A Network Pharmacology Approach to Reveal the Underlying Mechanisms of Paeonia lactiflora Pall. On the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 31827565
- PMCID: PMC6885190
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/8706589
A Network Pharmacology Approach to Reveal the Underlying Mechanisms of Paeonia lactiflora Pall. On the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the potential active compounds and underlying mechanisms of Paeonia lactiflora Pall. (PLP) on the treatment of Alzheimer's disease (AD) based on network pharmacology.
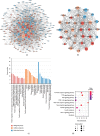
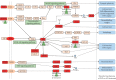
Methods: The active components of PLP were collected from Traditional Chinese Medicine System Pharmacology (TCMSP) database, and their possible target proteins were predicted using TCMSP, SwissTargetPrediction, and STITCH databases. The putative AD-related target proteins were identified from Therapeutic Target Database (TTD), GeneCards, and MalaCards database. The compound-target-disease network interactions were established to obtain the key targets about PLP acting on AD by network topology analysis. Then, the function annotation and signaling pathways of key targets were performed by GO and KEGG enrichment analysis using DAVID tools. Finally, the binding capacity between active ingredients and key targets was validated by molecular docking using SystemsDock tools.
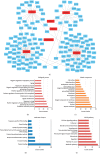
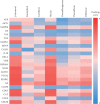
Results: There were 7 active compounds involving in 151 predicted targets identified in PLP. Besides, a total of 160 AD-related targets were identified. Among these targets, 30 shared targets of PLP and AD were acquired. After topological analysis of the PLP potential target-AD target network, 33 key targets that were highly responsible for the therapeutic effects of PLP on AD were obtained. Further GO and KEGG enrichment analysis showed that these key targets were significantly involved in multiple biological processes and pathways which participated in cell apoptosis and inflammatory response and maintained the function of neurons to accomplish the anti-AD activity. The molecular docking analysis verified that the 7 active compounds had definite affinity with the key targets.
Conclusions: The ameliorative effects of PLP on AD were predicted to be associated with regulating neural cell apoptosis, inflammatory response, and neurotrophy via various pathways such as PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, MAPK signaling pathway, and neurotrophin signaling pathway.
Copyright © 2019 Qiang Zeng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Uncovering the active compounds and effective mechanisms of the dried mature sarcocarp of Cornus officinalis Sieb. Et Zucc. For the treatment of Alzheimer's disease through a network pharmacology approach.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020 May 25;20(1):157. doi: 10.1186/s12906-020-02951-2. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020. PMID: 32450873 Free PMC article.
-
Network pharmacology-based analysis and experimental in vitro validation on the mechanism of Paeonia lactiflora Pall. in the treatment for type I allergy.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022 Jul 25;22(1):199. doi: 10.1186/s12906-022-03677-z. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022. PMID: 35879791 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Technology Reveals the Mechanism of the Therapeutic Effect of Xixin Decoction on Alzheimer's Disease.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2022;25(10):1785-1804. doi: 10.2174/1386207325666220523151119. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2022. PMID: 35616676
-
[Mechanism of Bupleurum scorzonerifolium and Paeonia lactiflora herbal pair against liver cancer: an exploration based on UPLC-Q-TOF-MS combined with network pharmacology].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022 Jul;47(13):3597-3608. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20220110.402. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35850814 Chinese.
-
A Network Pharmacology Approach to Estimate Potential Targets of the Active Ingredients of Epimedium for Alleviating Mild Cognitive Impairment and Treating Alzheimer's Disease.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Jan 28;2021:2302680. doi: 10.1155/2021/2302680. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 33574879 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Integrated network pharmacology and experimental validation to explore the mechanisms underlying naringenin treatment of chronic wounds.Sci Rep. 2023 Jan 4;13(1):132. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-26043-y. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36599852 Free PMC article.
-
A Network Pharmacology Approach to Explore the Mechanisms of Artemisiae scopariae Herba for the Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Feb 2;2021:6614039. doi: 10.1155/2021/6614039. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 33623529 Free PMC article.
-
Network pharmacology combined with molecular docking to explore the potential mechanisms for the antioxidant activity of Rheum tanguticum seeds.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022 May 3;22(1):121. doi: 10.1186/s12906-022-03611-3. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022. PMID: 35505340 Free PMC article.
-
The network pharmacology study and molecular docking to investigate the potential mechanism of Acoritataninowii Rhizoma against Alzheimer's Disease.Metab Brain Dis. 2023 Aug;38(6):1937-1962. doi: 10.1007/s11011-023-01179-6. Epub 2023 Apr 10. Metab Brain Dis. 2023. PMID: 37032419
-
Identification of Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha (TNF-α) Inhibitor in Rheumatoid Arthritis Using Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking.Front Pharmacol. 2021 May 21;12:690118. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.690118. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34093213 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

