Establishment of chemosensitivity tests in triple-negative and BRCA-mutated breast cancer patient-derived xenograft models
- PMID: 31821346
- PMCID: PMC6903765
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0225082
Establishment of chemosensitivity tests in triple-negative and BRCA-mutated breast cancer patient-derived xenograft models
Abstract
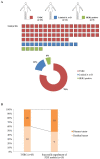
Purpose: A patient-derived xenograft (PDX) model is an in vivo animal model which provides biological and genomic profiles similar to a primary tumor. The characterization of factors that influence the establishment of PDX is crucial. Furthermore, PDX models can provide a platform for chemosensitivity tests to evaluate the effectiveness of a target agent before applying it in clinical trials.
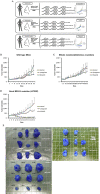
Methods: We implanted 83 cases of breast cancer into NOD.Cg-Prkdcscid Il2rgtm1Sug/Jic mice, to develop PDX models. Clinicopathological factors of primary tumors were reviewed to identify the factors affecting engraftment success rates. After the establishment of PDX models, we performed olaparib and carboplatin chemosensitivity tests. We used PDX models from triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) with neoadjuvant chemotherapy and/or germline BRCA1 mutations in chemosensitivity tests.
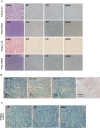
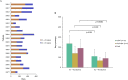
Results: The univariate analyses (p<0.05) showed factors which were significantly associated with successful engraftment of PDX models include poor histologic grade, presence of BRCA mutation, aggressive diseases, and death. Factors which were independently associated with successful engraftment of PDX models on multivariate analyses include poor histologic grade and aggressive diseases status. In chemosensitivity tests, a PDX model with the BRCA1 L1780P mutation showed partial response to olaparib and complete response to carboplatin.
Conclusions: Successful engraftment of PDX models was significantly associated with aggressive diseases. Patients who have aggressive diseases status, large tumors, and poor histologic grade are ideal candidates for developing successful PDX models. Chemosensitivity tests using the PDX models provide additional information about alternative treatment strategies for residual TNBC after neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
HSP has received honoraria from Aastrazenca, Dakeda, Ethicon, and Intuitive Surgical. JDL, JYK, SP, JHK, HJH, YAC, ARC, JHS, and SIK have nothing to declare. The authors would like to declare the following patents/patent applications associated with this research: Germline Pathogenic Mutation of BRCA1, L1780P (Patent pending, reference number; DPB172272). This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Co-targeting poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) and histone deacetylase (HDAC) in triple-negative breast cancer: Higher synergism in BRCA mutated cells.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Mar;99:543-551. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.01.045. Epub 2018 Feb 20. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29902865
-
Efficacy of Carboplatin Alone and in Combination with ABT888 in Intracranial Murine Models of BRCA-Mutated and BRCA-Wild-Type Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.Mol Cancer Ther. 2015 Apr;14(4):920-30. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-14-0474. Mol Cancer Ther. 2015. PMID: 25824335 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic and functional importance of the engraftment-associated genes in the patient-derived xenograft models of triple-negative breast cancers.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015 Nov;154(1):13-22. doi: 10.1007/s10549-015-3585-y. Epub 2015 Oct 5. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015. PMID: 26438141
-
Role of Carboplatin in the Treatment of Triple Negative Early- Stage Breast Cancer.Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2015;10(2):101-10. doi: 10.2174/1574887110666150624101343. Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2015. PMID: 26104428 Review.
-
Olaparib for the treatment of BRCA-mutated advanced ovarian cancer.Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2016 Jul 15;73(14):1037-41. doi: 10.2146/ajhp150550. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2016. PMID: 27385701 Review.
Cited by
-
Activity of docetaxel, carboplatin, and doxorubicin in patient-derived triple-negative breast cancer xenografts.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 29;11(1):7064. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-85962-4. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33782404 Free PMC article.
-
The Essential Factors of Establishing Patient-derived Tumor Model.J Cancer. 2021 Jan 1;12(1):28-37. doi: 10.7150/jca.51749. eCollection 2021. J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33391400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reversion of pathogenic BRCA1 L1780P mutation confers resistance to PARP and ATM inhibitor in breast cancer.iScience. 2024 Jul 6;27(8):110469. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110469. eCollection 2024 Aug 16. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39156639 Free PMC article.
-
Peritoneal metastasis of colorectal cancer (pmCRC): identification of predictive molecular signatures by a novel preclinical platform of matching pmCRC PDX/PD3D models.Mol Cancer. 2021 Oct 21;20(1):129. doi: 10.1186/s12943-021-01430-7. Mol Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34670579 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Effects of Cancer Stem Cells in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer and Brain Metastasis: Challenges and Solutions.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jul 31;12(8):2122. doi: 10.3390/cancers12082122. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32751846 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kaitin KI, Healy EM. The new drug approvals of 1996, 1997, and 1998: Drug development trends in the user fee era. Drug Inf J. 2000;34(1):1–14. WOS:000085436000001.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

