miR-200a Attenuated Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity through Upregulation of Nrf2 in Mice
- PMID: 31781322
- PMCID: PMC6875222
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/1512326
miR-200a Attenuated Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity through Upregulation of Nrf2 in Mice
Abstract
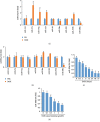
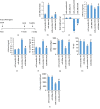
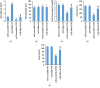
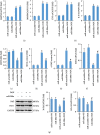
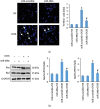
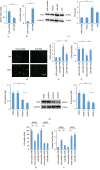
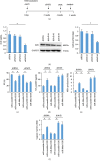
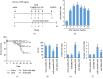
Nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (Nrf2) was closely involved in doxorubicin- (DOX-) induced cardiotoxicity. MicroRNA-200a (miR-200a) could target Keap1 mRNA and promote degradation of Keap1 mRNA, resulting in Nrf2 activation. However, the role of miR-200a in DOX-related cardiotoxicity remained unclear. Our study is aimed at investigating the effect of miR-200a on DOX-induced cardiotoxicity in mice. For cardiotropic expression, male mice received an injection of an adeno-associated virus 9 (AAV9) system carrying miR-200a or miR-scramble. Four weeks later, mice received a single intraperitoneal injection of DOX at 15 mg/kg. In our study, we found that miR-200a mRNA was the only microRNA that was significantly decreased in DOX-treated mice and H9c2 cells. miR-200a supplementation blocked whole-body wasting and heart atrophy caused by acute DOX injection, decreased the levels of cardiac troponin I and the N-terminal probrain natriuretic peptide, and improved cardiac and adult cardiomyocyte contractile function. Moreover, miR-200a reduced oxidative stress and cardiac apoptosis without affecting matrix metalloproteinase and inflammatory factors in mice with acute DOX injection. miR-200a also attenuated DOX-induced oxidative injury and cell loss in vitro. As expected, we found that miR-200a activated Nrf2 and Nrf2 deficiency abolished the protection provided by miR-200a supplementation in mice. miR-200a also provided cardiac benefits in a chronic model of DOX-induced cardiotoxicity. In conclusion, miR-200a protected against DOX-induced cardiotoxicity via activation of the Nrf2 signaling pathway. Our data suggest that miR-200a may represent a new cardioprotective strategy against DOX-induced cardiotoxicity.
Copyright © 2019 Xiaoping Hu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MiR-24-3p Attenuates Doxorubicin-induced Cardiotoxicity via the Nrf2 Pathway in Mice.Curr Med Sci. 2022 Feb;42(1):48-55. doi: 10.1007/s11596-022-2536-1. Epub 2022 Jan 28. Curr Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 35089495
-
Activation of Nrf2 by miR-152 Inhibits Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity via Attenuation of Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Jan 26;2021:8860883. doi: 10.1155/2021/8860883. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 33574984 Free PMC article.
-
miR-451 Silencing Inhibited Doxorubicin Exposure-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Mice.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Jul 4;2019:1528278. doi: 10.1155/2019/1528278. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31355248 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs target the PI3K/Akt/p53 and the Sirt1/Nrf2 signaling pathways in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2023 Feb;37(2):e23261. doi: 10.1002/jbt.23261. Epub 2022 Nov 23. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 36416353 Review.
-
Natural compounds against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: A review on the involvement of Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway.Phytother Res. 2021 Mar;35(3):1163-1175. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6882. Epub 2020 Sep 28. Phytother Res. 2021. PMID: 32985744 Review.
Cited by
-
Cardiomyocyte Atrophy, an Underestimated Contributor in Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Feb 25;9:812578. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.812578. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35282350 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amniotic Fluid microRNA in Severe Twin-Twin Transfusion Syndrome Cardiomyopathy-Identification of Differences and Predicting Demise.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2022 Jan 23;9(2):37. doi: 10.3390/jcdd9020037. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2022. PMID: 35200691 Free PMC article.
-
Selenium Attenuates Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity Through Nrf2-NLRP3 Pathway.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2022 Jun;200(6):2848-2856. doi: 10.1007/s12011-021-02891-z. Epub 2021 Aug 30. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2022. PMID: 34462843
-
Dissecting the Crosstalk Between Nrf2 and NF-κB Response Pathways in Drug-Induced Toxicity.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Feb 2;9:809952. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.809952. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35186957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in Chemoprotection and Doxorubicin Resistance: Potential Application in Drug Discovery.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Feb 26;10(3):349. doi: 10.3390/antiox10030349. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33652780 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Maksimenko A. V., Vavaev A. V. Antioxidant enzymes as potential targets in cardioprotection and treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Enzyme antioxidants: the next stage of pharmacological counterwork to the oxidative stress. Heart International. 2012;7(1):p. hi.2012.e3. doi: 10.4081/hi.2012.e3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

