Avelumab plus axitinib vs sunitinib for advanced renal cell carcinoma: Japanese subgroup analysis from JAVELIN Renal 101
- PMID: 31883418
- PMCID: PMC7060483
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.14294
Avelumab plus axitinib vs sunitinib for advanced renal cell carcinoma: Japanese subgroup analysis from JAVELIN Renal 101
Abstract
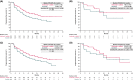
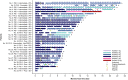
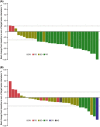
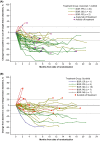
The phase 3 JAVELIN Renal 101 trial of avelumab + axitinib vs sunitinib in patients with treatment-naive advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) demonstrated significantly improved progression-free survival (PFS) and higher objective response rate (ORR) with the combination vs sunitinib. Japanese patients enrolled in the study (N = 67) were randomized to receive avelumab + axitinib (N = 33) or sunitinib (N = 34); 67% vs 59% had PD-L1+ tumors (≥1% of immune cells) and 6%/64%/27% vs 6%/82%/12% had International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium (IMDC) favorable/intermediate/poor risk status. In patients who received avelumab + axitinib vs sunitinib, median PFS (95% confidence interval [CI]) was not estimable (8.1 months, not estimable) vs 11.2 months (1.6 months, not estimable) (hazard ratio [HR], 0.49; 95% CI, 0.152, 1.563) in patients with PD-L1+ tumors and 16.6 months (8.1 months, not estimable) vs 11.2 months (4.2 months, not estimable) (HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.296, 1.464) in patients irrespective of PD-L1 expression. Median overall survival (OS) has not been reached in either arm in patients with PD-L1+ tumors and irrespective of PD-L1 expression. ORR (95% CI) was 60.6% (42.1%, 77.1%) vs 17.6% (6.8%, 34.5%) in patients irrespective of PD-L1 expression. Common treatment-emergent adverse events (all grade; grade ≥3) in each arm were hand-foot syndrome (64%; 9% vs 71%; 9%), hypertension (55%; 30% vs 44%; 18%), hypothyroidism (55%; 0% vs 24%; 0%), dysgeusia (21%; 0% vs 56%; 0%) and platelet count decreased (3%; 0% vs 65%; 32%). Avelumab + axitinib was efficacious and tolerable in treatment-naive Japanese patients with advanced RCC, which is consistent with results in the overall population.
Keywords: Japan; avelumab; axitinib; phase 3 JAVELIN Renal 101 clinical trial; renal cell carcinoma.
© 2019 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Motohide Uemura has nothing to disclose. Yoshihiko Tomita has received honoraria from Pfizer, Astellas, Novartis, Ono, Sanofi‐Aventis and BMS; reports a consulting or advisory role for Novartis, Ono, Taiho and MSD; and reports institutional research funding from Pfizer, Ono, Takeda and Astellas. Hideaki Miyake has nothing to disclose. Shingo Hatakeyama has received honoraria from Pfizer, Astellas, Kissei, Sanofi and Ono; and reports institutional research funding from Pfizer, Astellas, Kissei, Sanofi, Ono, Bristol, Janssen and Kaneka. Hiro‐omi Kanayama has received honoraria from Pfizer and reports institutional research funding from Pfizer. Kazuyuki Numakura has received honoraria from Pfizer, Astellas, Ono, Kyowa Kirin and AstraZeneca, and research funding from the Ministry of Education (Japan; Grants‐in‐Aid for Scientific Research). Toshio Takagi has received honoraria from Novartis, Ono and BMS. Tomoyuki Kato has received honoraria from Pfizer, Novartis, Ono, Taiho, Chugai, Bayer and Astellas. Masatoshi Eto has received honoraria from Ono, BMS, Pfizer, Novartis and Bayer; reports a consulting or advisory role for Ono, BMS, Pfizer and Novartis; and has received research funding from Ono, Pfizer, Novartis and Bayer. Wataru Obara has nothing to disclose. Hirotsugu Uemura has received honoraria from Ono, BMS, AstraZeneca, MSD and Janssen; reports a consulting or advisory role for Sanofi and Ono; is a member of a speaker’s bureau for MSD, Janssen, BMS, Pfizer and Bayer; and has received research funding from Pfizer, Janssen, Taiho, AstraZeneca, Astellas, Takeda and Ono. Toni K. Choueiri reports grants received during the conduct of the study from Pfizer; personal fees received outside the conduct of the study from Agensys, Alexion, Alligent, American Society of Clinical Oncology, Analysis Group, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Celldex, Cerulean, Clinical Care Options, Corvus, Dana‐Farber Cancer Institute, EMD Serono, Eisai, Exelixis, Foundation Medicine, Genentech/Roche, GSK, Harborside Press, Heron, Ipsen, Kidney Cancer Association,
Figures
Similar articles
-
Extended follow-up from JAVELIN Renal 101: subgroup analysis of avelumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib by the International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium risk group in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma.ESMO Open. 2023 Jun;8(3):101210. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2023.101210. Epub 2023 Apr 25. ESMO Open. 2023. PMID: 37104931 Free PMC article.
-
Avelumab plus Axitinib versus Sunitinib for Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma.N Engl J Med. 2019 Mar 21;380(12):1103-1115. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1816047. Epub 2019 Feb 16. N Engl J Med. 2019. PMID: 30779531 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Updated efficacy results from the JAVELIN Renal 101 trial: first-line avelumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma.Ann Oncol. 2020 Aug;31(8):1030-1039. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.04.010. Epub 2020 Apr 25. Ann Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32339648 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Avelumab and axitinib in the treatment of renal cell carcinoma: safety and efficacy.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2020 May;20(5):343-354. doi: 10.1080/14737140.2020.1756780. Epub 2020 May 7. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2020. PMID: 32293937 Review.
-
Avelumab and axitinib combination therapy for the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma.Future Oncol. 2020 Dec;16(36):3021-3034. doi: 10.2217/fon-2020-0586. Epub 2020 Aug 28. Future Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32856478 Review.
Cited by
-
The Effects of Axitinib plus Tislelizumab in the Treatment of Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma.J Oncol. 2022 Mar 24;2022:2700166. doi: 10.1155/2022/2700166. eCollection 2022. J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35368892 Free PMC article.
-
Avelumab in Combination with Axitinib as First-Line Treatment in Patients with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Results from the Phase 1b VEGF Liver 100 Trial.Liver Cancer. 2021 Jun;10(3):249-259. doi: 10.1159/000514420. Epub 2021 Apr 7. Liver Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34239811 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and management of proteinuria associated with vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment in advanced renal cell carcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, and thyroid cancer.Int J Urol. 2024 May;31(5):465-474. doi: 10.1111/iju.15409. Epub 2024 Feb 6. Int J Urol. 2024. PMID: 38318663 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Real-world outcomes of avelumab plus axitinib as first-line therapy in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma in Japan: A multicenter, retrospective, observational study (J-DART).Int J Urol. 2024 Mar;31(3):265-272. doi: 10.1111/iju.15345. Epub 2023 Dec 18. Int J Urol. 2024. PMID: 38110838 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in Real-World Outcomes in Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma from the Molecular-Targeted Therapy Era to the Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Era.Target Oncol. 2022 May;17(3):307-319. doi: 10.1007/s11523-022-00879-w. Epub 2022 Apr 23. Target Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35460475
References
-
- Choueiri TK, Motzer RJ. Systemic therapy for metastatic renal‐cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:354‐366. - PubMed
-
- Kidney cancer early detection, diagnosis, and staging. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/kidney-cancer/detection-diagnosis-staging..... Accessed May 10, 2019.
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network . NCCN guidelines: Kidney cancer. 2019. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/PDF/kidney.pdf. Accessed May 10, 2019.
-
- Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P, et al. Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic renal‐cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:115‐124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

