Determination of Anlotinib, a Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, in Rat Plasma by UHPLC-MS/MS and Its Application to a Pharmacokinetic Study
- PMID: 31886022
- PMCID: PMC6925768
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/5016757
Determination of Anlotinib, a Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, in Rat Plasma by UHPLC-MS/MS and Its Application to a Pharmacokinetic Study
Abstract
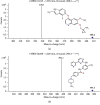
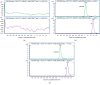
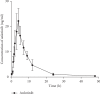
Anlotinib is a novel inhibitor of receptor kinase tyrosine with multitargets and has a broad spectrum of inhibitory action on tumor angiogenesis and growth. A simple and rapid UHPLC-MS/MS bioanalytical method was validated for the determination of anlotinib in rat plasma, using imatinib as an internal standard. An Acquity BEH C18 column was used to separate analytes. The eluents consisted of formic acid/water (0.1 : 100, v/v) and acetonitrile with a mobile phase. A triple quadrupole mass spectrometer was operated for the quantification with multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) to determine transitions: 408.2 ⟶ 339.1 for anlotinib, and 494.3 ⟶ 394.1 for imatinib. The validated range was 0.1-50 ng/mL for anlotinib. Mean recovery rate of anlotinib in plasma was ≥99.32% and reproducible. Also, the intra- and interday precisions were both below 15%. This robust method was successfully applied to support the pharmacokinetic study of anlotinib in rats.
Copyright © 2019 Zhe Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in publication of this research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
UHPLC-ESI-MS/MS determination and pharmacokinetic study of two alkaloid components in rat plasma after oral administration of the extract of Corydalis bungeana Turcz.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2014 Jun 1;960:59-66. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2014.04.009. Epub 2014 Apr 18. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 24786221
-
Establishment and validation of a LC-MS/MS method for the determination of anlotinib in human plasma: Application to therapeutic drug monitoring.Biomed Chromatogr. 2022 Dec;36(12):e5501. doi: 10.1002/bmc.5501. Epub 2022 Oct 5. Biomed Chromatogr. 2022. PMID: 36082703
-
Development and validation of UHPLC-MS/MS assay for rapid determination of a carvone Schiff base of isoniazid (CSB-INH) in rat plasma: application to pharmacokinetic study.Biomed Chromatogr. 2015 Jun;29(6):876-82. doi: 10.1002/bmc.3368. Epub 2014 Nov 6. Biomed Chromatogr. 2015. PMID: 25378280
-
Determination of songorine in rat plasma by UPLC-MS/MS: Assay development and application to pharmacokinetic study.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2015 Oct 1;1002:234-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2015.08.037. Epub 2015 Aug 28. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 26342165
-
Determination and pharmacokinetic study of two triterpenoid saponins in rat plasma after oral administration of the extract of Aralia elata leaves by UHPLC-ESI-MS/MS.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2015 Mar 15;985:164-71. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2015.01.036. Epub 2015 Feb 3. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 25687802
Cited by
-
Pretreatment and analysis techniques development of TKIs in biological samples for pharmacokinetic studies and therapeutic drug monitoring.J Pharm Anal. 2024 Apr;14(4):100899. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2023.11.006. Epub 2023 Nov 28. J Pharm Anal. 2024. PMID: 38634061 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mross K., Frost A., Steinbild S., et al. A phase I dose-escalation study of regorafenib (BAY 73-4506), an inhibitor of oncogenic, angiogenic, and stromal kinases, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clinical Cancer Research. 2012;18(9):2658–2667. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-11-1900. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
