The S phase checkpoint promotes the Smc5/6 complex dependent SUMOylation of Pol2, the catalytic subunit of DNA polymerase ε
- PMID: 31765407
- PMCID: PMC6876773
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008427
The S phase checkpoint promotes the Smc5/6 complex dependent SUMOylation of Pol2, the catalytic subunit of DNA polymerase ε
Abstract
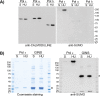
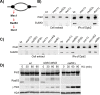
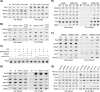
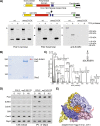
Replication fork stalling and accumulation of single-stranded DNA trigger the S phase checkpoint, a signalling cascade that, in budding yeast, leads to the activation of the Rad53 kinase. Rad53 is essential in maintaining cell viability, but its targets of regulation are still partially unknown. Here we show that Rad53 drives the hyper-SUMOylation of Pol2, the catalytic subunit of DNA polymerase ε, principally following replication forks stalling induced by nucleotide depletion. Pol2 is the main target of SUMOylation within the replisome and its modification requires the SUMO-ligase Mms21, a subunit of the Smc5/6 complex. Moreover, the Smc5/6 complex co-purifies with Pol ε, independently of other replisome components. Finally, we map Pol2 SUMOylation to a single site within the N-terminal catalytic domain and identify a SUMO-interacting motif at the C-terminus of Pol2. These data suggest that the S phase checkpoint regulate Pol ε during replication stress through Pol2 SUMOylation and SUMO-binding ability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sumoylation of the DNA polymerase ε by the Smc5/6 complex contributes to DNA replication.PLoS Genet. 2019 Nov 25;15(11):e1008426. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008426. eCollection 2019 Nov. PLoS Genet. 2019. PMID: 31765372 Free PMC article.
-
ATPase-dependent control of the Mms21 SUMO ligase during DNA repair.PLoS Biol. 2015 Mar 12;13(3):e1002089. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002089. eCollection 2015 Mar. PLoS Biol. 2015. PMID: 25764370 Free PMC article.
-
Sumoylation of Smc5 Promotes Error-free Bypass at Damaged Replication Forks.Cell Rep. 2019 Dec 3;29(10):3160-3172.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.10.123. Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 31801080
-
Smc5/6 complex regulates Sgs1 recombination functions.Curr Genet. 2017 Jun;63(3):381-388. doi: 10.1007/s00294-016-0648-5. Epub 2016 Sep 23. Curr Genet. 2017. PMID: 27664093 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The S-phase checkpoint: targeting the replication fork.Biol Cell. 2009 Aug 19;101(11):617-27. doi: 10.1042/BC20090053. Biol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19686094 Review.
Cited by
-
Multifaceted roles of SUMO in DNA metabolism.Nucleus. 2024 Dec;15(1):2398450. doi: 10.1080/19491034.2024.2398450. Epub 2024 Sep 17. Nucleus. 2024. PMID: 39287196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The SMC5/6 complex: folding chromosomes back into shape when genomes take a break.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Mar 21;52(5):2112-2129. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae103. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38375830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The multi-functional Smc5/6 complex in genome protection and disease.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2023 Jun;30(6):724-734. doi: 10.1038/s41594-023-01015-6. Epub 2023 Jun 19. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37336994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sumo-regulatory SENP2 controls the homeostatic squamous mitosis-differentiation checkpoint.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Aug 16;15(8):596. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06969-z. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 39152119 Free PMC article.
-
Esc2 orchestrates substrate-specific sumoylation by acting as a SUMO E2 cofactor in genome maintenance.Genes Dev. 2021 Feb 1;35(3-4):261-272. doi: 10.1101/gad.344739.120. Epub 2021 Jan 14. Genes Dev. 2021. PMID: 33446573 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kotsantis P, Petermann E, Boulton SJ. Mechanisms of Oncogene-Induced Replication Stress: Jigsaw Falling into Place. Cancer Discov. 2018;8(5):537–55. 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-17-1461 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

