Antioxidant CoQ10 Restores Fertility by Rescuing Bisphenol A-Induced Oxidative DNA Damage in the Caenorhabditis elegans Germline
- PMID: 31852725
- PMCID: PMC7017011
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.119.302939
Antioxidant CoQ10 Restores Fertility by Rescuing Bisphenol A-Induced Oxidative DNA Damage in the Caenorhabditis elegans Germline
Abstract
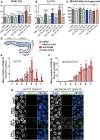
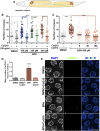
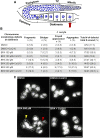
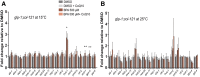
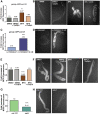
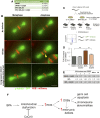
Endocrine-disrupting chemicals are ubiquitously present in our environment, but the mechanisms by which they adversely affect human reproductive health and strategies to circumvent their effects remain largely unknown. Here, we show in Caenorhabditis elegans that supplementation with the antioxidant Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) rescues the reprotoxicity induced by the widely used plasticizer and endocrine disruptor bisphenol A (BPA), in part by neutralizing DNA damage resulting from oxidative stress. CoQ10 significantly reduces BPA-induced elevated levels of germ cell apoptosis, phosphorylated checkpoint kinase 1 (CHK-1), double-strand breaks (DSBs), and chromosome defects in diakinesis oocytes. BPA-induced oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and increased gene expression of antioxidant enzymes in the germline are counteracted by CoQ10. Finally, CoQ10 treatment also reduced the levels of aneuploid embryos and BPA-induced defects observed in early embryonic divisions. We propose that CoQ10 may counteract BPA-induced reprotoxicity through the scavenging of reactive oxygen species and free radicals, and that this natural antioxidant could constitute a low-risk and low-cost strategy to attenuate the impact on fertility by BPA.
Keywords: Bisphenol A; C. elegans; Coenzyme Q10; germline; meiosis.
Copyright © 2020 by the Genetics Society of America.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Counteracting Environmental Chemicals with Coenzyme Q10: An Educational Primer for Use with "Antioxidant CoQ10 Restores Fertility by Rescuing Bisphenol A-Induced Oxidative DNA Damage in the Caenorhabditis elegans Germline".Genetics. 2020 Dec;216(4):879-890. doi: 10.1534/genetics.120.303577. Genetics. 2020. PMID: 33268390 Free PMC article.
-
Coenzyme Q10 ameliorates BPA-induced apoptosis by regulating autophagy-related lysosomal pathways.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021 Sep 15;221:112450. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112450. Epub 2021 Jun 26. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021. PMID: 34186417
-
Bisphenol A exposure accelerated the aging process in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans.Toxicol Lett. 2015 Jun 1;235(2):75-83. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2015.03.010. Epub 2015 Mar 24. Toxicol Lett. 2015. PMID: 25819108
-
Beneficial antioxidant effects of Coenzyme Q10 on reproduction.Vitam Horm. 2023;121:143-167. doi: 10.1016/bs.vh.2022.10.004. Epub 2022 Dec 7. Vitam Horm. 2023. PMID: 36707133 Review.
-
Induction of oxidative stress by bisphenol A and its pleiotropic effects.Environ Mol Mutagen. 2017 Mar;58(2):60-71. doi: 10.1002/em.22072. Epub 2017 Feb 9. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2017. PMID: 28181297 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Counteracting Environmental Chemicals with Coenzyme Q10: An Educational Primer for Use with "Antioxidant CoQ10 Restores Fertility by Rescuing Bisphenol A-Induced Oxidative DNA Damage in the Caenorhabditis elegans Germline".Genetics. 2020 Dec;216(4):879-890. doi: 10.1534/genetics.120.303577. Genetics. 2020. PMID: 33268390 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of protective effect of resveratrol and coenzyme Q10 against cyclophosphamide-induced lipid peroxidation, oxidative stress and DNA damage in rats.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2023 Dec 30;13(1):tfad123. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfad123. eCollection 2024 Feb. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2023. PMID: 38173543 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Protecting Compounds as Potential Geroprotectors.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 24;21(12):4484. doi: 10.3390/ijms21124484. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32599754 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial Epigenetics and Environmental Health: Making a Case for Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals.Toxicol Sci. 2020 Nov 1;178(1):16-25. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfaa129. Toxicol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32777053 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fighting Bisphenol A-Induced Male Infertility: The Power of Antioxidants.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Feb 15;10(2):289. doi: 10.3390/antiox10020289. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33671960 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

