Soluble CD146, a cerebrospinal fluid marker for neuroinflammation, promotes blood-brain barrier dysfunction
- PMID: 31903117
- PMCID: PMC6929609
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.37142
Soluble CD146, a cerebrospinal fluid marker for neuroinflammation, promotes blood-brain barrier dysfunction
Abstract
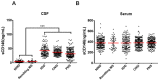
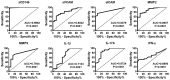
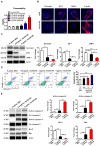
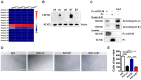
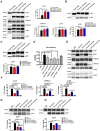
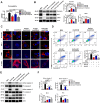
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) dysfunction is an initial event of various neuroinflammatory diseases. However, the absence of reliable markers and mechanisms for BBB damage greatly limits the diagnosis and treatment of neuroinflammatory diseases. Soluble CD146 (sCD146) is mainly derived from vascular endothelial cells (ECs) and highly elevated in inflammatory settings. Based on a small cohort, our previous study showed that sCD146 is elevated in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of multiple sclerosis (MS), which is accompanied with BBB damage. Nevertheless, whether sCD146 monitors and regulates the BBB dysfunction remains unknown. Methods: Coupled serum and CSF samples from patients with or without neuroinflammatory diseases were collected via multicenter collaborations. sCD146 was measured by sandwich ELISA using anti-CD146 antibodies AA1 and AA98, both of which were generated in our laboratory. The correlations between sCD146 and other clinical parameters or inflammatory factors were analyzed by Spearman's correlation coefficient analysis. The role of sCD146 on BBB function was examined in an in vitro BBB model. Results: Between July 20, 2011, and February 31, 2017, we collected coupled serum and CSF samples from 823 patients, of which 562 (68.3%) had neuroinflammatory diseases, 44 (5.3%) had remitting MS, and 217 (26.4%) had non-inflammatory neurological diseases (NIND). We found that sCD146 in CSF, but not in serum, is abnormally elevated in neuroinflammatory diseases (37.3 ± 13.3 ng/mL) compared with NIND (4.7 ± 2.9 ng/mL) and remitting MS (4.6 ± 3.5 ng/mL). Abnormally elevated CSF sCD146 is significantly correlated with the hyperpermeability-related clinical parameters of BBB and neuroinflammation-related factors. Moreover, CSF sCD146 shows higher sensitivity and specificity for evaluating BBB damage. Using an in vitro BBB model, we found that sCD146 impairs BBB function by promoting BBB permeability via an association with integrin αvβ1. Blocking integrin αvβ1 significantly attenuates sCD146-induced hyperpermeability of the BBB. Conclusion: Our study provides convincing evidence that CSF sCD146 is a sensitive marker of BBB damage and neuroinflammation. Furthermore, sCD146 is actively involved in BBB dysfunction.
Keywords: blood-brain barrier damage and neuroinflammation.; cerebrospinal fluid; sCD146.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
High Level of Soluble CD146 In Cerebrospinal Fluid Might be a Biomarker of Severity of Anti-N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptor Encephalitis.Front Immunol. 2021 Jun 16;12:680424. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.680424. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34220828 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble CD146 in cerebrospinal fluid of active multiple sclerosis.Neuroscience. 2013 Apr 3;235:16-26. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.01.020. Epub 2013 Jan 16. Neuroscience. 2013. PMID: 23333866
-
Plasma and cerebrospinal fluid inflammation and the blood-brain barrier in older surgical patients: the Role of Inflammation after Surgery for Elders (RISE) study.J Neuroinflammation. 2021 Apr 30;18(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02145-8. J Neuroinflammation. 2021. PMID: 33931093 Free PMC article.
-
Immune cell trafficking across the barriers of the central nervous system in multiple sclerosis and stroke.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Mar;1862(3):461-71. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2015.10.018. Epub 2015 Oct 23. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26527183 Review.
-
CD146/sCD146 in the Pathogenesis and Monitoring of Angiogenic and Inflammatory Diseases.Biomedicines. 2020 Dec 10;8(12):592. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8120592. Biomedicines. 2020. PMID: 33321883 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Systemic Inflammation in the CNS: A Silent History of Neuronal Damage.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 25;24(15):11902. doi: 10.3390/ijms241511902. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison the therapeutic effects of bone marrow CD144+ endothelial cells and CD146+ mesenchymal stem cells in POF rats.Bioimpacts. 2023;13(6):495-504. doi: 10.34172/bi.2023.27781. Epub 2023 Jul 29. Bioimpacts. 2023. PMID: 38022384 Free PMC article.
-
CD146/Soluble CD146 Pathway Is a Novel Biomarker of Angiogenesis and Inflammation in Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021 Jul 1;62(9):32. doi: 10.1167/iovs.62.9.32. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021. PMID: 34293080 Free PMC article.
-
CD146, a therapeutic target involved in cell plasticity.Sci China Life Sci. 2024 Aug;67(8):1563-1578. doi: 10.1007/s11427-023-2521-x. Epub 2024 Apr 9. Sci China Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38613742 Review.
-
IL-37 exerts therapeutic effects in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis through the receptor complex IL-1R5/IL-1R8.Theranostics. 2021 Jan 1;11(1):1-13. doi: 10.7150/thno.47435. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33391457 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akaishi T, Narikawa K, Suzuki Y, Mitsuzawa S, Tsukita K, Kuroda H. et al. Importance of the quotient of albumin, quotient of immunoglobulin G and reibergram in inflammatory neurological disorders with disease-specific patterns of blood-brain barrier permeability. Neurol Clin Neurosci. 2015;3:94–100.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

