MFN1-dependent alteration of mitochondrial dynamics drives hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by glucose metabolic reprogramming
- PMID: 31819189
- PMCID: PMC7052272
- DOI: 10.1038/s41416-019-0658-4
MFN1-dependent alteration of mitochondrial dynamics drives hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by glucose metabolic reprogramming
Abstract
Background: Mitochondrial dynamics plays an important role in tumour progression. However, how these dynamics integrate tumour metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) metastasis is still unclear.
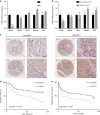
Methods: The mitochondrial fusion protein mitofusin-1 (MFN1) expression and its prognostic value are detected in HCC. The effects and underlying mechanisms of MFN1 on HCC metastasis and metabolic reprogramming are analysed both in vitro and in vivo.
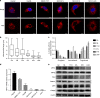
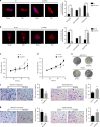
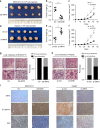
Results: Mitochondrial dynamics, represented by constant fission and fusion, are found to be associated with HCC metastasis. High metastatic HCC displays excessive mitochondrial fission. Among genes involved in mitochondrial dynamics, MFN1 is identified as a leading downregulated candidate that is closely associated with HCC metastasis and poor prognosis. While promoting mitochondrial fusion, MFN1 inhibits cell proliferation, invasion and migration capacity both in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, disruption of mitochondrial dynamics by depletion of MFN1 triggers the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of HCC. Moreover, MFN1 modulates HCC metastasis by metabolic shift from aerobic glycolysis to oxidative phosphorylation. Treatment with glycolytic inhibitor 2-Deoxy-D-glucose (2-DG) significantly suppresses the effects induced by depletion of MFN1.
Conclusions: Our results reveal a critical involvement of mitochondrial dynamics in HCC metastasis via modulating glucose metabolic reprogramming. MFN1 may serve as a novel potential therapeutic target for HCC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Increased mitochondrial fission promotes autophagy and hepatocellular carcinoma cell survival through the ROS-modulated coordinated regulation of the NFKB and TP53 pathways.Autophagy. 2016 Jun 2;12(6):999-1014. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2016.1166318. Epub 2016 Apr 28. Autophagy. 2016. PMID: 27124102 Free PMC article.
-
MCUR1 facilitates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis via the mitochondrial calcium dependent ROS/Nrf2/Notch pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Mar 25;38(1):136. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1135-x. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30909929 Free PMC article.
-
FUNDC2 promotes liver tumorigenesis by inhibiting MFN1-mediated mitochondrial fusion.Nat Commun. 2022 Jun 17;13(1):3486. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-31187-6. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35710796 Free PMC article.
-
Reprogramming of glucose metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma: Progress and prospects.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Dec 7;22(45):9933-9943. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i45.9933. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 28018100 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perspectives of Molecular Therapy-Targeted Mitochondrial Fission in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Dec 29;2020:1039312. doi: 10.1155/2020/1039312. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. Retraction in: Biomed Res Int. 2024 Jan 9;2024:9856592. doi: 10.1155/2024/9856592. PMID: 33457401 Free PMC article. Retracted. Review.
Cited by
-
Suppressing MTERF3 inhibits proliferation of human hepatocellular carcinoma via ROS-mediated p38 MAPK activation.Commun Biol. 2024 Jan 5;7(1):18. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-05664-7. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 38177713 Free PMC article.
-
Rab32 promotes glioblastoma migration and invasion via regulation of ERK/Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Mar 15;14(3):198. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05721-3. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 36922509 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial dynamics in health and disease: mechanisms and potential targets.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 Sep 6;8(1):333. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01547-9. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 37669960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver to Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Story of (Mal)Adapted Mitochondria.Biology (Basel). 2023 Apr 14;12(4):595. doi: 10.3390/biology12040595. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37106795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The metabolic adaptation mechanism of metastatic organotropism.Exp Hematol Oncol. 2021 Apr 29;10(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s40164-021-00223-4. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33926551 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Caruso S, Calatayud AL, Pilet J, La Bella T, Rekik S, Imbeaud S, et al. Analysis of liver cancer cell lines identifies agents with likely efficacy against hepatocellular carcinoma and markers of response. Gastroenterology. 2019;157:760–76.. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81672820/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)/International
- 31722016/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)/International
- 81930074/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

