Induction of Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus-Encoded Thymidine Kinase (ORF21) by X-Box Binding Protein 1
- PMID: 31801863
- PMCID: PMC7022350
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01555-19
Induction of Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus-Encoded Thymidine Kinase (ORF21) by X-Box Binding Protein 1
Abstract
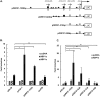
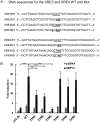
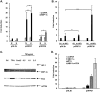
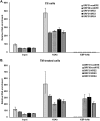
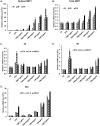
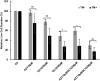
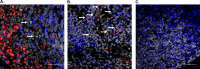
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) is the causative agent for Kaposi sarcoma (KS), primary effusion lymphoma (PEL), and multicentric Castleman disease (MCD). Like other herpesviruses, it has latent and lytic repertoires. However, there is evidence that some lytic genes can be directly activated by certain cellular factors. Cells undergoing endoplasmic reticulum stress express spliced X-box binding protein 1 (XBP-1s). XBP-1s is also present in large amounts in germinal center B cells. XBP-1s can activate the KSHV replication and transcription activator (RTA) and lytic replication. It can also directly activate KSHV-encoded viral interleukin-6 (vIL-6) and, thus, contribute to the pathogenesis of KSHV MCD. KSHV thymidine kinase (TK), the ORF21 gene product, can enhance the production of dTTP and is important for lytic replication. It can also phosphorylate zidovudine and ganciclovir to toxic moieties, enabling treatment of KSHV-MCD with these drugs. We show here that XBP-1s can directly activate ORF21 and that this activation is mediated primarily through two XBP-response elements (XRE) on the ORF21 promoter region. Deletion or mutation of these elements eliminated XBP-1s-induced upregulation of the promoter, and chromatin immunoprecipitation studies provide evidence that XBP-1s can bind to both XREs. Exposure of PEL cells to a chemical inducer of XBP-1s can induce ORF21 within 4 hours, and ORF21 expression in the lymph nodes of patients with KSHV-MCD is predominantly found in cells with XBP-1. Thus, XBP-1s may directly upregulate KSHV ORF21 and, thus, contribute to the pathogenesis of KSHV-MCD and the activity of zidovudine and valganciclovir in this disease.IMPORTANCE Spliced X-box binding protein 1 (XBP-1s), part of the unfolded protein response and expressed in developing germinal center B cells, can induce Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) lytic replication and directly activate viral interleukin-6 (vIL-6). We show here that XBP-1s can also directly activate KSHV ORF21, a lytic gene. ORF21 encodes KSHV thymidine kinase (TK), which increases the pool of dTTP for viral replication and enhances lytic replication. Direct activation of ORF21 by XBP-1s can enhance viral replication in germinal center B cells and contribute to the pathogenesis of KSHV multicentric Castleman disease (MCD). KSHV-MCD is characterized by systemic inflammation caused, in part, by lytic replication and overproduction of KSHV vIL-6 in XBP-1s-expressing lymph node plasmablasts. KSHV thymidine kinase can phosphorylate zidovudine and ganciclovir to toxic moieties, and direct activation of ORF21 by XBP-1s may also help explain the effectiveness of zidovudine and valganciclovir in the treatment of KSHV-MCD.
Keywords: HHV-8; KSHV; Kaposi; ORF21; XBP-1; herpesvirus; thymidine kinase.
Copyright © 2020 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Induction of Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus-Encoded Viral Interleukin-6 by X-Box Binding Protein 1.J Virol. 2015 Oct 21;90(1):368-78. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01192-15. Print 2016 Jan 1. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26491160 Free PMC article.
-
X box binding protein XBP-1s transactivates the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) ORF50 promoter, linking plasma cell differentiation to KSHV reactivation from latency.J Virol. 2007 Dec;81(24):13578-86. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01663-07. Epub 2007 Oct 10. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17928342 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus ORF21 Tyrosine Kinase and Viral Lytic Reactivation by Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Approved for Clinical Use.J Virol. 2020 Feb 14;94(5):e01791-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01791-19. Print 2020 Feb 14. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 31826996 Free PMC article.
-
Pathological Features of Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Infection.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1045:357-376. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-7230-7_16. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 29896675 Review.
-
Recent Advances in Developing Treatments of Kaposi's Sarcoma Herpesvirus-Related Diseases.Viruses. 2021 Sep 9;13(9):1797. doi: 10.3390/v13091797. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34578378 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
HIV-associated cancers and lymphoproliferative disorders caused by Kaposi sarcoma herpesvirus and Epstein-Barr virus.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2024 Sep 12;37(3):e0002223. doi: 10.1128/cmr.00022-23. Epub 2024 Jun 20. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2024. PMID: 38899877 Review.
-
Folate-Targeted Nanocarriers Co-Deliver Ganciclovir and miR-34a-5p for Combined Anti-KSHV Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 2;25(5):2932. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052932. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38474177 Free PMC article.
-
Insight into Oncogenic Viral Pathways as Drivers of Viral Cancers: Implication for Effective Therapy.Curr Oncol. 2023 Feb 5;30(2):1924-1944. doi: 10.3390/curroncol30020150. Curr Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36826111 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment of tumor-associated macrophages with PD-1 monoclonal antibodies affects vascular generation in cervical cancer via the PD-1/IRE1α/SHP2/HIF1α signaling pathway.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Aug 28;16(17):12335-12345. doi: 10.18632/aging.206090. Epub 2024 Aug 28. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 39207449 Free PMC article.
-
A Role for the Chicken Interferon-Stimulated Gene CMPK2 in the Host Response Against Virus Infection.Front Microbiol. 2022 May 11;13:874331. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.874331. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35633731 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Soulier J, Grollet L, Oksenhendler E, Cacoub P, Cazals-Hatem D, Babinet P, d'Agay MF, Clauvel JP, Raphael M, Degos L, Sigaux F. 1995. Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in multicentric Castleman’s disease. Blood 86:1276–1280. doi:10.1182/blood.V86.4.1276.bloodjournal8641276. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

