The Human Isoform of RNA Polymerase II Subunit hRPB11bα Specifically Interacts with Transcription Factor ATF4
- PMID: 31878192
- PMCID: PMC6981380
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21010135
The Human Isoform of RNA Polymerase II Subunit hRPB11bα Specifically Interacts with Transcription Factor ATF4
Abstract
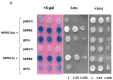
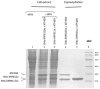
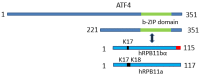
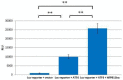
Rpb11 subunit of RNA polymerase II of Eukaryotes is related to N-terminal domain of eubacterial α subunit and forms a complex with Rpb3 subunit analogous to prokaryotic α2 homodimer, which is involved in RNA polymerase assembly and promoter recognition. In humans, a POLR2J gene family has been identified that potentially encodes several hRPB11 proteins differing mainly in their short C-terminal regions. The functions of the different human specific isoforms are still mainly unknown. To further characterize the minor human specific isoform of RNA polymerase II subunit hRPB11bα, the only one from hRPB11 (POLR2J) homologues that can replace its yeast counterpart in vivo, we used it as bait in a yeast two-hybrid screening of a human fetal brain cDNA library. By this analysis and subsequent co-purification assay in vitro, we identified transcription factor ATF4 as a prominent partner of the minor RNA polymerase II (RNAP II) subunit hRPB11bα. We demonstrated that the hRPB11bα interacts with leucine b-Zip domain located on the C-terminal part of ATF4. Overexpression of ATF4 activated the reporter more than 10-fold whereas co-transfection of hRPB11bα resulted in a 2.5-fold enhancement of ATF4 activation. Our data indicate that the mode of interaction of human RNAP II main (containing major for of hRPB11 subunit) and minor (containing hRPB11bα isoform of POLR2J subunit) transcription enzymes with ATF4 is certainly different in the two complexes involving hRPB3-ATF4 (not hRPB11a-ATF4) and hRpb11bα-ATF4 platforms in the first and the second case, respectively. The interaction of hRPB11bα and ATF4 appears to be necessary for the activation of RNA polymerase II containing the minor isoform of the hRPB11 subunit (POLR2J) on gene promoters regulated by this transcription factor. ATF4 activates transcription by directly contacting RNA polymerase II in the region of the heterodimer of α-like subunits (Rpb3-Rpb11) without involving a Mediator, which provides fast and highly effective activation of transcription of the desired genes. In RNA polymerase II of Homo sapiens that contains plural isoforms of the subunit hRPB11 (POLR2J), the strength of the hRPB11-ATF4 interaction appeared to be isoform-specific, providing the first functional distinction between the previously discovered human forms of the Rpb11 subunit.
Keywords: ATF4; RNA polymerase II; hRPB11a; hRPB11bα; human isoforms of Rpb11; yeast two-hybrid system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Functional interaction of the subunit 3 of RNA polymerase II (RPB3) with transcription factor-4 (ATF4).FEBS Lett. 2003 Jul 17;547(1-3):15-9. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(03)00659-8. FEBS Lett. 2003. PMID: 12860379
-
A minor isoform of the human RNA polymerase II subunit hRPB11 (POLR2J) interacts with several components of the translation initiation factor eIF3.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2011 Aug;76(8):976-80. doi: 10.1134/S0006297911080141. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2011. PMID: 22022972
-
The interacting RNA polymerase II subunits, hRPB11 and hRPB3, are coordinately expressed in adult human tissues and down-regulated by doxorubicin.FEBS Lett. 1998 May 8;427(2):236-40. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(98)00431-1. FEBS Lett. 1998. PMID: 9607318
-
Interactions between subunits of the Mediator complex with gene-specific transcription factors.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2011 Sep;22(7):759-68. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2011.07.022. Epub 2011 Aug 4. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 21839847 Review.
-
Biology of Activating Transcription Factor 4 (ATF4) and Its Role in Skeletal Muscle Atrophy.J Nutr. 2022 Apr 1;152(4):926-938. doi: 10.1093/jn/nxab440. J Nutr. 2022. PMID: 34958390 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of a two metastasis-related prognostic signature in the process of predicting the survival of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2023 Aug 19;13(1):13513. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-40740-2. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37598251 Free PMC article.
-
POLR2J expression promotes glioblastoma malignancy by regulating oxidative stress and the STAT3 signaling pathway.Am J Cancer Res. 2024 May 15;14(5):2037-2054. doi: 10.62347/JEWM7691. eCollection 2024. Am J Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38859843 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics Methods in Medical Genetics and Genomics.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 28;21(17):6224. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176224. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32872128 Free PMC article.
-
Current Insights in Elucidation of Possible Molecular Mechanisms of the Juvenile Form of Batten Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 29;21(21):8055. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218055. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33137890 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Study of Organoids from Patient-Derived Normal and Tumor Colon and Rectal Tissue.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Aug 15;12(8):2302. doi: 10.3390/cancers12082302. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32824266 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

