The Non-Canonical Aspects of MicroRNAs: Many Roads to Gene Regulation
- PMID: 31752361
- PMCID: PMC6912820
- DOI: 10.3390/cells8111465
The Non-Canonical Aspects of MicroRNAs: Many Roads to Gene Regulation
Abstract
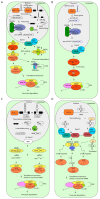
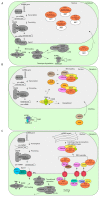
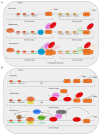
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are critical regulators of gene expression. As miRNAs are frequently deregulated in many human diseases, including cancer and immunological disorders, it is important to understand their biological functions. Typically, miRNA-encoding genes are transcribed by RNA Polymerase II and generate primary transcripts that are processed by RNase III-endonucleases DROSHA and DICER into small RNAs of approximately 21 nucleotides. All miRNAs are loaded into Argonaute proteins in the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) and act as post-transcriptional regulators by binding to the 3'- untranslated region (UTR) of mRNAs. This seed-dependent miRNA binding inhibits the translation and/or promotes the degradation of mRNA targets. Surprisingly, recent data presents evidence for a target-mediated decay mechanism that controls the level of specific miRNAs. In addition, several non-canonical miRNA-containing genes have been recently described and unexpected functions of miRNAs have been identified. For instance, several miRNAs are located in the nucleus, where they are involved in the transcriptional activation or silencing of target genes. These epigenetic modifiers are recruited by RISC and guided by miRNAs to specific loci in the genome. Here, we will review non-canonical aspects of miRNA biology, including novel regulators of miRNA expression and functions of miRNAs in the nucleus.
Keywords: MicroRNAs; biogenesis; non-canonical; nuclear localization; transcriptional regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of microRNA biogenesis.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Aug;15(8):509-24. doi: 10.1038/nrm3838. Epub 2014 Jul 16. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 25027649 Review.
-
MicroRNA Expression: Protein Participants in MicroRNA Regulation.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1617:27-37. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7046-9_2. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28540674 Review.
-
Protocols for the Analysis of microRNA Expression, Biogenesis, and Function in Immune Cells.Curr Protoc Immunol. 2019 Sep;126(1):e78. doi: 10.1002/cpim.78. Curr Protoc Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31483103 Free PMC article.
-
SmD1 Modulates the miRNA Pathway Independently of Its Pre-mRNA Splicing Function.PLoS Genet. 2015 Aug 26;11(8):e1005475. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005475. eCollection 2015 Aug. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 26308709 Free PMC article.
-
Intracellular and extracellular microRNA: An update on localization and biological role.Prog Histochem Cytochem. 2016 Nov;51(3-4):33-49. doi: 10.1016/j.proghi.2016.06.001. Epub 2016 Jun 25. Prog Histochem Cytochem. 2016. PMID: 27396686 Review.
Cited by
-
Specific microRNAs for Modulation of Autophagy in Spinal Cord Injury.Brain Sci. 2022 Feb 11;12(2):247. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12020247. Brain Sci. 2022. PMID: 35204010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of AUF1 in modulating the proliferation, migration and senescence of skin cells.Exp Ther Med. 2022 Jan;23(1):45. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10967. Epub 2021 Nov 14. Exp Ther Med. 2022. PMID: 34934424 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Circ_Arf3/miR-452-5p/Mbnl1 Axis Regulates Proliferation and Expression of Fibrosis-Related Proteins of Mouse Mesangial Cells Under High Glucose.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2023 Jul 11;16:2105-2116. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S400530. eCollection 2023. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2023. PMID: 37457110 Free PMC article.
-
Long Non-Coding RNA ZEB2-AS1 Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression by Regulating The miR-582-5p/FOXC1 Axis.Cell J. 2022 Jun;24(6):285-293. doi: 10.22074/cellj.2022.7963. Epub 2022 Jun 29. Cell J. 2022. PMID: 35892230 Free PMC article.
-
Global profiling and annotation of templated isomiRs dynamics across Caenorhabditis elegans development.RNA Biol. 2022 Jan;19(1):928-942. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2022.2099646. RNA Biol. 2022. PMID: 35848953 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

