Hedgehog Signaling Inhibition by Smoothened Antagonist BMS-833923 Reduces Osteoblast Differentiation and Ectopic Bone Formation of Human Skeletal (Mesenchymal) Stem Cells
- PMID: 31871467
- PMCID: PMC6907053
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/3435901
Hedgehog Signaling Inhibition by Smoothened Antagonist BMS-833923 Reduces Osteoblast Differentiation and Ectopic Bone Formation of Human Skeletal (Mesenchymal) Stem Cells
Abstract
Background: Hedgehog (Hh) signaling is essential for osteoblast differentiation of mesenchymal progenitors during endochondral bone formation. However, the critical role of Hh signaling during adult bone remodeling remains to be elucidated.
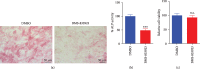
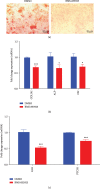
Methods: A Smoothened (SMO) antagonist/Hedgehog inhibitor, BMS-833923, identified during a functional screening of a stem cell signaling small molecule library, was investigated for its effects on the osteoblast differentiation of human skeletal (mesenchymal) stem cells (hMSC). Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity and Alizarin red staining were employed as markers for osteoblast differentiation and in vitro mineralization capacity, respectively. Global gene expression profiling was performed using the Agilent® microarray platform. Effects on in vivo ectopic bone formation were assessed by implanting hMSC mixed with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate granules subcutaneously in 8-week-old female nude mice, and the amount of bone formed was assessed using quantitative histology.
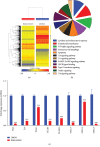
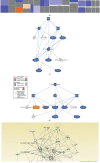
Results: BMS-833923, a SMO antagonist/Hedgehog inhibitor, exhibited significant inhibitory effects on osteoblast differentiation of hMSCs reflected by decreased ALP activity, in vitro mineralization, and downregulation of osteoblast-related gene expression. Similarly, we observed decreased in vivo ectopic bone formation. Global gene expression profiling of BMS-833923-treated compared to vehicle-treated control cells, identified 348 upregulated and 540 downregulated genes with significant effects on multiple signaling pathways, including GPCR, endochondral ossification, RANK-RANKL, insulin, TNF alpha, IL6, and inflammatory response. Further bioinformatic analysis employing Ingenuity Pathway Analysis revealed significant enrichment in BMS-833923-treated cells for a number of functional categories and networks involved in connective and skeletal tissue development and disorders, e.g., NFκB and STAT signaling.
Conclusions: We identified SMO/Hedgehog antagonist (BMS-833923) as a powerful inhibitor of osteoblastic differentiation of hMSC that may be useful as a therapeutic option for treating conditions associated with high heterotopic bone formation and mineralization.
Copyright © 2019 Nihal AlMuraikhi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Notch Signaling Inhibition by LY411575 Attenuates Osteoblast Differentiation and Decreased Ectopic Bone Formation Capacity of Human Skeletal (Mesenchymal) Stem Cells.Stem Cells Int. 2019 Aug 22;2019:3041262. doi: 10.1155/2019/3041262. eCollection 2019. Stem Cells Int. 2019. PMID: 31534459 Free PMC article.
-
Stem cell library screen identified ruxolitinib as regulator of osteoblastic differentiation of human skeletal stem cells.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018 Nov 21;9(1):319. doi: 10.1186/s13287-018-1068-x. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 30463599 Free PMC article.
-
Tankyrase inhibitor XAV-939 enhances osteoblastogenesis and mineralization of human skeletal (mesenchymal) stem cells.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 7;10(1):16746. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-73439-9. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33028869 Free PMC article.
-
[RESEARCH PROGRESS OF Hedgehog SIGNALING PATHWAY IN REGULATING BONE FORMATION AND OSTEOGENIC DIFFERENTIATION OF BONE MESENCHYMAL STEM CELLS].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2016 Dec 8;30(12):1545-1550. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.20160318. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 29786349 Review. Chinese.
-
Wnt and hedgehog signaling pathways in bone development.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008 Feb;90 Suppl 1:19-24. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.G.01174. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008. PMID: 18292352 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of hedgehog signaling in the pathogenesis and therapy of heterotopic ossification.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Sep 19;12:1454058. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1454058. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39364140 Free PMC article. Review.
-
On the horizon: Hedgehog signaling to heal broken bones.Bone Res. 2022 Feb 15;10(1):13. doi: 10.1038/s41413-021-00184-8. Bone Res. 2022. PMID: 35165260 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer Stem Cell for Tumor Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Sep 26;13(19):4814. doi: 10.3390/cancers13194814. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34638298 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Eradicating the tumor "seeds": nanomedicines-based therapies against cancer stem cells.Daru. 2023 Jun;31(1):83-94. doi: 10.1007/s40199-023-00456-0. Epub 2023 Mar 27. Daru. 2023. PMID: 36971921 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Smoothened in Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 18;21(18):6863. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186863. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32962123 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

