Covalent Inhibition of the Histamine H3 Receptor
- PMID: 31835873
- PMCID: PMC6943558
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24244541
Covalent Inhibition of the Histamine H3 Receptor
Abstract
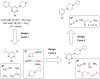
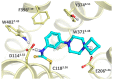
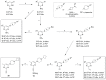
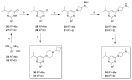
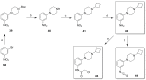
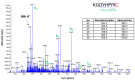
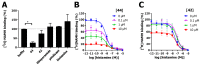
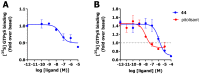
Covalent binding of G protein-coupled receptors by small molecules is a useful approach for better understanding of the structure and function of these proteins. We designed, synthesized and characterized a series of 6 potential covalent ligands for the histamine H3 receptor (H3R). Starting from a 2-amino-pyrimidine scaffold, optimization of anchor moiety and warhead followed by fine-tuning of the required reactivity via scaffold hopping resulted in the isothiocyanate H3R ligand 44. It shows high reactivity toward glutathione combined with appropriate stability in water and reacts selectively with the cysteine sidechain in a model nonapeptide equipped with nucleophilic residues. The covalent interaction of 44 with H3R was validated with washout experiments and leads to inverse agonism on H3R. Irreversible binder 44 (VUF15662) may serve as a useful tool compound to stabilize the inactive H3R conformation and to study the consequences of prolonged inhibition of the H3R.
Keywords: G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR); Histamine H3 receptor; covalent binder; isothiocyanate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Synthesis and in vitro pharmacology of a series of new chiral histamine H3-receptor ligands: 2-(R and S)-Amino-3-(1H-imidazol-4(5)-yl)propyl ether derivatives.J Med Chem. 1999 Apr 8;42(7):1193-202. doi: 10.1021/jm980408v. J Med Chem. 1999. PMID: 10197963
-
Guided rational design with scaffold hopping leading to novel histamine H3 receptor ligands.Bioorg Chem. 2021 Dec;117:105411. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105411. Epub 2021 Oct 8. Bioorg Chem. 2021. PMID: 34653944
-
Identification of Histamine H3 Receptor Ligands Using a New Crystal Structure Fragment-based Method.Sci Rep. 2017 Jul 6;7(1):4829. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-05058-w. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28684785 Free PMC article.
-
Histamine H3 receptor as a drug discovery target.J Med Chem. 2011 Jan 13;54(1):26-53. doi: 10.1021/jm100064d. Epub 2010 Nov 9. J Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21062081 Review. No abstract available.
-
Several down, a few to go: histamine H3 receptor ligands making the final push towards the market?Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2011 Dec;20(12):1629-48. doi: 10.1517/13543784.2011.625010. Epub 2011 Oct 13. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2011. PMID: 21992603 Review.
Cited by
-
Structure-Based Design of Biologically Active Compounds.Molecules. 2020 Jul 8;25(14):3115. doi: 10.3390/molecules25143115. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32650470 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and Structure-Activity Relationships of New 2-Phenoxybenzamides with Antiplasmodial Activity.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Oct 30;14(11):1109. doi: 10.3390/ph14111109. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34832891 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a Conformational Histamine H3 Receptor Biosensor for the Synchronous Screening of Agonists and Inverse Agonists.ACS Sens. 2020 Jun 26;5(6):1734-1742. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.0c00397. Epub 2020 May 28. ACS Sens. 2020. PMID: 32397705 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mocking T.A.M., Bosma R., Rahman S.N., Verweij E.W.E., McNaught-Flores D.A., Vischer H.F., Leurs R. Molecular Aspects of Histamine Receptors. In: Blandina P., Passani M.B., editors. Histamine Receptors: Preclinical and Clinical Aspects. Springer International Publishing; Cham, Switzerland: 2016. pp. 1–49.
-
- Schlicker E., Kathmann M. Role of the Histamine H3 Receptor in the Central Nervous System. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2017;241:277–299. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

