Fatty Acids of Marine Mollusks: Impact of Diet, Bacterial Symbiosis and Biosynthetic Potential
- PMID: 31835867
- PMCID: PMC6995604
- DOI: 10.3390/biom9120857
Fatty Acids of Marine Mollusks: Impact of Diet, Bacterial Symbiosis and Biosynthetic Potential
Abstract
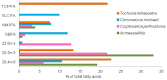
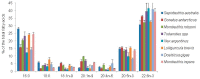
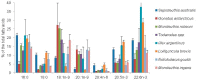
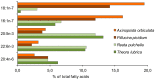
The n-3 and n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) families are essential for important physiological processes. Their major source are marine ecosystems. The fatty acids (FAs) from phytoplankton, which are the primary producer of organic matter and PUFAs, are transferred into consumers via food webs. Mollusk FAs have attracted the attention of researchers that has been driven by their critical roles in aquatic ecology and their importance as sources of essential PUFAs. The main objective of this review is to focus on the most important factors and causes determining the biodiversity of the mollusk FAs, with an emphasis on the key relationship of these FAs with the food spectrum and trophic preference. The marker FAs of trophic sources are also of particular interest. The discovery of new symbioses involving invertebrates and bacteria, which are responsible for nutrition of the host, deserves special attention. The present paper also highlights recent research into the molecular and biochemical mechanisms of PUFA biosynthesis in marine mollusks. The biosynthetic capacities of marine mollusks require a well-grounded evaluation.
Keywords: biosynthesis; fatty acids; mollusks; symbiotic bacteria.
Conflict of interest statement
The author states any potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Biosynthesis of polyunsaturated fatty acids in marine invertebrates: recent advances in molecular mechanisms.Mar Drugs. 2013 Oct 21;11(10):3998-4018. doi: 10.3390/md11103998. Mar Drugs. 2013. PMID: 24152561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The importance of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids as high-quality food in freshwater ecosystems with implications of global change.Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2024 Feb;99(1):200-218. doi: 10.1111/brv.13017. Epub 2023 Sep 19. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2024. PMID: 37724488
-
Multiple bacterial partners in symbiosis with the nudibranch mollusk Rostanga alisae.Sci Rep. 2022 Jan 7;12(1):169. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-03973-7. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 34997021 Free PMC article.
-
Differing Daphnia magna assimilation efficiencies for terrestrial, bacterial, and algal carbon and fatty acids.Ecology. 2014 Feb;95(2):563-76. doi: 10.1890/13-0650.1. Ecology. 2014. PMID: 24669748
-
Endogenous LC-PUFA biosynthesis capability in commercially important mollusks.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2022;62(10):2836-2844. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2020.1860896. Epub 2020 Dec 23. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2022. PMID: 33354986 Review.
Cited by
-
The influence of glacial melt and retreat on the nutritional condition of the bivalve Nuculana inaequisculpta (Protobranchia: Nuculanidae) in the West Antarctic Peninsula.PLoS One. 2020 May 21;15(5):e0233513. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0233513. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32437403 Free PMC article.
-
Molluscan Compounds Provide Drug Leads for the Treatment and Prevention of Respiratory Disease.Mar Drugs. 2020 Nov 19;18(11):570. doi: 10.3390/md18110570. Mar Drugs. 2020. PMID: 33228163 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fatty Acids of Echinoderms: Diversity, Current Applications and Future Opportunities.Mar Drugs. 2022 Dec 27;21(1):21. doi: 10.3390/md21010021. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 36662194 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nutraceutical and Medicinal Importance of Marine Molluscs.Mar Drugs. 2024 Apr 27;22(5):201. doi: 10.3390/md22050201. Mar Drugs. 2024. PMID: 38786591 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preventing illegal seafood trade using machine-learning assisted microbiome analysis.BMC Biol. 2024 Sep 11;22(1):202. doi: 10.1186/s12915-024-02005-w. BMC Biol. 2024. PMID: 39256748 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parrish C.C. Essential fatty acids in aquatic food webs. In: Arts M.T., Brett M.T., Kainz M.J., editors. Lipids in Aquatic Ecosystems. Springer; New York, NY, USA: 2009. pp. 309–326. - DOI
-
- Colombo S.M., Wacker A., Parrish C.C., Kainz M.J., Arts M.T. A fundamental dichotomy in long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid abundance between and within marine and terrestrial ecosystems. Environ. Rev. 2017;25:163–174. doi: 10.1139/er-2016-0062. - DOI
-
- Sargent J.H., Whittle K.J. Lipids and hydrocarbons in the marine food web. In: Longhurst A., editor. Analysis of Marine Ecosystems. Academic Press; New York, NY, USA: 1981. pp. 491–533.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

