Tumor microenvironment dictates regulatory T cell phenotype: Upregulated immune checkpoints reinforce suppressive function
- PMID: 31801611
- PMCID: PMC6894345
- DOI: 10.1186/s40425-019-0785-8
Tumor microenvironment dictates regulatory T cell phenotype: Upregulated immune checkpoints reinforce suppressive function
Abstract
Background: Regulatory T (Treg) cells have an immunosuppressive function in cancer, but the underlying mechanism of immunosuppression in the tumor microenvironment (TME) is unclear.
Methods: We compared the phenotypes of T cell subsets, including Treg cells, obtained from peripheral blood, malignant effusion, and tumors of 103 cancer patients. Our primary focus was on the expression of immune checkpoint (IC)-molecules, such as programmed death (PD)-1, T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin-domain containing (TIM)-3, T cell Ig and ITIM domain (TIGIT), and cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen (CTLA)-4, on Treg cells in paired lymphocytes from blood, peritumoral tissue, and tumors of 12 patients with lung cancer. To identify the immunosuppressive mechanisms acting on tumor-infiltrating Treg cells, we conducted immunosuppressive functional assays in a mouse model.
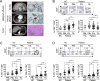
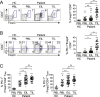
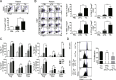
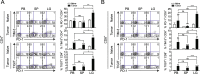
Results: CD8+, CD4+ T cells, and Treg cells exhibited a gradual upregulation of IC-molecules the closer they were to the tumor. Interestingly, PD-1 expression was more prominent in Treg cells than in conventional T (Tconv) cells. In lung cancer patients, higher levels of IC-molecules were expressed on Treg cells than on Tconv cells, and Treg cells were also more enriched in the tumor than in the peri-tumor and blood. In a mouse lung cancer model, IC-molecules were also preferentially upregulated on Treg cells, compared to Tconv cells. PD-1 showed the greatest increase on most cell types, especially Treg cells, and this increase occurred gradually over time after the cells entered the TME. PD-1 high-expressing tumor-infiltrating Treg cells displayed potent suppressive activity, which could be partially inhibited with a blocking anti-PD-1 antibody.
Conclusions: We demonstrate that the TME confers a suppressive function on Treg cells by upregulating IC-molecule expression. Targeting IC-molecules, including PD-1, on Treg cells may be effective for cancer treatment.
Keywords: Immune checkpoints; Programmed cell death 1 receptor; Regulatory T cells; Tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest that are relevant to this study.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Remodeling of the tumor microenvironment via disrupting Blimp1+ effector Treg activity augments response to anti-PD-1 blockade.Mol Cancer. 2021 Nov 20;20(1):150. doi: 10.1186/s12943-021-01450-3. Mol Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34798898 Free PMC article.
-
Preferential accumulation of regulatory T cells with highly immunosuppressive characteristics in breast tumor microenvironment.Oncotarget. 2017 May 16;8(20):33159-33171. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16565. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28388539 Free PMC article.
-
Immune Checkpoints in Circulating and Tumor-Infiltrating CD4+ T Cell Subsets in Colorectal Cancer Patients.Front Immunol. 2019 Dec 17;10:2936. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02936. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31921188 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
T-cell programming in pancreatic adenocarcinoma: a review.Cancer Gene Ther. 2017 Mar;24(3):106-113. doi: 10.1038/cgt.2016.66. Epub 2016 Dec 2. Cancer Gene Ther. 2017. PMID: 27910859 Review.
-
T Regulatory Cells and Priming the Suppressive Tumor Microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2019 Oct 15;10:2453. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02453. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31681327 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in 10 Years: Contribution of Basic Research and Clinical Application in Cancer Immunotherapy.Immune Netw. 2022 Feb 14;22(1):e2. doi: 10.4110/in.2022.22.e2. eCollection 2022 Feb. Immune Netw. 2022. PMID: 35291660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correlation of CCL8 expression with immune cell infiltration of skin cutaneous melanoma: potential as a prognostic indicator and therapeutic pathway.Cancer Cell Int. 2021 Nov 29;21(1):635. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-02350-8. Cancer Cell Int. 2021. PMID: 34844613 Free PMC article.
-
Immune Features of Tumor Microenvironment: A Genetic Spotlight.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024 Mar;82(1):107-118. doi: 10.1007/s12013-023-01192-7. Epub 2023 Oct 23. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024. PMID: 37870699 Review.
-
YTHDF2/m6 A/NF-κB axis controls anti-tumor immunity by regulating intratumoral Tregs.EMBO J. 2023 Aug 1;42(15):e113126. doi: 10.15252/embj.2022113126. Epub 2023 Jun 22. EMBO J. 2023. PMID: 37345898 Free PMC article.
-
Intrapleural interleukin-2-expressing oncolytic virotherapy enhances acute antitumor effects and T-cell receptor diversity in malignant pleural disease.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2022 Apr;163(4):e313-e328. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2020.11.160. Epub 2020 Dec 13. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2022. PMID: 33485667 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gettinger SN, Horn L, Gandhi L, Spigel DR, Antonia SJ, Rizvi NA, et al. Overall survival and long-term safety of Nivolumab (anti-programmed death 1 antibody, BMS-936558, ONO-4538) in patients with previously treated advanced non-small-cell lung Cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(18):2004. doi: 10.1200/jco.2014.58.3708. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Garon Edward B., Rizvi Naiyer A., Hui Rina, Leighl Natasha, Balmanoukian Ani S., Eder Joseph Paul, Patnaik Amita, Aggarwal Charu, Gubens Matthew, Horn Leora, Carcereny Enric, Ahn Myung-Ju, Felip Enriqueta, Lee Jong-Seok, Hellmann Matthew D., Hamid Omid, Goldman Jonathan W., Soria Jean-Charles, Dolled-Filhart Marisa, Rutledge Ruth Z., Zhang Jin, Lunceford Jared K., Rangwala Reshma, Lubiniecki Gregory M., Roach Charlotte, Emancipator Kenneth, Gandhi Leena. Pembrolizumab for the Treatment of Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. New England Journal of Medicine. 2015;372(21):2018–2028. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1501824. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nishikawa H, Sakaguchi S. Regulatory T cells in tumor immunity. Int J Cancer. 2010;127(4):759–767. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
