Lipidomic analysis of urinary exosomes from hereditary α-tryptasemia patients and healthy volunteers
- PMID: 31803861
- PMCID: PMC6892164
- DOI: 10.1096/fba.2019-00030
Lipidomic analysis of urinary exosomes from hereditary α-tryptasemia patients and healthy volunteers
Abstract
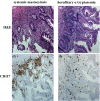
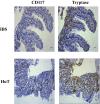
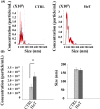
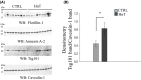
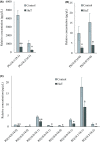
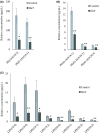
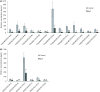
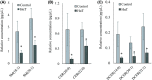
Exosomes are nano-sized vesicles that are involved in various biological processes including cell differentiation, proliferation, signaling, and intercellular communication. Urinary exosomes were isolated from a cohort of hereditary α-tryptasemia (HαT) patients and from healthy volunteers. There was a greater number of exosomes isolated from the urine in the HαT group compared to the control volunteers. Here, we investigated the differences in both lipid classes and lipid species within urinary exosomes of the two groups. Lipids were extracted from urinary exosomes and subjected to liquid chromatography mass spectrometry using a targeted approach. Various molecular species of glycerophospholipids, glycerolipids, and sterols were significantly reduced in HαT patients. Out of a possible 1127 lipids, 521 lipid species were detected, and relative quantities were calculated. Sixty-four lipids were significantly reduced in urinary exosomes of HαT patients compared to controls. All significantly reduced sphingolipids and most of the phospholipids were saturated or mono-unsaturated lipids. These results suggest exosome secretion is augmented in HαT patients and the lipids within these exosomes may be involved in various biological processes. The unique lipid composition of urinary exosomes from HαT patients will contribute to our understanding of the biochemistry of this disease.
Keywords: glycerolipids; glycerophospholipids; hereditary α-tryptasemia; lipidomics; sterols; urinary exosomes.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Statement There are no conflicts of interest to declare from any of the authors
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rapid and comprehensive 'shotgun' lipidome profiling of colorectal cancer cell derived exosomes.Methods. 2015 Oct 1;87:83-95. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2015.04.014. Epub 2015 Apr 20. Methods. 2015. PMID: 25907253 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular lipid species in urinary exosomes as potential prostate cancer biomarkers.Eur J Cancer. 2017 Jan;70:122-132. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2016.10.011. Epub 2016 Nov 30. Eur J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 27914242
-
Discrimination of urinary exosomes from microvesicles by lipidomics using thin layer liquid chromatography (TLC) coupled with MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry.Sci Rep. 2019 Sep 25;9(1):13834. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-50195-z. Sci Rep. 2019. Retraction in: Sci Rep. 2022 Feb 7;12(1):2327. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-06491-2 PMID: 31554842 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Exosomal lipid composition and the role of ether lipids and phosphoinositides in exosome biology.J Lipid Res. 2019 Jan;60(1):9-18. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R084343. Epub 2018 Aug 3. J Lipid Res. 2019. PMID: 30076207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipids in exosomes: Current knowledge and the way forward.Prog Lipid Res. 2017 Apr;66:30-41. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2017.03.001. Epub 2017 Mar 23. Prog Lipid Res. 2017. PMID: 28342835 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of lipids in exosome biology and intercellular communication: Function, analytics and applications.Traffic. 2021 Jul;22(7):204-220. doi: 10.1111/tra.12803. Epub 2021 Jun 11. Traffic. 2021. PMID: 34053166 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Urinary extracellular vesicles: A position paper by the Urine Task Force of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles.J Extracell Vesicles. 2021 May;10(7):e12093. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12093. Epub 2021 May 21. J Extracell Vesicles. 2021. PMID: 34035881 Free PMC article.
-
Current perspectives on clinical use of exosomes as novel biomarkers for cancer diagnosis.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 31;12:966981. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.966981. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36119470 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Femtoliter Injection of ESCRT-III Proteins into Adhered Giant Unilamellar Vesicles.Bio Protoc. 2022 Feb 20;12(4):e4328. doi: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4328. eCollection 2022 Feb 20. Bio Protoc. 2022. PMID: 35340293 Free PMC article.
-
Increased endothelial sodium channel activity by extracellular vesicles in human aortic endothelial cells: putative role of MLP1 and bioactive lipids.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2021 Sep 1;321(3):C535-C548. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00092.2020. Epub 2021 Jul 21. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34288724 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lyons JJ, Stotz SC, Chovanec J, et al. A common haplotype containing functional CACNA1H variants is frequently coinherited with increased TPSAB1 copy number. Genet Med. 2018;20:503‐512. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
