A model of DNA damage response activation at stalled replication forks by SPRTN
- PMID: 31831745
- PMCID: PMC6908633
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-13610-7
A model of DNA damage response activation at stalled replication forks by SPRTN
Abstract
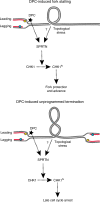
The process of DNA replication is threatened by many factors, including DNA lesions, and machineries acting as obstacles. Here we discuss and speculate on a recently proposed mechanism of DNA damage response activation in response to lesions that challenge the progression of DNA replication forks.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Stalled replication induces p53 accumulation through distinct mechanisms from DNA damage checkpoint pathways.Cancer Res. 2006 Feb 15;66(4):2233-41. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1790. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16489026
-
SPRTN protease and checkpoint kinase 1 cross-activation loop safeguards DNA replication.Nat Commun. 2019 Jul 17;10(1):3142. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11095-y. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31316063 Free PMC article.
-
High levels of RAD51 perturb DNA replication elongation and cause unscheduled origin firing due to impaired CHK1 activation.Cell Cycle. 2015;14(19):3190-202. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1055996. Cell Cycle. 2015. PMID: 26317153 Free PMC article.
-
ATR/Mec1: coordinating fork stability and repair.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2009 Apr;21(2):237-44. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2009.01.017. Epub 2009 Feb 21. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19230642 Review.
-
The ATR pathway: fine-tuning the fork.DNA Repair (Amst). 2007 Jul 1;6(7):953-66. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2007.02.015. Epub 2007 May 24. DNA Repair (Amst). 2007. PMID: 17531546 Review.
Cited by
-
DNA-protein crosslink proteases in genome stability.Commun Biol. 2021 Jan 4;4(1):11. doi: 10.1038/s42003-020-01539-3. Commun Biol. 2021. PMID: 33398053 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coordinated DNA polymerization by Polγ and the region of LonP1 regulated proteolysis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Jul 22;52(13):7863-7875. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae539. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38932681 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

