Oral administration of a synthetic vinyl-ether plasmalogen normalizes open field activity in a mouse model of rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata
- PMID: 31862688
- PMCID: PMC6994958
- DOI: 10.1242/dmm.042499
Oral administration of a synthetic vinyl-ether plasmalogen normalizes open field activity in a mouse model of rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata
Abstract
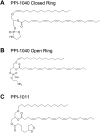
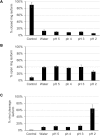
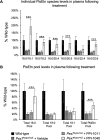
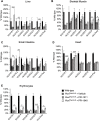
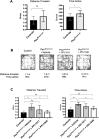
Rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata (RCDP) is a rare genetic disorder caused by mutations in peroxisomal genes essential for plasmalogen biosynthesis. Plasmalogens are a class of membrane glycerophospholipids containing a vinyl-ether-linked fatty alcohol at the sn-1 position that affect functions including vesicular transport, membrane protein function and free radical scavenging. A logical rationale for the treatment of RCDP is therefore the therapeutic augmentation of plasmalogens. The objective of this work was to provide a preliminary characterization of a novel vinyl-ether synthetic plasmalogen, PPI-1040, in support of its potential utility as an oral therapeutic option for RCDP. First, wild-type mice were treated with 13C6-labeled PPI-1040, which showed that the sn-1 vinyl-ether and the sn-3 phosphoethanolamine groups remained intact during digestion and absorption. Next, a 4-week treatment of adult plasmalogen-deficient Pex7hypo/null mice with PPI-1040 showed normalization of plasmalogen levels in plasma, and variable increases in plasmalogen levels in erythrocytes and peripheral tissues (liver, small intestine, skeletal muscle and heart). Augmentation was not observed in brain, lung and kidney. Functionally, PPI-1040 treatment normalized the hyperactive behavior observed in the Pex7hypo/null mice as determined by open field test, with a significant inverse correlation between activity and plasma plasmalogen levels. Parallel treatment with an equal amount of ether plasmalogen precursor, PPI-1011, did not effectively augment plasmalogen levels or reduce hyperactivity. Our findings show, for the first time, that a synthetic vinyl-ether plasmalogen is orally bioavailable and can improve plasmalogen levels in an RCDP mouse model. Further exploration of its clinical utility is warranted.This article has an associated First Person interview with the joint first authors of the paper.
Keywords: PPI-1040; Peroxisomal disorder; Plasmalogen; RCDP; Rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata.
© 2020. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsT.S., D.J. and S.A.R. are paid employees of Med-Life Discoveries LP, and were directly involved in the study design, data collection and analysis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
In vitro and in vivo plasmalogen replacement evaluations in rhizomelic chrondrodysplasia punctata and Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease using PPI-1011, an ether lipid plasmalogen precursor.Lipids Health Dis. 2011 Oct 18;10:182. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-10-182. Lipids Health Dis. 2011. PMID: 22008564 Free PMC article.
-
A Pex7 hypomorphic mouse model for plasmalogen deficiency affecting the lens and skeleton.Mol Genet Metab. 2010 Apr;99(4):408-16. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2009.12.005. Epub 2009 Dec 11. Mol Genet Metab. 2010. PMID: 20060764 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative analysis of ethanolamine plasmalogen species in red blood cells using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry for diagnosing peroxisome biogenesis disorders.Clin Chim Acta. 2023 Mar 1;542:117295. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2023.117295. Epub 2023 Mar 11. Clin Chim Acta. 2023. PMID: 36914043
-
Rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata, a peroxisomal biogenesis disorder caused by defects in Pex7p, a peroxisomal protein import receptor: a minireview.Neurochem Res. 1999 Apr;24(4):581-6. doi: 10.1023/a:1023957110171. Neurochem Res. 1999. PMID: 10227689 Review.
-
Plasmalogens and fatty alcohols in rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata and Sjögren-Larsson syndrome.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2015 Jan;38(1):111-21. doi: 10.1007/s10545-014-9795-3. Epub 2014 Nov 29. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2015. PMID: 25432520 Review.
Cited by
-
Plasmalogens Eliminate Aging-Associated Synaptic Defects and Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation in Mice.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Feb 23;9:815320. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.815320. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35281262 Free PMC article.
-
Marine Plasmalogens: A Gift from the Sea with Benefits for Age-Associated Diseases.Molecules. 2023 Aug 29;28(17):6328. doi: 10.3390/molecules28176328. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37687157 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alkyl-Acylglycerols and the Important Clinical Ramifications of Raising Plasmalogens in Dementia and Alzheimer's Disease.Integr Med (Encinitas). 2020 Jun;19(3):12-16. Integr Med (Encinitas). 2020. PMID: 33132773 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural Characterization and Quantitation of Ether-Linked Glycerophospholipids in Peroxisome Biogenesis Disorder Tissue by Ultraviolet Photodissociation Mass Spectrometry.Anal Chem. 2022 Sep 20;94(37):12621-12629. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.2c01274. Epub 2022 Sep 7. Anal Chem. 2022. PMID: 36070546 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetics, Mass Balance, Excretion, and Tissue Distribution of Plasmalogen Precursor PPI-1011.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Apr 25;10:867138. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.867138. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35547803 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barøy T., Koster J., Strømme P., Ebberink M. S., Misceo D., Ferdinandusse S., Holmgren A., Hughes T., Merckoll E., Westvik J. et al. (2015). A novel type of rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata, RCDP5, is caused by loss of the PEX5 long isoform. Hum. Mol. Genet. 24, 5845-5854. 10.1093/hmg/ddv305 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

