DNMT3b/OCT4 expression confers sorafenib resistance and poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma through IL-6/STAT3 regulation
- PMID: 31771617
- PMCID: PMC6878666
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-019-1442-2
DNMT3b/OCT4 expression confers sorafenib resistance and poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma through IL-6/STAT3 regulation
Erratum in
-
Correction to: DNMT3b/OCT4 expression confers sorafenib resistance and poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma through IL-6/STAT3 regulation.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Jan 13;39(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1518-z. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 31931847 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: The inflammatory cytokine interleukin-6 (IL-6) is critical for the expression of octamer-binding transcription factor 4 (OCT4), which is highly associated with early tumor recurrence and poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinomas (HCC). DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) family is closely linked with OCT4 expression and drug resistance. However, the underlying mechanism regarding the interplay between DNMTs and IL-6-induced OCT4 expression and the sorafenib resistance of HCC remains largely unclear.
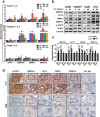
Methods: HCC tissue samples were used to examine the association between DNMTs/OCT4 expression levels and clinical prognosis. Serum levels of IL-6 were detected using ELISA assays (n = 144). Gain- and loss-of-function experiments were performed in cell lines and mouse xenograft models to determine the underlying mechanism in vitro and in vivo.
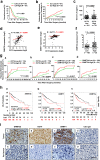
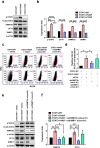
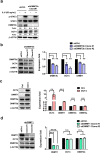
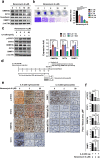
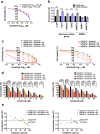
Results: We demonstrate that levels of DNA methyltransferase 3 beta (DNMT3b) are significantly correlated with the OCT4 levels in HCC tissues (n = 144), and the OCT4 expression levels are positively associated with the serum IL-6 levels. Higher levels of IL-6, DNMT3b, or OCT4 predicted early HCC recurrence and poor prognosis. We show that IL-6/STAT3 activation increases DNMT3b/1 and OCT4 in HCC. Activated phospho-STAT3 (STAT-Y640F) significantly increased DNMT3b/OCT4, while dominant negative phospho-STAT3 (STAT-Y705F) was suppressive. Inhibiting DNMT3b with RNA interference or nanaomycin A (a selective DNMT3b inhibitor) effectively suppressed the IL-6 or STAT-Y640F-induced increase of DNMT3b-OCT4 and ALDH activity in vitro and in vivo. The fact that OCT4 regulates the DNMT1 expressions were further demonstrated either by OCT4 forced expression or DNMT1 silence. Additionally, the DNMT3b silencing reduced the OCT4 expression in sorafenib-resistant Hep3B cells with or without IL-6 treatment. Notably, targeting DNMT3b with nanaomycin A significantly increased the cell sensitivity to sorafenib, with a synergistic combination index (CI) in sorafenib-resistant Hep3B cells.
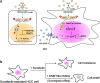
Conclusions: The DNMT3b plays a critical role in the IL-6-mediated OCT4 expression and the drug sensitivity of sorafenib-resistant HCC. The p-STAT3 activation increases the DNMT3b/OCT4 which confers the tumor early recurrence and poor prognosis of HCC patients. Findings from this study highlight the significance of IL-6-DNMT3b-mediated OCT4 expressions in future therapeutic target for patients expressing cancer stemness-related properties or sorafenib resistance in HCC.
Keywords: DNMT3b; Drug resistance; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Interleukin-6; OCT4; Phospho-STAT3.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activation of IL6/IGFIR confers poor prognosis of HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma through induction of OCT4/NANOG expression.Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Jan 1;21(1):201-10. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-3274. Clin Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25564572
-
SNGH16 regulates cell autophagy to promote Sorafenib Resistance through suppressing miR-23b-3p via sponging EGR1 in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Med. 2020 Jun;9(12):4324-4338. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3020. Epub 2020 Apr 23. Cancer Med. 2020. PMID: 32324343 Free PMC article.
-
Novel STAT3 oligonucleotide compounds suppress tumor growth and overcome the acquired resistance to sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024 Aug;45(8):1701-1714. doi: 10.1038/s41401-024-01261-4. Epub 2024 Apr 12. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024. PMID: 38609562
-
Deciphering STAT3 signaling potential in hepatocellular carcinoma: tumorigenesis, treatment resistance, and pharmacological significance.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023 Apr 21;28(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s11658-023-00438-9. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023. PMID: 37085753 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New insights on sorafenib resistance in liver cancer with correlation of individualized therapy.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2020 Aug;1874(1):188382. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2020.188382. Epub 2020 Jun 6. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32522600 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative oncology reveals DNMT3B as a molecular vulnerability in undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2022 Dec;45(6):1277-1295. doi: 10.1007/s13402-022-00717-1. Epub 2022 Oct 1. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2022. PMID: 36181640 Free PMC article.
-
Breaking the Barriers of Therapy Resistance: Harnessing Ferroptosis for Effective Hepatocellular Carcinoma Therapy.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2024 Jul 2;11:1265-1278. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S469449. eCollection 2024. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2024. PMID: 38974015 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Cytokines in the Different Stages of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Sep 29;13(19):4876. doi: 10.3390/cancers13194876. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34638361 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19-Induced Modifications in the Tumor Microenvironment: Do They Affect Cancer Reawakening and Metastatic Relapse?Front Oncol. 2020 Oct 26;10:592891. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.592891. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33194755 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic modification-related mechanisms of hepatocellular carcinoma resistance to immune checkpoint inhibition.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 4;13:1043667. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1043667. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36685594 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MOST 105-2628-B-038-008-MY3/Ministry of Science and Technology (VN)
- MOST 106-3114-B-038-001/Ministry of Science and Technology (VN)
- MOST 107-2321-B-038-002/Ministry of Science and Technology
- MOST 107-2314-B-038-057/Ministry of Science and Technology
- MOST108-2321-B-038-003/Ministry of Science and Technology
- DP2-107-21121-01-T-02/Ministry of Education (KR)
- DP2-108-21121-01-T-02-02/Ministry of Education
- CORPG6F0053/Chiayi Chang Gung Memorial Hospital (TW)
- CMRPG6F0163/Chiayi Chang Gung Memorial Hospital
- TMU-T104-06/Taipei Medical University (TW)
- TMU-T105-06/Taipei Medical University (TW)
- 105TMU-CIT-01-3/Taipei Medical University (TW)
- TMU-T106-03/Taipei Medical University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

