MicroRNA-1269 promotes cell proliferation via the AKT signaling pathway by targeting RASSF9 in human gastric cancer
- PMID: 31768130
- PMCID: PMC6873743
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-019-1026-4
MicroRNA-1269 promotes cell proliferation via the AKT signaling pathway by targeting RASSF9 in human gastric cancer
Abstract
Background: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play key roles in tumorigenesis and progression of gastric cancer (GC). miR-1269 has been reported to be upregulated in several cancers and plays a crucial role in carcinogenesis and cancer progression. However, the biological function of miR-1269 in human GC and its mechanism remain unclear and need to be further elucidated.
Methods: The expression of miR-1269 in GC tissues and cell lines was detected by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). Target prediction programs (TargetScanHuman 7.2 and miRBase) and a dual-luciferase reporter assay were used to confirm that Ras-association domain family 9 (RASSF9) is a target gene of miR-1269. The expression of RASSF9 was measured by qRT-PCR and Western blotting in GC tissues. MTT and cell counting assays were used to explore the effect of miR-1269 on GC cell proliferation. The cell cycle and apoptosis were measured by flow cytometry. RASSF9 knockdown and overexpression were used to further verify the function of the target gene.
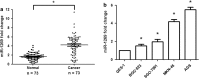
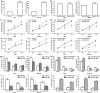
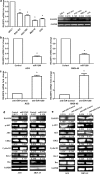
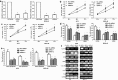
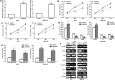
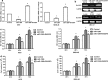
Results: We found that miR-1269 expression was upregulated in human GC tissues and cell lines. The overexpression of miR-1269 promoted GC cell proliferation and cell cycle G1-S transition and suppressed apoptosis. The inhibition of miR-1269 inhibited cell growth and G1-S transition and induced apoptosis. miR-1269 expression was inversely correlated with RASSF9 expression in GC tissues. RASSF9 was verified to be a direct target of miR-1269 by using a luciferase reporter assay. The overexpression of miR-1269 decreased RASSF9 expression at both the mRNA and protein levels, and the inhibition of miR-1269 increased RASSF9 expression. Importantly, silencing RASSF9 resulted in the same biological effects in GC cells as those induced by overexpression of miR-1269. Overexpression of RASSF9 reversed the effects of miR-1269 overexpression on GC cells. Both miR-1269 overexpression and RASSF9 silencing activated the AKT signaling pathway, which modulated cell cycle regulators (Cyclin D1 and CDK2). In contrast, inhibition of miR-1269 and RASSF9 overexpression inhibited the AKT signaling pathway. Moreover, miR-1269 and RASSF9 also regulated the Bax/Bcl-2 signaling pathway.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate that miR-1269 promotes GC cell proliferation and cell cycle G1-S transition by activating the AKT signaling pathway and inhibiting cell apoptosis via regulation of the Bax/Bcl-2 signaling pathway by targeting RASSF9. Our findings indicate an oncogenic role of miR-1269 in GC pathogenesis and the potential use of miR-1269 in GC therapy.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Gastric cancer; Proliferation; RASSF9; miR-1269.
© The Author(s) 2019.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-1254 exerts oncogenic effects by directly targeting RASSF9 in human breast cancer.Int J Oncol. 2018 Nov;53(5):2145-2156. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2018.4530. Epub 2018 Aug 21. Int J Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30132526
-
MicroRNA-770 affects proliferation and cell cycle transition by directly targeting CDK8 in glioma.Cancer Cell Int. 2018 Dec 3;18:195. doi: 10.1186/s12935-018-0694-9. eCollection 2018. Cancer Cell Int. 2018. PMID: 30524203 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-4268 inhibits cell proliferation via AKT/JNK signalling pathways by targeting Rab6B in human gastric cancer.Cancer Gene Ther. 2020 Jun;27(6):461-472. doi: 10.1038/s41417-019-0118-6. Epub 2019 Jul 15. Cancer Gene Ther. 2020. Retraction in: Cancer Gene Ther. 2023 Sep;30(9):1308. doi: 10.1038/s41417-023-00660-9. PMID: 31303644 Retracted.
-
MicroRNA-302b-3p Suppresses Cell Proliferation Through AKT Pathway by Targeting IGF-1R in Human Gastric Cancer.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;42(4):1701-1711. doi: 10.1159/000479419. Epub 2017 Jul 25. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28743112
-
MicroRNA-665 facilitates cell proliferation and represses apoptosis through modulating Wnt5a/β-Catenin and Caspase-3 signaling pathways by targeting TRIM8 in LUSC.Cancer Cell Int. 2021 Apr 15;21(1):215. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-01913-z. Cancer Cell Int. 2021. PMID: 33858426 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Role of Epigenetic Regulation in Plasticity of Tumor Immune Microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 2;12:640369. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.640369. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33868269 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of a prognostic prediction model based on microRNA-1269a in esophageal cancer.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2021 Aug 15;13(8):943-958. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v13.i8.943. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34457197 Free PMC article.
-
miR-1269a and miR-1269b: Emerging Carcinogenic Genes of the miR-1269 Family.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Feb 18;10:809132. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.809132. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35252180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-520f-3p inhibits proliferation of gastric cancer cells via targeting SOX9 and thereby inactivating Wnt signaling.Sci Rep. 2020 Apr 10;10(1):6197. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-63279-y. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32277152 Free PMC article.
-
RASSF9 promotes NSCLC cell proliferation by activating the MEK/ERK axis.Cell Death Discov. 2021 Jul 31;7(1):199. doi: 10.1038/s41420-021-00583-0. Cell Death Discov. 2021. PMID: 34341331 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

