Sini San ameliorates duodenal mucosal barrier injury and low‑grade inflammation via the CRF pathway in a rat model of functional dyspepsia
- PMID: 31746413
- PMCID: PMC6889936
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2019.4394
Sini San ameliorates duodenal mucosal barrier injury and low‑grade inflammation via the CRF pathway in a rat model of functional dyspepsia
Abstract
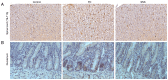
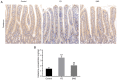
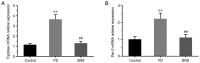
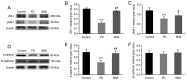
The gut‑brain interaction is associated with impaired duodenal mucosal integrity and low‑grade inflammation, which have been proven to be important pathological mechanisms of functional dyspepsia (FD). Sini San (SNS) is a classical Chinese medicine used to treat FD, but its underlying mechanisms are poorly understood. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the effects of SNS on duodenal mucosal barrier injury and low‑grade inflammation with FD, and to assess its potential molecular mechanisms on the brain‑gut axis. FD rats were established using the iodoacetamide and tail‑squeezed methods. The expression of corticotropin‑releasing factor (CRF), CRF receptor 1 (CRF‑R1) and CRF‑R2, were determined by western blot analysis and/or immunohistochemistry (IHC). In addition, mast cell (MC) migration was assessed by IHC with an anti‑tryptase antibody, and histamine concentration was quantified using ELISA. The mRNA expression levels of tryptase and protease‑activated receptor 2 (PAR‑2) were quantified using reverse transcription‑quantitative PCR, and the protein expression levels of zona occludens protein 1 (ZO‑1), junctional adhesion molecule 1 (JAM‑1), β‑catenin and E‑cadherin were determined via western blot analysis. It was demonstrated that the expression level of CRF was downregulated in the central nervous system and duodenum following SNS treatment, and that SNS modulated the expression of both CRF‑R1 and CRF‑R2. In addition, SNS suppressed MC infiltration and the activity of the tryptase/PAR‑2 pathway in the duodenum. Furthermore, treatment with SNS restored the normal expression levels of ZO‑1, JAM‑1 and β‑catenin in FD rats. These findings suggested that the therapeutic effects of SNS on FD were achieved by restoring mucosal barrier integrity and suppressing low‑grade inflammation in the duodenum, which was at least partially mediated via the CRF signaling pathway.
Keywords: Sini san; functional dyspepsia; corticotropin-releasing factor; mucosal barrier integrity; low-grade inflammation; mast cell.
Figures
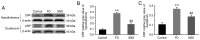
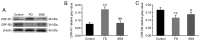
Similar articles
-
Sini-san improves duodenal tight junction integrity in a rat model of functional dyspepsia.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Aug 30;17(1):432. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-1938-2. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 28854971 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired duodenal mucosal integrity and low-grade inflammation in functional dyspepsia.Gut. 2014 Feb;63(2):262-71. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2012-303857. Epub 2013 Mar 8. Gut. 2014. PMID: 23474421
-
Deciphering the function of Xiangsha-Liujunzi-Tang in enhancing duodenal mucosal barrier by inhibiting MC/Tryptase/PAR-2 signaling pathway in functional dyspepsia rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Jan 30;319(Pt 1):116715. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116715. Epub 2023 Jun 10. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37308030
-
Novel concepts in the pathophysiology and treatment of functional dyspepsia.Gut. 2020 Mar;69(3):591-600. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-318536. Epub 2019 Nov 29. Gut. 2020. PMID: 31784469 Review.
-
Review article: Functional dyspepsia-a gastric disorder, a duodenal disorder or a combination of both?Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2023 Apr;57(8):851-860. doi: 10.1111/apt.17414. Epub 2023 Mar 1. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2023. PMID: 36859629 Review.
Cited by
-
Ameliorative effect and mechanism of Si-Ni-San on chronic stress-induced diarrhea-irritable bowel syndrome in rats.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 8;13:940463. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.940463. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36003517 Free PMC article.
-
Altered Vagal Signaling and Its Pathophysiological Roles in Functional Dyspepsia.Front Neurosci. 2022 Apr 22;16:858612. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.858612. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35527812 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation Ameliorates Functional Dyspepsia with Depressive-Like Behavior and Inhibits the Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis in a Rat Model.Dig Dis Sci. 2022 Oct;67(10):4719-4731. doi: 10.1007/s10620-021-07332-4. Epub 2022 Jan 22. Dig Dis Sci. 2022. PMID: 35064375
-
Neurotransmitter and neuropeptide regulation of mast cell function: a systematic review.J Neuroinflammation. 2020 Nov 25;17(1):356. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-02029-3. J Neuroinflammation. 2020. PMID: 33239034 Free PMC article.
-
Quantifying Liver-Stomach Disharmony Pattern of Functional Dyspepsia Using Multidimensional Analysis Methods.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Oct 10;2020:2562080. doi: 10.1155/2020/2562080. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 33101441 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Konturek SJ, Konturek PC, Pawlik T, Sliwowski Z, Ochmański W, Hahn EG. Duodenal mucosal protection by bicarbonate secretion and its mechanism. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2014;55(Suppl 2):S5–S17. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

