Deficiency of Urokinase Plasminogen Activator May Impair β Cells Regeneration and Insulin Secretion in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- PMID: 31756973
- PMCID: PMC6930534
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24234208
Deficiency of Urokinase Plasminogen Activator May Impair β Cells Regeneration and Insulin Secretion in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
: Background: The relationship between urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) and the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) was investigated in the study by using mice and cell models, as well as patients with T2DM.
Methods: In mice models, wild-type and uPA knockout (uPA-/-) BALB/c mice were used for induction of T2DM. In cell models, insulin secretion rate and β cell proliferation were assessed in normal and high glucose after treating uPA siRNA, uPA, or anti-uPA antibody. In our clinical study, patients with T2DM received an oral glucose-tolerance test, and the relationship between uPA and insulin secretion was assessed.
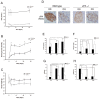
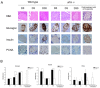
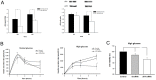
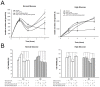
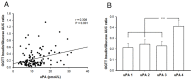
Results: Insulin particles and insulin secretion were mildly restored one month after induction in wild-type mice, but not in uPA-/- mice. In cell models, insulin secretion rate and cell proliferation declined in high glucose after uPA silencing either by siRNA or by anti-uPA antibody. After treatment with uPA, β cell proliferation increased in normal glucose. In clinical study, patients with T2DM and higher uPA levels had better ability of insulin secretion than those with lower uPA levels.
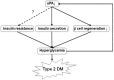
Conclusion: uPA may play a substantial role in insulin secretion, β cell regeneration, and progressive development of T2DM. Supplementation of uPA might be a novel approach for prevention and treatment of T2DM in the future.
Keywords: insulin secretion; type 2 diabetes mellitus; urokinase plasminogen activator; β cell regeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest
Figures

Similar articles
-
Expression of type-1 plasminogen activator inhibitor in the kidney of diabetic rat models.Thromb Res. 2003;111(4-5):301-9. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2003.09.023. Thromb Res. 2003. PMID: 14693179
-
Beta-cell function and mass in type 2 diabetes.Dan Med Bull. 2009 Aug;56(3):153-64. Dan Med Bull. 2009. PMID: 19728971
-
Tissue-type plasminogen activator deficiency delays bone repair: roles of osteoblastic proliferation and vascular endothelial growth factor.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2014 Aug 1;307(3):E278-88. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00129.2014. Epub 2014 Jun 10. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2014. PMID: 24918201
-
Role of beta-cell dysfunction, ectopic fat accumulation and insulin resistance in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2011 Aug;93 Suppl 1:S60-5. doi: 10.1016/S0168-8227(11)70015-8. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2011. PMID: 21864753 Review.
-
Transforming Growth Factor-Beta and Urokinase Type Plasminogen Interplay in Cancer.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2018;19(12):1155-1163. doi: 10.2174/1389203718666171030103801. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2018. PMID: 29086689 Review.
Cited by
-
Icariin Protects Mouse Insulinoma Min6 Cell Function by Activating the PI3K/AKT Pathway.Med Sci Monit. 2020 Sep 4;26:e924453. doi: 10.12659/MSM.924453. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 32885795 Free PMC article.
-
Catharanthus roseus Combined with Ursolic Acid Attenuates Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes through Insulin Secretion and Glycogen Storage.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Feb 18;2020:8565760. doi: 10.1155/2020/8565760. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 32148658 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Validation of the Putative Oncogenic Activity of PLAU.Biomedicines. 2022 Dec 30;11(1):102. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11010102. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36672610 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Levy J., Atkinson A.B., Bell P.M., McCance D.R., Hadden D.R. Beta-cell deterioration determines the onset and rate of progression of secondary dietary failure in type 2 diabetes mellitus: The 10-year follow-up of the belfast diet study. Diabet. Med. 1998;15:290–296. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9136(199804)15:4<290::AID-DIA570>3.0.CO;2-M. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

