A SUMO-dependent pathway controls elongating RNA Polymerase II upon UV-induced damage
- PMID: 31784551
- PMCID: PMC6884465
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-54027-y
A SUMO-dependent pathway controls elongating RNA Polymerase II upon UV-induced damage
Abstract
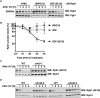
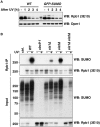
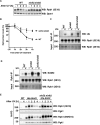
RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) is the workhorse of eukaryotic transcription and produces messenger RNAs and small nuclear RNAs. Stalling of RNAPII caused by transcription obstacles such as DNA damage threatens functional gene expression and is linked to transcription-coupled DNA repair. To restore transcription, persistently stalled RNAPII can be disassembled and removed from chromatin. This process involves several ubiquitin ligases that have been implicated in RNAPII ubiquitylation and proteasomal degradation. Transcription by RNAPII is heavily controlled by phosphorylation of the C-terminal domain of its largest subunit Rpb1. Here, we show that the elongating form of Rpb1, marked by S2 phosphorylation, is specifically controlled upon UV-induced DNA damage. Regulation of S2-phosphorylated Rpb1 is mediated by SUMOylation, the SUMO-targeted ubiquitin ligase Slx5-Slx8, the Cdc48 segregase as well as the proteasome. Our data suggest an RNAPII control pathway with striking parallels to known disassembly mechanisms acting on defective RNA polymerase III.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
SUMO-Chain-Regulated Proteasomal Degradation Timing Exemplified in DNA Replication Initiation.Mol Cell. 2019 Nov 21;76(4):632-645.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.08.003. Epub 2019 Sep 10. Mol Cell. 2019. PMID: 31519521 Free PMC article.
-
Rpb1 sumoylation in response to UV radiation or transcriptional impairment in yeast.PLoS One. 2009;4(4):e5267. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005267. Epub 2009 Apr 22. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19384408 Free PMC article.
-
Ccr4-Not maintains genomic integrity by controlling the ubiquitylation and degradation of arrested RNAPII.Genes Dev. 2019 Jun 1;33(11-12):705-717. doi: 10.1101/gad.322453.118. Epub 2019 Apr 4. Genes Dev. 2019. PMID: 30948432 Free PMC article.
-
DNA Damage-Induced RNAPII Degradation and Its Consequences in Gene Expression.Genes (Basel). 2022 Oct 26;13(11):1951. doi: 10.3390/genes13111951. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36360188 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome maintenance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: the role of SUMO and SUMO-targeted ubiquitin ligases.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Mar 17;45(5):2242-2261. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw1369. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28115630 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dynamic sumoylation of promoter-bound general transcription factors facilitates transcription by RNA polymerase II.PLoS Genet. 2021 Sep 29;17(9):e1009828. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009828. eCollection 2021 Sep. PLoS Genet. 2021. PMID: 34587155 Free PMC article.
-
Polymerases and DNA Repair in Neurons: Implications in Neuronal Survival and Neurodegenerative Diseases.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Jun 30;16:852002. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.852002. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35846567 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA-protein crosslink proteases in genome stability.Commun Biol. 2021 Jan 4;4(1):11. doi: 10.1038/s42003-020-01539-3. Commun Biol. 2021. PMID: 33398053 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

