The factors present in regenerating muscles impact bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal/stem cell fusion with myoblasts
- PMID: 31753006
- PMCID: PMC6873517
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-019-1444-1
The factors present in regenerating muscles impact bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal/stem cell fusion with myoblasts
Abstract
Background: Satellite cells, a population of unipotent stem cells attached to muscle fibers, determine the excellent regenerative capability of injured skeletal muscles. Myogenic potential is also exhibited by other cell populations, which exist in the skeletal muscles or come from other niches. Mesenchymal stromal/stem cells inhabiting the bone marrow do not spontaneously differentiate into muscle cells, but there is some evidence that they are capable to follow the myogenic program and/or fuse with myoblasts.
Methods: In the present study we analyzed whether IGF-1, IL-4, IL-6, and SDF-1 could impact human and porcine bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal/stem cells (hBM-MSCs and pBM-MSCs) and induce expression of myogenic regulatory factors, skeletal muscle-specific structural, and adhesion proteins. Moreover, we investigated whether these factors could induce both types of BM-MSCs to fuse with myoblasts. IGF-1, IL-4, IL-6, and SDF-1 were selected on the basis of their role in embryonic myogenesis as well as skeletal muscle regeneration.
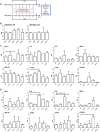
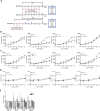
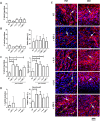
Results: We found that hBM-MSCs and pBM-MSCs cultured in vitro in the presence of IGF-1, IL-4, IL-6, or SDF-1 did not upregulate myogenic regulatory factors. Consequently, we confirmed the lack of their naïve myogenic potential. However, we noticed that IL-4 and IL-6 impacted proliferation and IL-4, IL-6, and SDF-1 improved migration of hBM-MSCs. IL-4 treatment resulted in the significant increase in the level of mRNA encoding CD9, NCAM, VCAM, and m-cadherin, i.e., proteins engaged in cell fusion during myotube formation. Additionally, the CD9 expression level was also driven by IGF-1 treatment. Furthermore, the pre-treatment of hBM-MSCs either with IGF-1, IL-4, or SDF-1 and treatment of pBM-MSCs either with IGF-1 or IL-4 increased the efficacy of hybrid myotube formation between these cells and C2C12 myoblasts.
Conclusions: To conclude, our study revealed that treatment with IGF-1, IL-4, IL-6, or SDF-1 affects BM-MSC interaction with myoblasts; however, it does not directly promote myogenic differentiation of these cells.
Keywords: BM-MSC; Fusion; IGF-1; IL-4; IL-6; Myogenic differentiation; SDF-1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Induction of bone marrow-derived cells myogenic identity by their interactions with the satellite cell niche.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018 Sep 27;9(1):258. doi: 10.1186/s13287-018-0993-z. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 30261919 Free PMC article.
-
Combined use of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells (BM-MSCs) and platelet rich plasma (PRP) stimulates proliferation and differentiation of myoblasts in vitro: new therapeutic perspectives for skeletal muscle repair/regeneration.Cell Tissue Res. 2018 Jun;372(3):549-570. doi: 10.1007/s00441-018-2792-3. Epub 2018 Feb 5. Cell Tissue Res. 2018. PMID: 29404727
-
Sdf-1 (CXCL12) induces CD9 expression in stem cells engaged in muscle regeneration.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015 Mar 24;6(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s13287-015-0041-1. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 25890097 Free PMC article.
-
The application of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and biomaterials in skeletal muscle regeneration.Regen Ther. 2020 Nov 28;15:285-294. doi: 10.1016/j.reth.2020.11.002. eCollection 2020 Dec. Regen Ther. 2020. PMID: 33426231 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Galectin-1 is a novel factor that regulates myotube growth in regenerating skeletal muscles.Curr Drug Targets. 2005 Jun;6(4):395-405. doi: 10.2174/1389450054021918. Curr Drug Targets. 2005. PMID: 16026258 Review.
Cited by
-
The CXCR4/SDF-1 Axis in the Development of Facial Expression and Non-somitic Neck Muscles.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Dec 22;8:615264. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.615264. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33415110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adult stem cell sources for skeletal and smooth muscle tissue engineering.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022 Apr 11;13(1):156. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-02835-x. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35410452 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of MSCs and Cell Fusion in Tissue Regeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 12;22(20):10980. doi: 10.3390/ijms222010980. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34681639 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single-cell profiling coupled with lineage analysis reveals vagal and sacral neural crest contributions to the developing enteric nervous system.Elife. 2023 Oct 25;12:e79156. doi: 10.7554/eLife.79156. Elife. 2023. PMID: 37877560 Free PMC article.
-
HMGB1 Promotes In Vitro and In Vivo Skeletal Muscle Atrophy through an IL-18-Dependent Mechanism.Cells. 2022 Dec 6;11(23):3936. doi: 10.3390/cells11233936. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36497194 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

