Hedgehog/GLI signaling in tumor immunity - new therapeutic opportunities and clinical implications
- PMID: 31878932
- PMCID: PMC6933925
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-019-0459-7
Hedgehog/GLI signaling in tumor immunity - new therapeutic opportunities and clinical implications
Abstract
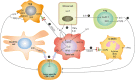
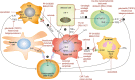
Uncontrolled activation of the Hedgehog/Glioma-associated oncogene (HH/GLI) pathway is a potent oncogenic driver signal promoting numerous cancer hallmarks such as proliferation, survival, angiogenesis, metastasis and metabolic rewiring. Several HH pathway inhibitors have already been approved for medical therapy of advanced and metastatic basal cell carcinoma and acute myeloid leukemia with partially impressive therapeutic activity. However, de novo and acquired resistance as well as severe side effects and unexplained lack of therapeutic efficacy are major challenges that urgently call for improved treatment options with more durable responses. The recent breakthroughs in cancer immunotherapy have changed our current understanding of targeted therapy and opened up promising therapeutic opportunities including combinations of selective cancer pathway and immune checkpoint inhibitors. Although HH/GLI signaling has been intensely studied with respect to the classical hallmarks of cancer, its role in the modulation of the anti-tumoral immune response has only become evident in recent studies. These have uncovered HH/GLI regulated immunosuppressive mechanisms such as enhanced regulatory T-cell formation and production of immunosuppressive cytokines. In light of these exciting novel data on oncogenic HH/GLI signaling in immune cross-talk and modulation, we summarize and connect in this review the existing knowledge from different HH-related cancers and chronic inflammatory diseases. This is to provide a basis for the investigation and evaluation of novel treatments combining immunotherapeutic strategies with approved as well as next-generation HH/GLI inhibitors. Further, we also critically discuss recent studies demonstrating a possible negative impact of current HH/GLI pathway inhibitors on the anti-tumoral immune response, which may explain some of the disappointing results of several oncological trials with anti-HH drugs. Additional file 1Video abstract. (9500 kb).
Keywords: Cancer immunotherapy; Chronic inflammation; Combination therapy; Immune checkpoint inhibitors; Immune evasion; Immunosuppression; Oncogenic Hedgehog/GLI signaling; Tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Emerging Roles of Hedgehog Signaling in Cancer Immunity.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 10;24(2):1321. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021321. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674836 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epidermal activation of Hedgehog signaling establishes an immunosuppressive microenvironment in basal cell carcinoma by modulating skin immunity.Mol Oncol. 2020 Sep;14(9):1930-1946. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12758. Epub 2020 Jul 21. Mol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32615027 Free PMC article.
-
DYRK1B as therapeutic target in Hedgehog/GLI-dependent cancer cells with Smoothened inhibitor resistance.Oncotarget. 2016 Feb 9;7(6):7134-48. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6910. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26784250 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting class I histone deacetylases by the novel small molecule inhibitor 4SC-202 blocks oncogenic hedgehog-GLI signaling and overcomes smoothened inhibitor resistance.Int J Cancer. 2018 Mar 1;142(5):968-975. doi: 10.1002/ijc.31117. Epub 2017 Nov 6. Int J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29055107 Free PMC article.
-
Acute myeloid leukemia - strategies and challenges for targeting oncogenic Hedgehog/GLI signaling.Cell Commun Signal. 2017 Jan 25;15(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s12964-017-0163-4. Cell Commun Signal. 2017. PMID: 28122581 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive analysis of prognostic and immunological role of basement membrane-related genes in soft tissue sarcoma.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024 Oct;12(10):e70037. doi: 10.1002/iid3.70037. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024. PMID: 39392257 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics Screen Reveals Gli-Mediated Hedgehog Signaling as an Associated Pathway to Poor Immune Infiltration of Dedifferentiated Liposarcoma.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jun 27;15(13):3360. doi: 10.3390/cancers15133360. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37444470 Free PMC article.
-
Current Status of Hedgehog Signaling Inhibitors.Curr Top Med Chem. 2024;24(3):243-258. doi: 10.2174/0115680266280850231221074340. Curr Top Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38231069 Review.
-
SMO mutation predicts the effect of immune checkpoint inhibitor: From NSCLC to multiple cancers.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 3;13:955800. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.955800. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36405701 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Roles of Hedgehog Signaling in Cancer Immunity.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 10;24(2):1321. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021321. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674836 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

