The effects of anti-VEGF and kinin B1 receptor blockade on retinal inflammation in laser-induced choroidal neovascularization
- PMID: 31883121
- PMCID: PMC7161546
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.14962
The effects of anti-VEGF and kinin B1 receptor blockade on retinal inflammation in laser-induced choroidal neovascularization
Abstract
Background and purpose: Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a complex neurodegenerative disease treated by anti-VEGF intravitreal injections. As inflammation is potentially involved in retinal degeneration, the pro-inflammatory kallikrein-kinin system is a possible alternative pharmacological target. Here, we investigated the effects of anti-VEGF and anti-B1 receptor treatments on the inflammatory mechanisms in a rat model of choroidal neovascularization (CNV).
Experimental approach: Immediately after laser-induced CNV, Long-Evans rats were treated by eye-drop application of a B1 receptor antagonist (R-954) or by intravitreal injection of B1 receptor siRNA or anti-VEGF antibodies. Effects of treatments on gene expression of inflammatory mediators, CNV lesion regression and integrity of the blood-retinal barrier was measured 10 days later in the retina. B1 receptor and VEGF-R2 cellular localization was assessed.
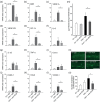
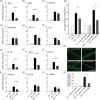
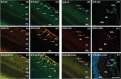
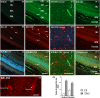
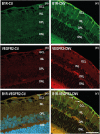
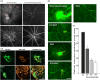
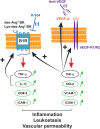
Key results: The three treatments significantly inhibited the CNV-induced retinal changes. Anti-VEGF and R-954 decreased CNV-induced up-regulation of B1 and B2 receptors, TNF-α, and ICAM-1. Anti-VEGF additionally reversed up-regulation of VEGF-A, VEGF-R2, HIF-1α, CCL2 and VCAM-1, whereas R-954 inhibited gene expression of IL-1β and COX-2. Enhanced retinal vascular permeability was abolished by anti-VEGF and reduced by R-954 and B1 receptor siRNA treatments. Leukocyte adhesion was impaired by anti-VEGF and B1 receptor inhibition. B1 receptors were found on astrocytes and endothelial cells.
Conclusion and implications: B1 receptor and VEGF pathways were both involved in retinal inflammation and damage in laser-induced CNV. The non-invasive, self-administration of B1 receptor antagonists on the surface of the cornea by eye drops might be an important asset for the treatment of AMD.
© 2019 The British Pharmacological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
VEGF receptor blockade markedly reduces retinal microglia/macrophage infiltration into laser-induced CNV.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 20;8(8):e71808. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071808. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23977149 Free PMC article.
-
Ocular application of the kinin B1 receptor antagonist LF22-0542 inhibits retinal inflammation and oxidative stress in streptozotocin-diabetic rats.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33864. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033864. Epub 2012 Mar 28. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22470485 Free PMC article.
-
Expression, distribution and function of kinin B1 receptor in the rat diabetic retina.Br J Pharmacol. 2018 Mar;175(6):968-983. doi: 10.1111/bph.14138. Epub 2018 Feb 13. Br J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29285756 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical evidence of intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide in the management of age-related macular degeneration.Curr Drug Targets. 2011 Feb;12(2):149-72. doi: 10.2174/138945011794182746. Curr Drug Targets. 2011. PMID: 20887246 Review.
-
[Novel approach for management of age-related macular degeneration--antiangiogenic therapy and retinal regenerative therapy].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2007 Mar;111(3):232-68; discussion 269. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2007. PMID: 17402564 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Dysregulation of histone deacetylases in ocular diseases.Arch Pharm Res. 2024 Jan;47(1):20-39. doi: 10.1007/s12272-023-01482-x. Epub 2023 Dec 27. Arch Pharm Res. 2024. PMID: 38151648 Review.
-
Differential Expression of Kinin Receptors in Human Wet and Dry Age-Related Macular Degeneration Retinae.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020 Jun 24;13(6):130. doi: 10.3390/ph13060130. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32599742 Free PMC article.
-
High Density Display of an Anti-Angiogenic Peptide on Micelle Surfaces Enhances Their Inhibition of αvβ3 Integrin-Mediated Neovascularization In Vitro.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020 Mar 22;10(3):581. doi: 10.3390/nano10030581. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32235802 Free PMC article.
-
Ang-1 and VEGF: central regulators of angiogenesis.Mol Cell Biochem. 2024 Apr 23. doi: 10.1007/s11010-024-05010-3. Online ahead of print. Mol Cell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38652215 Review.
-
Therapeutic effect of a traditional Chinese medicine formulation on experimental choroidal neovascularization in mouse.Int J Ophthalmol. 2021 Oct 18;14(10):1492-1500. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2021.10.04. eCollection 2021. Int J Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 34667724 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aiello, L. P. , Pierce, E. A. , Foley, E. D. , Takagi, H. , Chen, H. , Riddle, L. , … Smith, L. E. (1995). Suppression of retinal neovascularization in vivo by inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) using soluble VEGF‐receptor chimeric proteins. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 92, 10457–10461. 10.1073/pnas.92.23.10457 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

