A Small Compound KJ-28d Enhances the Sensitivity of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer to Radio- and Chemotherapy
- PMID: 31795418
- PMCID: PMC6928747
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20236026
A Small Compound KJ-28d Enhances the Sensitivity of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer to Radio- and Chemotherapy
Abstract
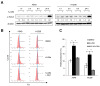
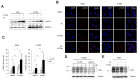
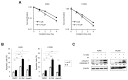
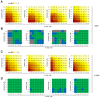
We previously reported on a poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) 1/2 inhibitor N-(3-(hydroxycarbamoyl)phenyl)carboxamide (designated KJ-28d), which increased the death of human ovarian cancer BRCA1-deficient SNU-251 cells. In the present study, we further investigated the antitumor activities of KJ-28d in BRCA-proficient non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells to expand the use of PARP inhibitors. KJ-28d significantly inhibited the growth of NSCLC cells in vitro and in vivo, and induced DNA damage and reactive oxygen species in A549 and H1299 cells. Combined treatment with KJ-28d and ionizing radiation led to increased DNA damage responses in A549 and H1299 cells compared to KJ-28d or ionizing radiation alone, resulting in apoptotic cell death. Moreover, the combination of KJ-28d plus a DNA-damaging therapeutic agent (carboplatin, cisplatin, paclitaxel, or doxorubicin) synergistically inhibited cell proliferation, compared to either drug alone. Taken together, the findings demonstrate the potential of KJ-28d as an effective anti-cancer therapeutic agent for BRCA-deficient and -proficient cancer cells. KJ-28d might have potential as an adjuvant when used in combination with radiotherapy or DNA-damaging agents, pending further investigations.
Keywords: DNA damage; chemotherapy; combination therapy; non-small cell lung cancer; poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor; radiotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
DNA methyltransferase inhibitors induce a BRCAness phenotype that sensitizes NSCLC to PARP inhibitor and ionizing radiation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Nov 5;116(45):22609-22618. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1903765116. Epub 2019 Oct 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31591209 Free PMC article.
-
Antitumor Activity of a Novel Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor AIU2001 Due to Abrogation of the DNA Damage Repair in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 24;20(19):4728. doi: 10.3390/ijms20194728. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31554189 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease activity enhances the antitumor activity of oxymatrine in lung cancer cells.Int J Oncol. 2016 Dec;49(6):2331-2340. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3734. Epub 2016 Oct 14. Int J Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27748797
-
PARP inhibitors: an interesting pathway also for non-small cell lung cancer?Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(24):3875-82. doi: 10.2174/13816128113196660765. Curr Pharm Des. 2014. PMID: 24191958 Review.
-
Poly (ADP-Ribose) Polymerases (PARPs) and PARP Inhibitor-Targeted Therapeutics.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2019;19(2):206-212. doi: 10.2174/1871520618666181109164645. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30417796 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular mechanisms of sensitivity and resistance to radiotherapy.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2024 Aug;41(4):517-524. doi: 10.1007/s10585-023-10260-4. Epub 2024 Jan 17. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2024. PMID: 38231337 Review.
-
Inhibition of DNA Repair Enzymes as a Valuable Pharmaceutical Approach.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 27;24(9):7954. doi: 10.3390/ijms24097954. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175662 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the Hippo pathway to prevent radioresistance brain metastases from the lung (Review).Int J Oncol. 2024 Jul;65(1):68. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2024.5656. Epub 2024 May 24. Int J Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38785155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
STC2 activates PRMT5 to induce radioresistance through DNA damage repair and ferroptosis pathways in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Redox Biol. 2023 Apr;60:102626. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.102626. Epub 2023 Feb 3. Redox Biol. 2023. PMID: 36764215 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing anti-tumour innate immunity by targeting the DNA damage response and pattern recognition receptors in combination with radiotherapy.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 29;12:971959. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.971959. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36106115 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- American-Cancer-Society . Cancer Facts & Figures 2019. American Cancer Society; Atlanta, GA, USA: 2019.
-
- Korea N.C.C. Annual Report of Cancer Statistics in Korea in 2016. Ntational Cancer Center Korea; Gyeonggi-do, Korea: 2016. [(accessed on 29 November 2019)]. Available online: https://www.cancer.go.kr/lay1/bbs/S1T674C680/B/26/list.do.
-
- Liu C.Y., Wang C.L., Li S.H., Hsu P.C., Chen C.H., Lin T.Y., Kuo C.H., Fang Y.F., Ko H.W., Yu C.T., et al. The efficacy of 40 mg versus dose de-escalation to less than 40 mg of afatinib (Giotrif) as the first-line therapy for patients with primary lung adenocarcinoma harboring favorable epidermal growth factor mutations. Oncotarget. 2017;8:97602–97612. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18746. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen Y., Chen G., Li J., Huang Y.Y., Li Y., Lin J., Chen L.Z., Lu J.P., Wang Y.Q., Wang C.X., et al. Association of Tumor Protein p53 and Ataxia-Telangiectasia Mutated Comutation With Response to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Mortality in Patients With Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. JAMA Netw. Open. 2019;2:e1911895. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.11895. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

