Metabolic Remodelling: An Accomplice for New Therapeutic Strategies to Fight Lung Cancer
- PMID: 31795465
- PMCID: PMC6943435
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox8120603
Metabolic Remodelling: An Accomplice for New Therapeutic Strategies to Fight Lung Cancer
Abstract
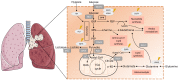
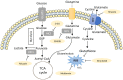
Metabolic remodelling is a hallmark of cancer, however little has been unravelled in its role in chemoresistance, which is a major hurdle to cancer control. Lung cancer is a leading cause of death by cancer, mainly due to the diagnosis at an advanced stage and to the development of resistance to therapy. Targeted therapeutic agents combined with comprehensive drugs are commonly used to treat lung cancer. However, resistance mechanisms are difficult to avoid. In this review, we will address some of those therapeutic regimens, resistance mechanisms that are eventually developed by lung cancer cells, metabolic alterations that have already been described in lung cancer and putative new therapeutic strategies, and the integration of conventional drugs and genetic and metabolic-targeted therapies. The oxidative stress is pivotal in this whole network. A better understanding of cancer cell metabolism and molecular adaptations underlying resistance mechanisms will provide clues to design new therapeutic strategies, including the combination of chemotherapeutic and targeted agents, considering metabolic intervenients. As cancer cells undergo a constant metabolic adaptive drift, therapeutic regimens must constantly adapt.
Keywords: cancer metabolism; lung cancer; new therapeutic strategies; reactive oxygen species (ROS); therapy resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mitochondrial biogenesis: pharmacological approaches.Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(35):5507-9. doi: 10.2174/138161282035140911142118. Curr Pharm Des. 2014. PMID: 24606795
-
Overview of resistance to systemic therapy in patients with breast cancer.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;608:1-22. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-74039-3_1. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 17993229 Review.
-
Inside the biochemical pathways of thymidylate synthase perturbed by anticancer drugs: Novel strategies to overcome cancer chemoresistance.Drug Resist Updat. 2015 Nov;23:20-54. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2015.10.003. Epub 2015 Oct 31. Drug Resist Updat. 2015. PMID: 26690339 Review.
-
The Metabolic Remodelling in Lung Cancer and Its Putative Consequence in Therapy Response.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1219:311-333. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-34025-4_16. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32130706 Review.
-
Emerging treatment for advanced lung cancer with EGFR mutation.Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2015;20(4):597-612. doi: 10.1517/14728214.2015.1058778. Epub 2015 Jul 8. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2015. PMID: 26153235 Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphodiesterase Inhibition to Sensitize Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer to Pemetrexed: A Double-Edged Strategy.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jul 6;16(13):2475. doi: 10.3390/cancers16132475. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39001537 Free PMC article.
-
Reprogramming of Lipid Metabolism in Lung Cancer: An Overview with Focus on EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Cells. 2022 Jan 25;11(3):413. doi: 10.3390/cells11030413. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35159223 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of MicroRNAs in Lung Cancer Metabolism.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Apr 5;13(7):1716. doi: 10.3390/cancers13071716. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33916349 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Control of Oxidative Stress in Cancer Chemoresistance: Spotlight on Nrf2 Role.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Mar 25;10(4):510. doi: 10.3390/antiox10040510. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33805928 Free PMC article. Review.
-
20-Hydroxyecdysone Confers Antioxidant and Antineoplastic Properties in Human Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells.Metabolites. 2023 May 15;13(5):656. doi: 10.3390/metabo13050656. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 37233697 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

