Activation of the IL-4/STAT6 Signaling Pathway Promotes Lung Cancer Progression by Increasing M2 Myeloid Cells
- PMID: 31798581
- PMCID: PMC6863933
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02638
Activation of the IL-4/STAT6 Signaling Pathway Promotes Lung Cancer Progression by Increasing M2 Myeloid Cells
Abstract
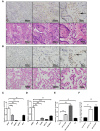
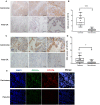
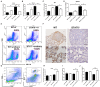
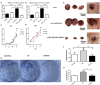
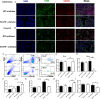
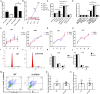
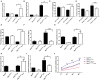
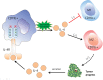
Emerging evidence shows that signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 (STAT6) plays critical roles in tumor development. We previously found high-level expression of STAT6 in human lung adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, specifically in infiltrated immune cells located in the lung interstitium. Nevertheless, the role of STAT6 signaling in lung carcinogenesis and lung cancer proliferation and its underlying mechanisms remain unclear. This study aimed to investigate the role of STAT6 and the interaction between STAT6 and the tumor microenvironment in pulmonary tumorigenesis. We established a murine model of primary lung carcinogenesis in STAT6-deficient (STAT6-/-) and STAT6 wild-type (WT) BALB/c mice using the carcinogen urethane. Two-month-old male mice were intraperitoneally injected with urethane (1 g/kg) dissolved in phosphate buffered saline (PBS). Primary tumors were monitored in vivo by positron emission tomography scanning. At 4, 6, and 9 months after urethane injection, lung tumors were harvested from the STAT6-/- and WT mice for analysis. Small interfering RNA was used to downregulate the expression of STAT6 in tumor cells. Fluorescence activated cell sorting analysis was used to analyze fluorescence-conjugated cell markers. Transwell assays were used in coculturing experiments. STAT6 protein expression was detected by Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. STAT6 mRNA expression was detected by quantitative real time-polymerase chain reaction. Cell Counting Kit-8 and colony formation assays were performed to evaluate cell proliferation. We detected high expression of STAT6 in CD11b+ cells of lung carcinoma. Our results indicate that STAT6 deficiency inhibits carcinogen-induced tumor growth and improves prognosis. STAT6 deficiency also decreased the mobilization and differentiation of CD11b+ cells. STAT6 deficiency in CD11b+ cells but not tumor cells decreased interleukin (IL)-4 secretion and the differentiation of CD11b+ cells into M2 macrophage cells. In conclusion, our findings indicate that IL-4/STAT6 signaling in CD11b+ cells promotes lung cancer progression by triggering an IL-4 positive feedback loop and increasing M2 myeloid cells. STAT6 may be a new therapeutic target for the prevention and treatment of lung cancer.
Keywords: CD11b; IL-4; STAT6; lung cancer; macrophage polarization.
Copyright © 2019 Fu, Jiang, Hao, Liu, Ding, Zhang, Yang and Li.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Histamine promotes the differentiation of macrophages from CD11b+ myeloid cells and formation of foam cells through a Stat6-dependent pathway.Atherosclerosis. 2017 Aug;263:42-52. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2017.05.024. Epub 2017 May 23. Atherosclerosis. 2017. PMID: 28600950
-
Disruption of STAT6 Signal Promotes Cardiac Fibrosis Through the Mobilization and Transformation of CD11b+ Immature Myeloid Cells.Front Physiol. 2020 Oct 22;11:579712. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.579712. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 33192584 Free PMC article.
-
Immune-mediated neuroprotection of axotomized mouse facial motoneurons is dependent on the IL-4/STAT6 signaling pathway in CD4(+) T cells.Exp Neurol. 2006 Sep;201(1):212-24. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2006.04.028. Epub 2006 Jun 27. Exp Neurol. 2006. PMID: 16806176
-
Tumor immunity: a balancing act between T cell activation, macrophage activation and tumor-induced immune suppression.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2005 Nov;54(11):1137-42. doi: 10.1007/s00262-005-0703-4. Epub 2005 May 5. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2005. PMID: 15877228 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The roles of post-translational modifications and coactivators of STAT6 signaling in tumor growth and progression.Future Med Chem. 2020 Nov;12(21):1945-1960. doi: 10.4155/fmc-2020-0224. Epub 2020 Aug 11. Future Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32779479 Review.
Cited by
-
Involvement of IL-4, IL-13 and Their Receptors in Pancreatic Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 15;22(6):2998. doi: 10.3390/ijms22062998. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33804263 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differentiation and Regulation of TH Cells: A Balancing Act for Cancer Immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2021 May 3;12:669474. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.669474. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34012451 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pan-cancer analysis reveals signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) gene family as biomarkers for prognostic prediction and therapeutic guidance.Front Genet. 2023 Mar 9;14:1120500. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1120500. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 36968603 Free PMC article.
-
STAT6/VDR Axis Mitigates Lung Inflammatory Injury by Promoting Nrf2 Signaling Pathway.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Jan 10;2022:2485250. doi: 10.1155/2022/2485250. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35047105 Free PMC article.
-
STAT6 mutations enriched at diffuse large B-cell lymphoma relapse reshape the tumor microenvironment.Int J Hematol. 2024 Mar;119(3):275-290. doi: 10.1007/s12185-023-03692-x. Epub 2024 Jan 29. Int J Hematol. 2024. PMID: 38285120 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

