Transactivator CIITA: Not (Quite) the Odd-One-Out Anymore among NLR Proteins.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 22;22(3):1074. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031074. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33499042 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory B Cells Expressing Granzyme B from Tolerant Renal Transplant Patients: Highly Differentiated B Cells with a Unique Pathway with a Specific Regulatory Profile and Strong Interactions with Immune System Cells.Cells. 2024 Jul 31;13(15):1287. doi: 10.3390/cells13151287. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39120317 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fielding CA, Aicheler R, Stanton RJ, Wang ECY, Han S, Seirafian S, Davies J, McSharry BP, Weekes MP, Antrobus PR, Prod'homme V, Blanchet FP, Sugrue D, Cuff S, Roberts D, Davison AJ, Lehner PJ, Wilkinson GWG, Tomasec P. 2014. Two novel human cytomegalovirus NK cell evasion functions target MICA for lysosomal degradation. PLoS Pathog 10:e1004058. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1004058. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fielding CA, Weekes MP, Nobre LV, Ruckova E, Wilkie GS, Paulo JA, Chang C, Suárez NM, Davies JA, Antrobus R, Stanton RJ, Aicheler RJ, Nichols H, Vojtesek B, Trowsdale J, Davison AJ, Gygi SP, Tomasec P, Lehner PJ, Wilkinson GW. 2017. Control of immune ligands by members of a cytomegalovirus gene expansion suppresses natural killer cell activation. Elife 6:e22206. doi:10.7554/eLife.22206. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dunn C, Chalupny NJ, Sutherland CL, Dosch S, Sivakumar PV, Johnson DC, Cosman D. 2003. Human cytomegalovirus glycoprotein UL16 causes intracellular sequestration of NKG2D ligands, protecting against natural killer cell cytotoxicity. J Exp Med 197:1427–1439. doi:10.1084/jem.20022059. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

