Neuroprotective Effect of SCM-198 through Stabilizing Endothelial Cell Function
- PMID: 31827699
- PMCID: PMC6885260
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/7850154
Neuroprotective Effect of SCM-198 through Stabilizing Endothelial Cell Function
Abstract
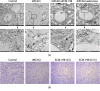
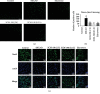
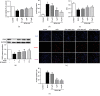
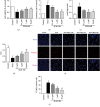
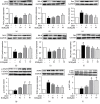
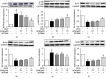
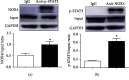
Leonurine, also named SCM-198, which was extracted from Herba leonuri, displayed a protective effect on various cardiovascular and brain diseases, like ischemic stroke. Ischemic stroke which is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality, ultimately caused irreversible neuron damage. This study is aimed at exploring the possible therapeutic potential of SCM-198 in the protection against postischemic neuronal injury and possible underlying mechanisms. A transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (tMCAO) rat model was utilized to measure the protective effect of SCM-198 on neurons. TEM was used to determine neuron ultrastructural changes. The brain slices were stained with Nissl staining solution for Nissl bodies. Fluoro-Jade B (FJB) was used for staining the degenerating neurons. In the oxygen-glucose deprivation and re-oxygenation (OGD/R) model of bEnd.3 cells treated with SCM-198 (0.1, 1, 10 μM). Then, the bEnd.3 cells were cocultured with SH-SY5Y cells. Cell viability, MDA level, CAT activity, and apoptosis were examined to evaluate the cytotoxicity of these treatments. Western blot and immunofluorescent assays were used to examine the expression of protein related to the p-STAT3/NOX4/Bcl-2 signaling pathway. Coimmunoprecipitation was performed to determine the interaction between p-STAT3 and NOX4. In the transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (tMCAO) rat model, we found that treatment with SCM-198 could ameliorate neuron morphology and reduce the degenerating cell and neuron loss. In the in vitro model of bEnd.3 cell oxygen-glucose deprivation and reoxygenation (OGD/R), treatment with SCM-198 restored the activity of catalase (CAT), improved the expression of Cu-Zn superoxide dismutase (SOD1), and decreased the malondialdehyde (MDA) production. SCM-198 treatment prevented OGD/R-induced cell apoptosis as indicated by increased cell viability and decreased the number of TUNEL-positive cells, accompanied with upregulation of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xl protein and downregulation Bax protein. The results were consistent with SH-SY5Y cells which coculture with bEnd.3 cells. The forthcoming study revealed that SCM-198 activated the p-STAT3/NOX4/Bcl-2 signaling pathway. All the data indicated that SCM-198 protected against oxidative stress and neuronal damage in in vivo and in vitro injury models via the p-STAT3/NOX4/Bcl-2 signaling pathway. Our results suggested that SCM-198 could be the potential drug for neuroprotective effect through stabilizing endothelial cell function.
Copyright © 2019 Qiu-Yan Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oxidative Injury in Ischemic Stroke: A Focus on NADPH Oxidase 4.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Feb 3;2022:1148874. doi: 10.1155/2022/1148874. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35154560 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isoquercetin attenuates oxidative stress and neuronal apoptosis after ischemia/reperfusion injury via Nrf2-mediated inhibition of the NOX4/ROS/NF-κB pathway.Chem Biol Interact. 2018 Mar 25;284:32-40. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2018.02.017. Epub 2018 Feb 16. Chem Biol Interact. 2018. PMID: 29454613
-
Novel Therapeutic Effects of Leonurine On Ischemic Stroke: New Mechanisms of BBB Integrity.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:7150376. doi: 10.1155/2017/7150376. Epub 2017 Jun 13. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017. PMID: 28690765 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective effects of syringic acid against OGD/R-induced injury in cultured hippocampal neuronal cells.Int J Mol Med. 2016 Aug;38(2):567-73. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2623. Epub 2016 Jun 3. Int J Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27278454
-
The two-pore domain potassium channel KCNK5 deteriorates outcome in ischemic neurodegeneration.Pflugers Arch. 2015 May;467(5):973-87. doi: 10.1007/s00424-014-1626-8. Epub 2014 Oct 15. Pflugers Arch. 2015. PMID: 25315980 Review.
Cited by
-
SIRT1 restores mitochondrial structure and function in rats by activating SIRT3 after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024 May 20;40(1):31. doi: 10.1007/s10565-024-09869-2. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38767771 Free PMC article.
-
H2S protects hippocampal neurons against hypoxia-reoxygenation injury by promoting RhoA phosphorylation at Ser188.Cell Death Discov. 2021 Jun 4;7(1):132. doi: 10.1038/s41420-021-00514-z. Cell Death Discov. 2021. PMID: 34088899 Free PMC article.
-
Electro-Acupuncture Improve the Early Pattern Separation in Alzheimer's Disease Mice via Basal Forebrain-Hippocampus Cholinergic Neural Circuit.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Feb 2;13:770948. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.770948. eCollection 2021. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35185516 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative Injury in Ischemic Stroke: A Focus on NADPH Oxidase 4.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Feb 3;2022:1148874. doi: 10.1155/2022/1148874. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35154560 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-204-3p/Nox4 Mediates Memory Deficits in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease.Mol Ther. 2021 Jan 6;29(1):396-408. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2020.09.006. Epub 2020 Sep 5. Mol Ther. 2021. PMID: 32950103 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

